- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Irregular heart rhythm is always an indicator of a malfunction in the cardiovascular system. Frequent attacks lead to serious consequences. Pathology requires timely treatment. Next, consider what is paroxysmal tachycardia, what is the danger of the disease, and what kind of therapy is required.
What is this disease
Code, according to ICD-10, paroxysmal tachycardia has 147. The disease is an increase in heart rate that develops suddenly. The attack resembles an extrasystole in its etiology, therefore, with repeated repetitions, we can talk about tachycardia paroxysm.
It is important to consult a doctor in time to avoid unpleasant consequences, including cardiac arrest.
Disease development
The heart muscle works as a result of the occurrence of impulses in the muscle itself. An electrical signal propagates through the fibers and causes alternate contraction of the atria and ventricles. If he meets some obstacle on the way, then the rhythm is broken. Muscle fibers contract over the existingbarrier, which leads to the return of the impulse and the formation of a focus of excitation.
Against the background of an attack of paroxysmal tachycardia, the time to restore the heart muscle is reduced, the process of blood ejection into the aorta is disrupted. This does not go unnoticed for the functioning of the brain and other internal organs.
What happens during an attack
In the absence of any pathologies, the heart muscle begins to contract as a result of impulses that occur in the main pacemaker - the sinus node. Their frequency is normally 60-90 per minute. If more, then they talk about the development of tachycardia.
The paroxysmal form has some of its own characteristics:
- The role of the pacemaker is the pathological part of the heart muscle, which should be engaged in the conduction of impulses.
- Heart rate saved.
- The attack comes on suddenly and also stops.
- Paroxysm is not normal, even in the absence of other symptoms.

It is important to distinguish between sinus tachycardia and paroxysmal tachycardia. For this, several signs are taken into account:
- Heart rate. There is an increase in both forms.
- Heart rate. The correct sequence of atrial and ventricular contractions is maintained.
- The source of impulse in sinus tachycardia is the main pacemaker, and in paroxysmal pathological focus in the heart.
- Current pathology. Sinus tachycardia develops gradually and also slowlyfades away, and paroxysmal is characterized by suddenness.
- Value for the body. The sinus form may be a variant of the norm, but the paroxysmal form is always an indicator of pathology.
Disease classification
In medicine, the issue of classification is approached taking into account various factors.
If we take into account the localization of an attack of paroxysmal tachycardia (ICD 10 assigned the disease code 147), then the following forms are distinguished:
- Atrial. The focus of additional excitation develops in one of the atria. It begins to replace the sinus section. Heart rate is stable but high.
- Atrioventricular. Excitation develops in the area above the ventricle. There are fewer contractions than in the previous form, but impulses follow from the atria to the ventricles and vice versa.
- Ventricular paroxysmal tachycardia. The rhythm of heart contractions is not stable, the ventricles contract more often than the atria. It is considered the most dangerous form, as it quickly leads to the development of heart failure.
The first type of disease and the second can be combined into one form. In such cases, they speak of supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia.
The pathology may also not proceed in the same way, given this fact, they distinguish:
- Sharp shape.
- Chronic.
- Recurrent.
Depending on the mechanism of development of supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia, there are:
- Ectopic form. There are lesions in the heart muscle.
- Reciprocal.
- Multi-focus.
Given the form and course of the pathology, the doctor selects the tactics of treatment.
Causes of disease
It is difficult to determine exactly what triggered the development of an attack, but several reasons can be identified that significantly increase the risk of paroxysmal tachycardia.
If a person does not have a history of heart disease, then an attack can be provoked:
- Excessive exercise.
- Mental overexertion.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Smoking.
- Eating spicy food.
- Strong coffee or tea.
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland.
- Renal abnormalities.
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Using toxic drugs, especially cardiac glycosides or antiarrhythmics.

