- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Renal nephritis is an inflammatory disease of this paired organ, which can have a different etiology, pathomorphological and symptomatic features, as well as a mechanism of development. It usually manifests itself in the growth, partial or complete destruction of the kidney tissue.
Why does this disease occur? What symptoms indicate its presence? What is needed for treatment? What could be the consequences? Well, this and much more will be discussed now.
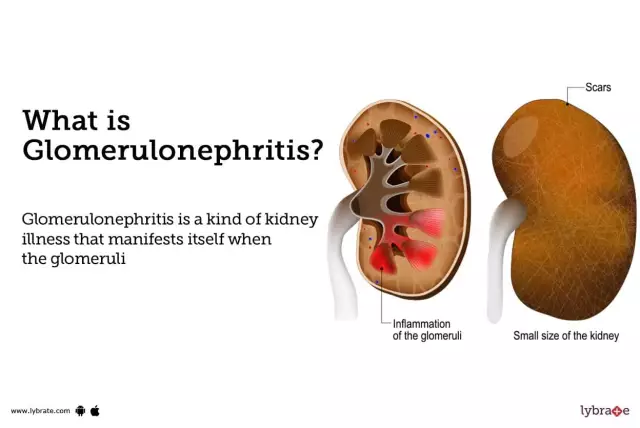
Glomerulonephritis
This is the first type of disease to be noted. It is characterized by damage to the renal glomeruli. Causes include:
- Streptococcal infection (pneumonia, tonsillitis, streptoderma, scarlet fever).
- Measles, SARS, chicken pox.
- Long stay in the cold.
Symptoms of this type of kidney nephritis appear after 1-3weeks after an infectious disease, and they are as follows:
- Changes in urine.
- Fever.
- Chills.
- General weakness.
- Nausea.
- Headache.
- Decreased appetite.
- Pain in the lumbar region.
- Pale skin.
- Puffiness of the face.
- Hypertension.
Chronic kidney nephritis of this type can occur in nephrotic form (urinary symptoms predominate), hypertensive (increased blood pressure), mixed (all signs appear), latent (mild nephrotic syndrome) and hematuric (erythrocytes are present in the urine).

Pyelonephritis
This is a disease of a purulent nature, the appearance of which is provoked by violations of the normal outflow of urine that occur for various functional and organic reasons.
Predisposing factors include immune disorders, diabetes, chronic inflammation and frequent hypothermia. In women, it often occurs after acute cystitis.
Often the disease is asymptomatic. Purulent nephritis is a kidney disease that must be treated at an early stage, in all subsequent therapy it will be ineffective, since the function of the organ will already be impaired.
The disease begins to manifest itself with a sharp rise in temperature to 40 ° C. Then the following symptoms appear:
- Profuse sweating.
- Dull unilateral pain in the lumbar region.
- Cloudy or reddish urine.
- Lossappetite.
- Severe weakness and headache.
- Sometimes nausea and vomiting.
A laboratory test can detect bacteriuria, proteinuria and microhematuria. Also, leukocytosis is observed in the patient's blood, and in 30% of cases - an increase in nitrogenous slags.
Untreated acute form of this disease is a common cause of chronic kidney nephritis in humans. What does it mean? That attention should be paid to the first symptoms that appear. Since pyelonephritis can develop on both sides, and the progressive disease of this form leads to the development of renal failure, arterial hypertension and a decrease in the specific gravity of urine.

Interstitial nephritis
This disease is characterized by an abacterial inflammation of the tubule of the kidneys and interstitial tissue. This type of kidney nephritis is an independent disease. It proceeds in a nosological form and has symptoms that are largely similar to the previous type of disease (purulent).
However, there are significant differences. So, in the case of this disease, kidney tissue is not destroyed. The disease affects the connective tissue, not spreading to the renal calyces and pelvis.
But you can't see it with the naked eye. And the clinical picture is the same as with pyelonephritis. It is important to prevent the transition of the disease into a chronic form, otherwise the person will develop fibrosis, which later forms the stroma of the organ. At the same time, the tubules die. At the final stage, the glomeruli are damaged.
If you start interstitial nephritis of the kidneys, then a person will have nephrosclerosis. This process is irreversible and life-threatening.
Ray Jade
This is a rather rare type of disease. Because it is the result of radiation exposure to which the body was exposed.
It is because of this that dystrophic changes occur in the epithelium of the renal tubules, which causes atrophy.
As a rule, this disease is diagnosed in those patients who underwent radiation therapy as part of cancer treatment, as well as in those who live in an area with an increased background radiation.
Radiation nephritis of the kidneys, the symptoms of which are almost identical to those listed above, often has a chronic form, and almost always leads to the development of failure.

