- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Paroxysmal tachycardia - a sharp and sudden acceleration of the heartbeat. It is associated with the influence of an ectopic focus, which generates impulses for myocardial contraction.
Causes and types

Paroxysmal tachycardia occurs with heart attack, myocarditis, atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis. In the etiology of the development of this pathology, cardiomyopathies and hypertension are distinguished. In addition, paroxysmal tachycardias develop without organic damage to the myocardium. So, they can be observed with neurocirculatory dystonia, abuse of coffee or alcohol, with hormonal disorders.
The following types of this heart rhythm disorder are distinguished:
- supraventricular - characterized by the formation of an ectopic focus in the atrioventricular node or in the atria (paroxysmal atrial tachycardia);
- if additional impulses come from the ventricles, then this indicates the development of a ventricular paroxysmal heart rhythm.
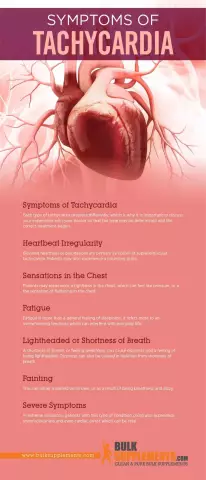
Clinical manifestations

An attack of such tachycardia occurs and disappears suddenly. It lastsfrom a few seconds to several days. The patient experiences a sudden push in the region of the heart, which turns into a pronounced heartbeat and discomfort in the chest. Sometimes patients report pain in the heart and shortness of breath. Quite often, paroxysmal tachycardias are accompanied by general weakness and dizziness. Sometimes there is an increase in blood pressure, a feeling of lack of air or a coma in the throat. There may be excessive urination after the attack ends.
Less often, with paroxysmal tachycardia, neurological symptoms in the form of aphasia and hemiparesis are observed. There may also be manifestations of autonomic dysfunction. Patients complain of nausea and sweating, subfebrile temperature and flatulence. After an attack, polyuria is characteristic, urine is excreted of low density. Protracted paroxysmal tachycardias are manifested by a decrease in blood pressure, weakness and loss of consciousness.
Treatment

With paroxysmal tachycardia, you can try to eliminate the attack using reflex methods. So, you can massage the carotid sinus, hold your breath and immerse your face in cold water for 30 seconds, inflate a balloon or press your eyeballs with moderate force.
Drug therapy involves taking special medications. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Novocainamide, Propafenone, Amiodarone, Verapamil. With the ineffectiveness of pharmacological treatment, they resort to electrical defibrillation, especially in cases where developingcoronary insufficiency or arrhythmic collapse.
When severe paroxysmal tachycardia occurs, surgery is effective because it involves isolation or direct removal of the ectopic lesion in the heart. Surgical treatment is also indicated for frequent relapses of the disease and ineffectiveness of antiarrhythmic drugs.