These reasons can be attributed to external ones, but there are also internal ones, among which:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Presence of myocardial infections.
- Congenital heart disease.
- Myocarditis.
- Mitral valve prolapse.
- Prolonged stress.
- Psychic stress.
- Rheumatism.
Bouts of paroxysmal tachycardia can disturb not only older patients, but also young people and even children.
Causes of the development of the disease in children
Pathology can manifest itself in childhood. Paroxysm altachycardia (ICD classifies it as a serious illness) in children often develops against the background of the following reasons:
- Congenital diseases of the nervous system, such as hydrocephalus, increased intracranial pressure.
- Pathologies of the adrenal glands.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Congenital heart defects.
- Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome.
- Infectious diseases of the heart muscle.
- Disturbances in the work of the autonomic nervous system.
Paroxysmal tachycardia, ICD code 147, requires urgent treatment in children.
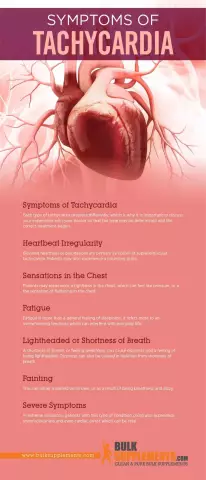
Symptoms of disease
An attack of pathology always develops suddenly. This is the difference between paroxysmal tachycardia and the usual violation of the heart rhythm. The patient at this moment feels:
- A sharp push behind the sternum. This is the main symptom of paroxysmal tachycardia.
- Heartbeat is rapid and increased.
- May feel dizzy.
- Headache.
- Feeling of a lump in the throat.
- Tinnitus.
- Pain in the region of the heart of a compressive nature.
- Possible autonomic disorders in the form of: increased sweating, an attack of nausea and vomiting, a slight increase in body temperature.

After the cessation of the attack, there is increased urination. If the attack of paroxysmal nodal tachycardia is prolonged, then the following violations are possible:
- General weakness.
- Lower blood pressure.
- Loss of consciousness.
At the momentprolonged attack, it is important to provide first aid to a person.
Diagnosis of disease
It is enough for an experienced specialist to listen to the patient's complaints to suggest the presence of paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia. Next, the patient is sent for an ECG. Research will show:
- Correct sinus rhythm with increased to 140-200 beats per minute.
- The P wave is visible before the contraction of the ventricles, but in a modified form.
- The QRS complex is neither widened nor deformed.
- Atrioventricular node showing a negative P wave after QRS or no QRS.

Additional studies are:
- MRI.
- Ultrasound examination of the heart muscle.
- Monitoring ECG during the day.
- Diagnostic tests after exercise.
- Coronography.
- Heart rate monitoring.
- EchoCG. The study allows you to detect inflammatory processes in the myocardium and evaluate its contractility.
After confirming the diagnosis (paroxysmal tachycardia code 147), the doctor prescribes therapy. It may be outpatient or require hospitalization.
Tachycardia in children
We have already met the causes that can provoke a disease in childhood, and then we will consider the symptoms.
In children, the heart rate at the time of an attack reaches 200 per minute. The duration can be from severalminutes to 3-4 hours. If you make a cardiogram at this moment, the specialist will notice specific changes.
The manifestations of pathology are influenced by many provoking factors, including:
- Difficult pregnancy in a woman.
- Difficult birth.
- There are cases of psychosomatic and vegetative diseases, as well as disorders of the nervous system in the family.
- Features of the conduction system of the heart muscle.
- WPW syndrome.