Shunt jade
Another rare form of the disease. This ailment is characterized by the combination of antibody complexes near the glomeruli of the kidneys. The disease is serious, as it often leads to the appearance of blood clots in the renal veins. It is also characterized by a violation of the excretory function of the organ, due to which the outflow of urine is disturbed.
In simple terms, immune complexes are fixed on the kidney vessels and interfere with the normal functioning of the organ.
The disease proceeds like glomerulonephritis. Symptoms are similar.
Hereditary Jade
This is the last kind of disease. Hereditary nephritis - inflammation of the kidneys, which is a genetically determined glomerulopathy notimmune character.
In other words, its appearance in the human body is associated only with the kidney pathologies that have been present since birth. Also, according to statistics, in addition to the peculiar structure of glomerular basement membranes, such patients are also diagnosed with problems with vision and hearing.
It should be noted that this is not a particularly rare disease, since one case occurs in 5000 of the population. Typically, signs of the lesion are detected between the ages of three and ten years. This happens, as a rule, by chance - in the form of an isolated urinary syndrome. And the earliest symptom is hematuria.

Consequences
Jade is a kidney disease that often resolves with complications. Especially if a person paid attention to the symptoms late, and began to be treated somewhat belatedly. Often, patients also have to contend with these accompanying unpleasant phenomena:
- Paresthesia. It manifests itself in tingling and numbness of the skin.
- Cramps, muscle pain.
- Shortness of breath.
- Accumulation of fluid in places where it should not be (in the heart - hydropericardium, in the lungs - hydrothorax).
- Swelling of the limbs.
- Uremia.
But the worst consequence is kidney failure. When it violates all the functions of the body. And here's what happens:
- Harmful metabolic products are no longer excreted from the body, which is fraught with intoxication.
- The osmotic pressure of the blood is no longer regulated.
- The process is brokenhematopoiesis. After all, he althy kidneys secrete erythropoietin, an active substance that activates the formation of red blood cells.
- Regulation of the content of ions in the blood stops.
- Hormones stop being produced as before.
Symptoms such as itchy skin, abdominal pain, bitterness and dryness in the mouth, diarrhea, stomach and nosebleeds, epidermal hemorrhages and increased susceptibility to infections usually indicate the presence of this complication.
Diagnosis
It includes the following procedures:
- Medical examination and history taking.
- Surveying urine for analysis, checking this biomaterial according to Nechiporenko. This technique allows you to detect even hidden diseases of the urinary system.
- Urine test according to Volgard or Zimnitsky.
- Blood donation for biochemical analysis. This biomaterial usually shows signs of leukocytosis, a decrease in the total protein level, an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and an increase in the level of C-reactive protein.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys. This is a classic method that makes it possible to painlessly and safely assess the condition of an organ and identify the presence of possible pathologies.
In some cases, the patient may be referred for MRI, CT and radiopaque urography.

