- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Such a joyful event as a long-awaited pregnancy, unfortunately, can overshadow some unpleasant moments. For example, it can be exacerbations of chronic diseases against the background of hormonal changes in the body. And only taking into account the influence of extragenital pathology on pregnancy, you can successfully bear and give birth to a he althy baby without risking your own he alth or even life.
What is extragenital pathology in pregnant women
All diseases, syndromes and conditions of a pregnant woman that are not of a gynecological nature and are not obstetric complications are classified in one group, which is called "extragenital pathologies" (EGP).

This begs a logical question: are there many pregnant women with extragenital pathology? The statistics in this regard are not very encouraging. howPractice shows that the number of women suffering from chronic diseases is only growing every year. To date, only about 40% of pregnancies pass without any complications. The threat of abortion and late toxicosis are the two most common problems that are observed in those with extragenital pathology. But besides them, there are other diseases that also belong to EGP.
Diseases that are included in the concept of "extragenital pathology":
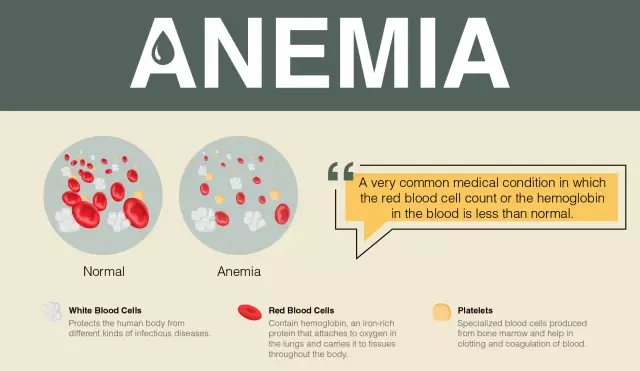
- severe anemia;
- arterial hypertension;
- myocarditis;
- heart defects;
- rheumatism;
- liver disease;
- kidney disease;
- diseases of connective tissues;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory diseases;
- viral hepatitis and infections.
Let's stop and consider in more detail each of the groups of diseases. This will help to better understand how pregnancy and childbirth go with extragenital pathology and what special measures need to be taken in each individual case.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Diseases from this group occur in 2-5% of pregnant women. If any cardiovascular disease is detected, a pregnant woman should immediately contact a local therapist. Based on the results of the examinations, the doctor will decide on the possibility of carrying a pregnancy or terminating it.

If missingsevere extragenital pathology (development of heart failure grade 3-4 with palpitations and shortness of breath with minimal exertion or at rest), then there are no prerequisites for miscarriage. In such cases, only the necessary medical therapy is selected, which will help maintain the stability of the mother and the unborn baby.
Rheumatism during pregnancy
In the event of an exacerbation of rheumatism, the question of prolonging the pregnancy is very acute. If the problem manifests itself in the first trimester, a decision is made to terminate the pregnancy, since in this case drugs are needed that are incompatible with its further development in the early stages.
If extragenital pathology in the form of rheumatism has manifested itself for a period of more than 24 weeks, successful treatment becomes possible with the preservation of the life of the unborn child.
However, the presence of this disease in 40% of cases is accompanied by late toxicosis, possible fetal hypoxia and the emergence of a high risk of abortion. Newborns, on the other hand, are particularly prone to allergies and infectious diseases.
Hypertension
Pregnancy on the background of extragenital pathology in the form of hypertension is quite common. An increase in blood pressure can provoke premature birth or become one of the causes of placental abruption. 40% of pregnant women with hypertension suffer from manifestations of late toxicosis, which can cause fetal hypoxia.
In the absence of any complications in the formcoronary insufficiency, placental abruption, cerebrovascular accidents "hypertension" (as an extragenital pathology) and "pregnancy" are quite compatible concepts. The only thing is that the expectant mother should observe the regimes of work and rest as much as possible, as well as limit the intake of s alt (no more than 5 mg per day).
Hypotension
Lowering blood pressure during pregnancy carries no less risks than its increase. Women with extragenital pathology in the form of hypotension are at high risk of spontaneous abortion at any time. They may have problems associated with violations in the attachment and separation of the placenta, as well as complications of the birth process. In addition, there may be delays in the development of the fetus due to poor blood flow in the placenta.
Arrhythmia
There are three main types of disease: atrial fibrillation, extrasystoles and paroxysmal tachycardia.
Atrial fibrillation is the most dangerous, as it can lead to pulse deficits and heart failure. Also, with this disease, a large percentage of mortality is observed: perinatal - 50%, maternal - 20%. Therefore, when atrial fibrillation is detected, a decision is made to deliver by caesarean section, natural childbirth is prohibited.
Extrasystole usually does not require special treatment and does not carry much danger. As a rule, it is observed in the last months of pregnancy (third trimester), and its appearance is provoked by a rise in the diaphragm andemotional arousal during childbirth.
Paroxysmal tachycardia is very rare and has a reflex character. Signs of the disease can be dizziness, weakness, pain in the heart, nausea. To improve the condition, sedatives are usually used.
Diseases of the kidneys and urinary organs
Extragenital pathology in pregnant women in the area of the urinary organs most often manifests itself in the form of urolithiasis or pyelonephritis.
Urolithiasis
It is accompanied by pain in the lower back, discomfort and pain during urination. In addition, there may be nausea, vomiting, constipation, and in the case of pyelonephritis, fever and inflammatory changes in the blood.
Regardless of the gestational age, surgery may be scheduled if necessary. If after their implementation and a course of drug therapy, the functionality of the kidneys is restored, the pregnancy is preserved.
Acute Gestational Pyelonephritis
Most often, the disease occurs for a period of about 12 weeks, although it can be observed throughout pregnancy. This extragenital pathology is accompanied by fever and chills.
Treatment is carried out in a hospital with the use of antibacterial drugs. At the end of the course of therapy, a pregnant woman must take uroantiseptics of plant origin (kidney teas, etc.).
If there are no complications, further pregnancy and childbirth are normal.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis issevere extragenital pathology, during which prolongation of pregnancy is contraindicated, as it leads to the development of renal failure.
Fortunately, the disease is quite rare among pregnant women - only in one case in a thousand.
Gastrointestinal diseases
Extragenital pathology in the form of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is not a contraindication to pregnancy. Women who have gastritis, duodenitis or even peptic ulcer safely bear and give birth to a he althy baby.
The only thing that can be a problem for a pregnant woman is reflux. Because of them, the expectant mother develops heartburn, which intensifies every month until the very birth. In addition, a pregnant woman may be disturbed by constant constipation.

