- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Organisms that exist at the expense of other organisms (hosts) are called parasites. They feed on living plants, blood, animal or human cells. Ectoparasites are creatures that parasitize on the surface of the skin or external organs, as opposed to endoparasites that live inside the organisms or tissues of the host.
Varieties
Distinguish between temporary and permanent ectoparasites depending on their ability to live in the external environment:
- Permanent, can only exist by parasitizing on the surface or inside the host organism, multiplying in this environment.
- Temporary use the skin, hair or hair of animals, as well as external organs only for food. Most often it is blood or skin flakes.
Most of them belong to the type of arthropods with special adaptations for attaching to the body of the host. The photos of ectoparasites presented in the article clearly show that they are equipped with special claws (louse) or spikes on the hypostome (ixodid tick) to stay on the surface. Most parasites belong to the class of insects orarachnids (mites). But other types of animals are also represented, such as leeches.
Lice
Permanent ectoparasites of humans and other animals are, first of all, lice. Tiny wingless insects have a mouth organ that can pierce the skin of the host, feeding on its blood. They were first discovered in the feathers of a bird that lived millions of years ago. Depending on the habitat, they are distinguished:
- Dress louse (constantly found in underwear).
- The head, whose paws are adapted to exist in hair with a round section.
- Pubic, for which the most suitable medium is lower body hair with a triangular section.
Lice live up to 40-45 days, but each female is able to lay up to 15 eggs daily. Having an oblong shape, they differ in white color and reach a length of up to 1 mm. Live eggs - nits, are firmly glued to the fabric or hair, having a he althy sheen. If preventive measures are not followed, the spread of ectoparasites occurs very quickly and leads to a disease (lice) called pediculosis. Lice are carriers of infections, the most dangerous of which is typhus.

How to get rid of?
The main source of infection is pediculosis patients. Pets are not carriers of this disease. Ectoparasites are organisms that adapt well to the environment and gradually adapt to certain poisons. Lice removal should take place in twostage:
- Removal of blood-sucking insects.
- Combing out nits.
When using folk remedies, it should be remembered that at home it is impossible to get rid of ectoparasites in one day. The best remedies are hellebore water (a solution of vegetable poison available in the pharmacy network), an onion-garlic mask, kerosene, 9% vinegar, half diluted with water, and tar soap. Boys can have their heads shaved, adult women can use hair dye containing hydrogen peroxide.
Nits are combed out mechanically using a fine comb (frequency - 0.3 mm) using a solution of vinegar. Cotton wool soaked in the solution should be passed between the teeth. Combing must be carried out on paper or cloth, so that after the procedure they can be immediately removed or disinfected. The fight against ectoparasites is a specialized area of specialized medical centers, so if you need an urgent solution to the problem, you can resort to their services. They have state of the art chemicals.
Temporary ectoparasites
Insects and arachnids that sit on the host's body only for eating (mosquitoes, ixodid ticks, horseflies, bedbugs) are temporary ectoparasites. Why are they dangerous?
- Bloodsuckers carry a number of serious diseases: malaria, dengue fever, encephalitis, Lyme disease and others. They are often difficult to recognize, because the symptoms at the first stage resemble acute respiratory infections. In the United States, a type of "kissing bug" has been identified that infects Chagas disease. When she is struckheart, intestines and other important organs. The bug got its name because it bites on the lips or eyelids of a person, while simultaneously performing an act of defecation. When combing the wound, involuntarily a person introduces an infection into the blood. It is estimated that up to 300,000 Americans may be infected with the disease.
- Insect bites cause allergic reactions, especially wasps, bees, midges.
- Scratching affected areas due to the toxic effect of saliva can provoke skin diseases: eczema, dermatitis.
Ectoparasites include ticks, which are the most difficult to remove from the human and animal body. If a mosquito or a midge can be swatted, then the ixodid tick should be removed in compliance with the rules.
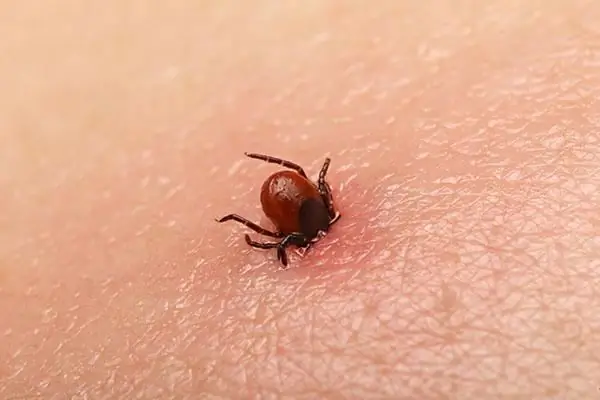

