- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
In cases where medical staff need to quickly increase the concentration of any drug component in the patient's body, they resort to the bolus method of administering the active substance. Such an injection consists in the introduction of a large volume of the drug and contributes to the accelerated onset of the drug. A bolus is a technique often followed by a drip, which already helps to gradually transport the remaining required volume of the drug formulation into the patient's tissues. The procedure can be performed both intravenously or intramuscularly, as well as subcutaneously and intrathecally.
Description of the technique
Understanding what a bolus administration of a drug means, it is worth understanding that this method of transporting the drug contributes to the maximum increase in the concentration of the drug used at the end of the manipulation. Later, over time, the level of concentration will gradually decrease. Measurement of the concentration of the pharmacological composition in the blood plasma immediately afterbolus procedures can be used to calculate the volume of distribution of a drug.

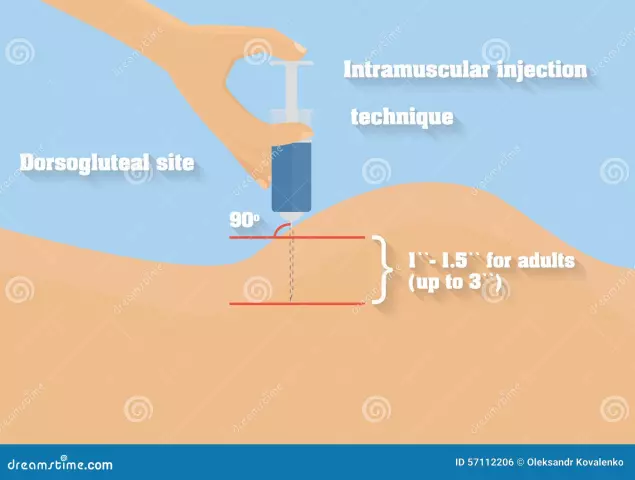
Intramuscular injections
The bolus is the method most commonly used to administer classic vaccines when it comes to intramuscular injections. When injected into the muscle, the patient's body gets time to absorb the incoming drug and produce antibodies to strengthen immunity.
Medications with analgesic effect, contraceptive hormonal compounds and testosterone can also be administered intramuscularly. In most cases, for intramuscular injections of the bolus type, such areas of the human body as the upper shoulder region or the upper thigh area are involved. The fact is that these zones are characterized by increased muscle mass, as well as the ability to spread the injected drug over the surface of the muscle.
Injection of drugs into a vein
Intravenous bolus injection is a technique for transporting a drug directly into a patient's vein. Such manipulations are often carried out before the patient is put on a dropper, in order to increase the quantitative indicator of the drug in a short time by means of an injection, and then supplement it to the desired volume by the drip method. Most often, such a chain is used when it is necessary to transport antibiotics and drugs for chemotherapy into the patient's body. The initial bolus injection allows clinicians to quickly control the fever and control the infection before the main course of therapy begins.

Subcutaneous bolus injections
In some cases, physicians also resort to subcutaneous bolus injections when drug release is needed. Such injections allow the drug to penetrate biological membranes gradually, which will provide a lasting result.
This method, for example, is used in the treatment of drug addicts in a hospital. The technique will be especially useful when, as a result of drug addiction, a person’s veins have become unsuitable for medical injections. Morphine and insulin can also be administered subcutaneously.

Intrathecal injection
Intrathecal bolus injection is the release of medication directly into the arachnoid of the patient's spinal cord. The technique is used in many cases, for example, when it is necessary to administer an anesthetic to a woman during childbirth. Also, the procedure is effectively used in order to administer painkillers and chemotherapy drugs.
Where the bolus injection will be administered depends directly on the goals pursued by the doctor, on the needs of the patient, as well as on the desired speed with which the drug should work. The procedure is very effective when you need to provide an ambulance to a person, as well as in situations where cancer or diabetes is being treated. The bolus method of administration allows you to accelerate the onset of action of the drug, which in some cases determines whether the patient survives or not.