Drug therapy
Adequate treatment of kidney nephritis can only be prescribed by a doctor after an examination. Which drugs will have to be treated depends on the type, form of the disease, as well asindividual characteristics of the patient.
But, as a rule, one of the following is prescribed:
- Antibacterial drugs: Cefalexin, Ampicillin, Erythromycin. They provoke the destruction of harmful bacteria in the kidneys, and therefore form the basis of therapy. After all, the most important thing in treatment is a direct impact on the cause.
- Antihypertensive drugs: Zenusin, Hemiton, Isoptin, Adelfan, Triniton. They normalize blood pressure. Contraindications are cardiovascular diseases, stomach and duodenal ulcers, as well as individual intolerance to the components.
- Cardiac medicines: Diroton, Enam, Captopril. They normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system. These drugs should be used with caution. If a person has low blood pressure, hypersensitivity to ATP inhibitors, aortic or mitral stenosis, then he should not take them.
- Immunosuppressants: Cytoxan, Leukeran, Imuran. These drugs artificially suppress the immune system, which helps to minimize swelling of the kidneys. But when the functions of the bone marrow are suppressed, they must be abandoned.
- Diuretics: Spironol, Hypothiazid, Aldopur, Furosemide. These drugs help increase the rate of urine formation and its exit from the body. They should not be taken in case of liver or kidney failure, as well as if a person has increased venous pressure, diabetes mellitus or anuria.
With kidney nephritis, the most effective drugs are Renel N, Canephron, Hepabel,"Artibel", "Urostin" and "Nefroks". The patient is also prescribed vitamins and calcium.
If the case is severe, then a person may be referred for a procedure to cleanse the blood of accumulated toxins (hemosorption and plasmapheresis).

Folk remedies
Much has been said above about the symptoms of kidney disease. Nephritis is a serious disease, and it is necessary to take a responsible approach to its treatment. Some even decide to supplement drug therapy with the use of folk remedies. There are dozens of different recipes, and here are the most popular ones:
- Carrot seeds (3 tablespoons) pour boiling water (1 l). Let it brew overnight, then strain. Drink on an empty stomach 4-6 times a day in small portions.
- Dissolve the mummy (1 g) in 1 liter of boiled water. Drink twice a day for 0.5 cup half an hour before meals.
- Cook figs in milk. Strain. Drink fig milk 2 cups a day.
- Gooseberries (2 tablespoons) pour 1 glass of water, put on fire for 10 minutes. Boil, add one tablespoon of honey, mix. Drink 4 times a day for 0.5 cups.
- Corn stigmas (1 tsp) pour a glass of boiling water and boil for 20 minutes. Then let it brew for half an hour and strain. Every three hours, drink 2 tbsp. l.
- Hop cones (2 tablespoons) pour boiling water (0.5 l), let it brew for 2 hours and strain. Drink 4 times a day for 0.5 cups.
- Dioecious nettle (1 tablespoon) pour a glass of boiled water. Let it brew for 10 minutes, then strain. Drink 1 three times a dayArt. l.
- Crushed calamus rhizome (1 tsp) pour a glass of boiling water. Infuse for 20 minutes, strain. Drink 4 times a day for 0.5 cups half an hour before meals.
There are many more recipes. The use of folk remedies really helps to smooth out the symptoms of kidney nephritis. They can contribute to the treatment, but only if it is approved by the doctor.

Nutritional nuances
Diet for kidney nephritis is mandatory. But you need to start it with a few fasting days. Not the easiest time for the patient, as he will be banned from almost all food and liquid. However, this is not shown for all patients. Fasting days are needed or not - the doctor will say after the examination. And they are like this:
- Sugar day. A person drinks 5 cups of tea with sugar (50 g each) per day.
- Potato. It is necessary to bake 1 kilogram of tubers in the oven and consume this volume in 5 equal doses for the whole day.
- Pumpkin. One pumpkin should be baked and eaten in 5 servings.
- Watermelon. The same as in the previous cases. One watermelon for 5 meals.
Then, when a person starts to follow a diet, he will need to give up such products:
- Fish and meat.
- Food containing sodium.
- Alcohol.
- S alt.
- Soups with fish and meat broths.
- Mushrooms and legumes.
- Everything fried, greasy, spicy and starchy.
- Chocolate.
- Confectionery fat and lard.
- Smoked meats andcanned food.
- Caviar.
- Sausages, hard cheeses.
- Mustard, horseradish, onion, garlic.
You will also need to cut back on fluid intake. The patient can drink as much as the previous day came out of it. The list of allowed products looks like this:
- Bread without s alt.
- Vegetable soups with cereals.
- Lean meat (rabbit, veal, turkey).
- Eggs (2 pieces per day - maximum).
- Limited milk soups.
- Med.
- Cucumbers, carrots, cabbage.
- Natural fruit drinks, juices, fruit compotes, herbal teas.
A diet built on the basis of these principles will help unload the kidneys, remove incompletely oxidized metabolic products and toxins from the body, and also avoid poisoning by protein metabolism products.