Tick removal
There are several myths about how to get rid of a dangerous arachnid. The most common among them:
- The tick must be lubricated with vegetable oil or paraffin so that it pulls out its proboscis, lacking oxygen.
- It is necessary to remove a bloodsucker only in a medical facility.
The most dangerous part of the tick's body is its head, where the virus is concentrated. Through saliva, it enters the wound, so any pressure on the arachnid's body can provoke an acceleration of the infection process. It is impossible to tear off parts or squeeze out an arthropod creature. Ectoparasites are organisms that have hooks, claws, or suckers that cannot be left in the host's body. In the absence of oxygen, theymay die, but it will be more difficult to pull them out.
It is best to remove the tick with a thread, forming a loop that must be tightened. The ends should be pulled up with confident movements. If the head still remains in the wound, it must be removed with a needle treated with an antiseptic. The body of the tick must be delivered to the infectious disease specialist for examination in the laboratory within two days. According to statistics, 20% of arachnids are carriers of infectious diseases.
Fleas
Up to 400 species of fleas are distributed throughout the country. Their feature is that each animal has its own varieties. Ectoparasites of dogs - Ctenocephalides canis. Insects are secondarily wingless, having adapted to parasitizing on the skin. They are dangerous because they pass from animals to humans and vice versa, being blood-sucking arthropods. Approximately 10% of the population can be found in the coat of dogs. Black crumbs (remnants of digested blood) on the back are evidence of flea infestation that left their excrement.
Insects are less active in the cold season, but in summer and spring they cause great trouble to animals: allergic itching, painful wounds on the body, infection with endoparasites, and infectious diseases, including plague, dangerous to humans. Fleas live up to two years, laying their eggs in garbage and rodent burrows. The white larvae resemble worms. Therefore, the processing of pet hair must be combined with the disinfestation of the home. Insecticide preparations of a new generationhave low toxicity to pets and are sold as drops, shampoos, collars and sprays.

Vlaseeds
The most common ectoparasites of cats are lice eaters, although they are found in all pets with hair. Insects of yellowish-gray color with a large quadrangular head and a flat body reach a maximum size of 2 mm, but reproduce very rapidly: the female is able to lay up to hundreds of eggs tightly attached to the hairs. In a month, from the larvae after a triple molt, adults are formed, unadapted to a long stay outside the fur of animals. Their food is skin flakes and wool. They do not dig into the blood, but do not shun their clots, located on the edges of wounds or scratches.
Vlaseaters don't survive on human skin because they love warmth. Thanks to this feature, they are easy to detect on a pet. It is enough to bring an incandescent lamp to the cat, and in a few minutes ectoparasites will begin to gather on the tips of the hairs, reaching for the heat. Even an animal that does not leave the dwelling can become infected with lice: through rodents, in the absence of sanitation, good nutrition and keeping in a damp room. Vlasoyed - carriers of hemobartenellosis, tapeworms and a number of infections that threaten the life of a pet. To remove them, it is necessary not only to apply insecticidal agents, but also to comb out the larvae by analogy with a person.
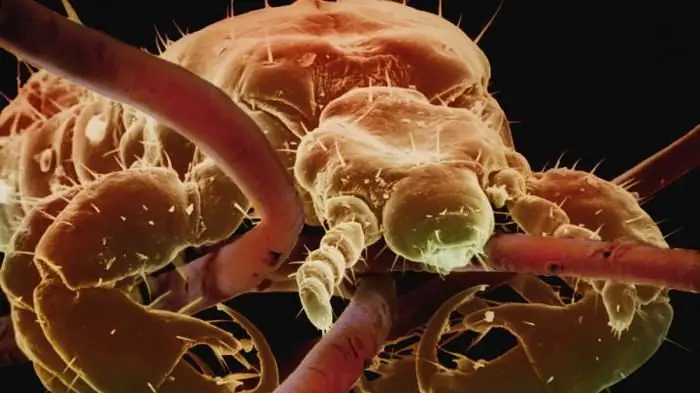
Scabies mite
Ectoparasites arenot only organisms living on the surface of the skin, but also arthropods penetrating the epidermis. A prominent representative is the scabies mite, or scabies itch. Due to its small size, it is impossible to see it with the naked eye, but the paths that it leaves when moving in the stratum corneum of the epidermis and traces of eczema are confirmation of a person's disease with scabies. Ways of infection are contact with a sick person or common household items. Signs that require medical attention include:
- Itching worse at night.
- Barely visible lines on the skin (up to 8 mm) with traces of a rash at the ends.
- Combs.
- Formation of purulent crusts.
- Localization in places of the thinnest skin areas (in a child - all over the body).
It is impossible to remove a tick without treatment. The whole body of the patient is treated with antiparasitic drugs. Antihistamines are taken internally, and all clothing and household items are boiled or steamed.
Mandatory ectoparasite treatment
What does it include?
- Preventive measures (vaccinations, planned disinsection of the home, preventive treatment of animal hair with special sprays monthly from April to November, regardless of walking the pet).
- Compliance with the sanitary and hygienic standards of the dwelling and keeping the animal.
- Periodic inspection of the coat and skin of a pet, especially after walking.
- Course of treatment of contact persons with contagious forms of the disease in the family(scabies, pediculosis).
- Combing after treatment for infestation with lice or withers. Mandatory sanitization of the entire dwelling.