Very often, the provocateur of an attack that has begun is emotional overstrain or increased physical activity. Most often in children, an attack develops at night or in the evening, but it is not excluded during the day. According to statistics, if it develops for the first time, then in 90% of cases it can be quickly stopped. With repeated attacks, medical assistance is indispensable.
Danger of disease
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia is dangerous for its negative consequences. Complications of the disease include:
- Ventricular fibrillation, which can be fatal.
- Development of acute heart failure.
- Cardiogenic shock.
- Edema of lung tissue.
- Angina.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Progression of chronic heart failure
The development of complications depends on the state of the heart muscle and the presence of concomitant pathologies of the internal organs.
First aid to the sick
When symptoms of paroxysmal tachycardia appear, it is important to provide a person with first aid. It is as follows:
- Help the person sit or lie down on the couch.
- Open the top buttons of clothing to allow free breathing.
- Open window for fresh air.
- Reassure the patient.
You can stop an attack with the help of vagal techniques that will reduce the effect on the heart muscle of the sympathoadrenal system. The essence of the techniques is as follows:
- Apply normal strain.
- Try to exhale sharply, but keep your mouth and nasal passages closed. This is a Valsalva maneuver.
- Ashner's test. Press on the inner corners of the eyeballs.
- Wash yourself with cold water.
- Try to induce a gag reflex.
- Press on the area of the carotid sinuses in the region of the carotid arteries.
These techniques do not always give the desired result, therefore, to stop an attack of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, it is necessary to use antiarrhythmic drugs.
- Intravenously administered 10% ATP solution or 5% Glucose solution, but this can be done if there is no low blood pressure.
- At low pressure, inject Novocainamide together with Metazon or Adrenaline.
- If a supraventricular form of pathology is observed, then use Amiodarone, Digoxin, Disopyramide.
- In some cases, the use of b-blockers gives a positive effect.
If it didn't helphelp, paroxysmal tachycardia does not recede, it is urgent to call a doctor.
Pathology Therapy
After first aid, when an attack recurs several times a month, serious treatment is required. If the ventricular form of tachycardia, then the patient is urgently hospitalized. In other cases, you can undergo therapy on an outpatient basis.
Treatment for each patient is selected individually, taking into account the frequency of attacks, the form of pathology, localization and course. Concomitant pathologies must be taken into account.
Therapy aims not only to eliminate the attacks of the disease, but also the causes that provoked them. Sometimes this requires the patient to undergo a series of additional examinations. The doctor most often prescribes the following list of drugs to the patient:
- "Cardaron" to improve heart rate.
- To block adrenaline, they prescribe "A Tenolol".
- Verapamil is a calcium blocker.
- To restore the Glycine rhythm.
- Valocardin is prescribed as a sedative.
- "Hawthorn Tincture".

The listed drugs alleviate the patient's condition, but to increase the effectiveness, the appointment of antiarrhythmics is required. These medicines are administered only intravenously in a hospital under the supervision of a physician:
- Quinidine.
- Aymalin.
- Etmozin.
If therapy does not give noticeable positive results and seizuresare repeated, then an electrical impulse is assigned.
In severe cases, an operation is recommended, during which mechanical, laser, cryogenic or chemical destruction will be carried out. It is possible that the patient will need a pacemaker.
Prognosis for the patient
It depends on several factors:
- Forms of paroxysmal tachycardia.
- Duration and frequency of seizures.
- Presence of complications.
- States of the heart muscle.
If the myocardium has extensive lesions, then the risk of developing ventricular fibrillation and heart failure increases. The supraventricular form has the best prognosis. It has the least effect on the overall he alth of a person, but it is almost impossible to completely get rid of it. The course of this form is most often due to the physiological characteristics of the heart muscle and the underlying disease, which has become a provocateur of the development of seizures.
Less favorable prognosis for the ventricular form, which develops against the background of cardiac pathologies. But regular visits to the doctor and taking prescribed drugs several times reduces the likelihood of developing sudden heart failure and death.
Disease prevention
It is impossible to completely prevent the development of paroxysmal tachycardia, but you can reduce the likelihood of its occurrence. To do this, you must follow some preventive measures:
- Timely treat any infectious diseases in the body.
- See a doctor whenthe appearance of problems in the work of the heart muscle.
- Keep a he althy lifestyle.
- Exclude smoking and alcohol abuse.
- Reconsider the diet, on the table there should be only wholesome and he althy food with lots of vitamins and essential substances.
- Avoid increased physical and mental stress.
- If you have increased nervous excitability, take mild sedatives.
- Do not abuse strong coffee and tea.
- When prescribing therapy to prevent new attacks, you should regularly take the drugs recommended by your doctor.

The disease can be de alt with if you do not ignore the unpleasant symptoms and see a doctor. Timely treatment will help get rid of attacks of paroxysmal tachycardia.