- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Pathologies of the urinary system are very common. Damage to the kidneys causes the development of their functional failure. What are the features of chronic inflammation of the kidneys? What therapy is required?
Chronic nephritis
Chronic inflammation localized in the kidneys is called "nephritis". Usually there is a bilateral lesion of organs. The etiological factor of the disease can be different. It is on the cause of occurrence that the classification of nephrites is based. All these variants of inflammation differ not only in nature, but also in the clinical picture.

Etiology
One of the etiological options is pyelonephritis, which is more common in the female half of the population. Inflammation affects the calyx and pelvis, and the cause of such a lesion is an infection. It enters the kidney either with blood (hematogenous) or through the urethra. The inflammatory process is accompanied by a violation of urination, and blood can be detected in the urine. The pains are localized in the lumbar region, they become intense during the period of exacerbation.
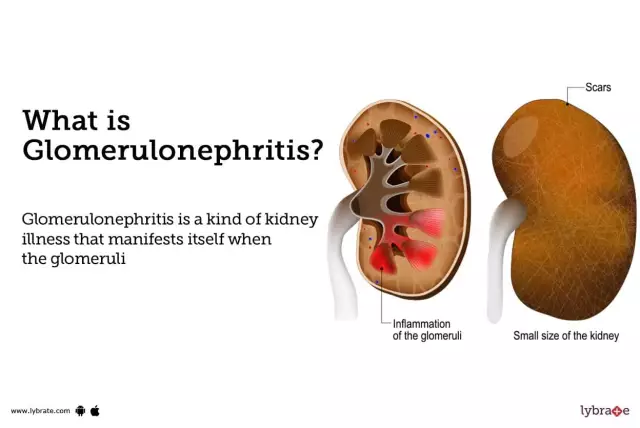
Another option is glomerulonephritis, whichaffects the glomeruli and partially tubules. Immune disorders can provoke the inflammatory process. Also predisposing factors are oncological formations and abscesses. The chronic process is characterized by relapses. During this period, nausea, xerostomia, weakness and impaired stool occur.

Radiation nephritis occurs after exposure of the body to ionizing radiation. There is a rapid inflammation of the tubules, accompanied by early dystrophy, and after - atrophy. This causes kidney failure. In the chronic period, weakness and increased blood pressure are disturbing.
Tubulointerstitial nephritis is another type of pathology. Inflammation covers the tubules, as well as interstitial, or intermediate, tissue. The reason may be the action of toxic drugs, some drugs. Possible viral nature of the disease. Organs are characterized by hypertrophy - they increase in size, their function is impaired.
Also isolated hereditary jade. It includes Alport's syndrome, which is accompanied by impaired hearing and vision. In men, the pathology is more severe.
What are the symptoms of all types of nephritis?
The chronic form is characterized by a constant edematous syndrome, which is a sign of a metabolic disorder. In a laboratory study, albuminuria and cholesterolemia are noted. In addition, the syndrome of arterial hypertension is characteristic, that is, a periodic increase in pressure.
Later stages are characterized bydeterioration of kidney function, which is observed syndrome of intoxication. As a result, toxins and slags (nitrogenous compounds) appear in the blood. Symptoms of this syndrome are fatigue, general malaise, headaches and high blood pressure. With an increase in uremia, that is, the accumulation of uric acid, it is possible to excrete it with sweat. The skin becomes dry. In more severe cases, death is possible.
Exacerbation: symptoms
During the recurrence of the chronic form, the main complaint is severe pain localized in the lumbar and pelvic region. Urination becomes painful, there is a burning sensation. Laboratory research allows to detect blood, purulent discharge in the urine. There is oliguria - a decrease in diuresis. Edema persists. Complementary are headaches, nausea (often vomiting), fatigue, xerostomia, diarrhea, fever and hypertension. Chronic nephritis can turn into an exacerbation when overheating, hypothermia, infectious process.

Pathogenesis
Chronic nephritis is usually the outcome of the acute variant. Inflammatory phenomena subside and are supplemented by hyperplastic processes. During nephritis, the activity of fibroblasts is activated, the main function of which is the formation of connective tissue components. When stimulating their activity, sclerosis occurs. Structural elements of the kidney are irreversibly replaced by connective tissue. Since it does not perform functions specific to the renal parenchyma, the activity of the urinarysystem is disturbed - kidney failure develops.
Diagnosis
Glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, tubulointerstitial nephritis and other types must be differentiated from each other, as well as from other pathologies. The diagnosis is based on questioning, examination and the results of additional methods. First of all, the patient is interviewed, finding out the likely etiology - infections, toxic effects, medication, and so on. Among the standard methods are urine and blood tests that will help detect pathology. Urinary tests are recommended, for example, according to Zimnitsky and Nechiporenko. They will help track not only the composition of urine, but also the state of daily diuresis. An effective diagnostic method is a biopsy, that is, tissue sampling for histological examination. It will help track the processes of sclerosis. Ultrasound, X-ray examination and tomography are also practiced.
Additional methods allow you to confirm the diagnosis. Nephritis can be suspected on the basis of complaints (edema and arterial hypertension).

Therapy
Treatment of kidney nephritis depends on the etiology of the disease. For example, bacterial pathologies require the appointment of antibiotics ("Cefuroxime", "Ciprofloxacin"). A viral cause (eg, tubulointerstitial nephritis) requires appropriate antiviral therapy. That is why it is important to differentiate the various etiological variants of the disease.
In addition to etiotropic therapy, symptomatic treatment is required. Appointedcytostatics ("Doxorubicin", "Cyclophosphamide"), which help protect functional cells. During the period of relapse, anti-inflammatory drugs are needed that reduce pain, plethora and swelling in the area of the pathological process. An increase in blood pressure requires the use of antihypertensive drugs ("Lisinopril", "Captopril").

Diet
During the period of illness, you should monitor nutrition. Chronic nephritis affects the kidneys, therefore, the excretory function is disturbed. That is why you should stop eating too much s alt. Canned food, spices and drinking large amounts of alcohol are contraindicated.
Prevention
Renal nephritis of the chronic type is usually the outcome of an acute one. Therefore, preventive measures consist in the early diagnosis and subsequent treatment of acute inflammation of the kidneys. It is possible to suspect the disease at an early stage if regular medical examinations are carried out - deviations in the general analysis of urine are an indicator that the patient should be sent for a consultation with a nephrologist.

Jade is a disease of the kidneys, leading to a violation of their function. The chronic form is irreversible and leads to the formation of renal failure. Pathology requires a lifestyle correction and the use of a number of drugs. Timely treatment of the acute form will help prevent its formation. Timely diagnosis will help.