Usually, the appearance of heartburn is observed from the 20-22nd week of pregnancy, but at this time it is periodic and quickly passes. At 30 weeks, every third woman complains about it, and closer to childbirth, this number increases, and three out of four pregnant women experience unpleasant symptoms.
As for constipation, their number also increases towards the end of pregnancy. It is highly undesirable to allow such a condition, since it can worsen the general well-being of a pregnant woman and affect the contractile function of the muscles of the uterus. And hard straining during bowel movements can cause uterine tone and lead to premature termination of pregnancy.
The main and most effective way to get rid ofof the problems described above is a special diet that includes foods that have a slight laxative effect (beets, prunes, wheat bran, etc.), as well as bifidobacteria (kefir).
Respiratory diseases
The common cold, as a rule, does not cause significant harm to a pregnant woman and her fetus. But with bronchitis and pneumonia, things are a little worse.

Acute and chronic bronchitis
Bronchitis is characterized by damage to the bronchial mucosa and is an inflammatory disease. It is accompanied by chest pains, severe coughing, and in some cases severe symptoms of intoxication.
Chronic bronchitis is not the reason why continuation of pregnancy is impossible. The presence of minor complications in the form of shortness of breath with minimal exertion or respiratory failure of the first degree is also allowed. But it is worth considering in advance that such a pregnancy will be difficult.
In cases of respiratory failure of the second or third degree, a decision is made to terminate the pregnancy in order to preserve the he alth and life of the woman.
Acute and chronic pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory infectious disease that affects the lungs. It is accompanied by a high fever and other symptoms, depending on the type of pathogen and the reaction of the pregnant woman's body to it.
Hospitalization of pregnant women with extragenital pathology in the form of pneumonia is mandatory!Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a general practitioner and an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Asthma
Obvious symptoms of this disease are asthma attacks that occur at night or in the morning and are accompanied by a strong dry cough and expiratory dyspnea. The attack ends with expectoration of a small amount of purulent sputum.
Mild to moderate bronchial asthma is not an indication for abortion, but it can cause premature birth, late toxicosis, weak labor and bleeding during the birth process.
Liver disease
Due to impaired estrogen inactivation in the liver, chronic diseases such as cirrhosis and hepatitis can cause infertility. If pregnancy does occur, the likelihood of a favorable outcome is very small. In such cases, it often ends in prematurity, the birth of dead children, as well as a high percentage of maternal deaths during the birth process. In addition, during pregnancy, a woman may begin to develop liver failure.
If an exacerbation of chronic diseases was detected before the 20th week, the pregnancy is terminated. If more than 20 weeks have passed, then everything possible is done to prolong it, since an abortion can only aggravate the situation.
If chronic liver diseases do not worsen during pregnancy, there are no indications for its termination and the percentage of a successful outcome is almost the same as in he althy women.
Endocrine diseases
To the mostcommon endocrine diseases include diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis and hypothyroidism. Let's take a closer look at each of them.

Diabetes
The disease is characterized by an insufficient amount of insulin or its insufficient effectiveness, resulting in carbohydrate intolerance and metabolic disorders. In the future, changes in the organs and tissues of the body may be observed.
Diabetes mellitus manifests itself in the form of weight loss, visual impairment, skin itching, polyuria, thirst. For an accurate diagnosis of the disease, it is necessary to pass tests for blood sugar, as well as a urine test.
Women with diabetes during pregnancy are hospitalized at least three times: at the initial stages, within 20-24 weeks and at 34-36 weeks.
Diabetes mellitus (as an extragenital pathology) and pregnancy are quite compatible. The disease is not an indication for abortion, and the very birth of a child is allowed both naturally and with the help of a caesarean section.
The only thing to consider: a pregnant woman should be tested and examined by doctors at least 2-4 times a month.
Thyrotoxicosis
The disease is associated with changes in the thyroid gland: its enlargement and hyperfunction. Thyrotoxicosis is accompanied by a strong heartbeat, sweating, fatigue, a feeling of heat, sleep disturbances, hand tremors and increased blood pressure. As a result, the disease mayprovoke severe toxicosis and miscarriage.
With a mild form of thyrotoxicosis, pregnancy is relatively normal, with a moderate and severe form, a decision is made to terminate it.
During the birth process, all necessary measures are taken to help avoid possible bleeding.
Hypothyroidism
The disease is also associated with thyroid disorders that result from surgery or are congenital defects.
During hypothyroidism, metabolic-hypothermic or cardiovascular syndromes, as well as edematous and skin changes, can be observed. The disease does not have the best effect on the unborn child: he may have congenital defects or lag behind in mental development.
In the presence of moderate and severe forms of the disease, pregnancy and childbirth are contraindicated.
Viral infections
The presence of viral infections during pregnancy can harm not only the he alth of the expectant mother, but also her unborn baby.

ARVI and influenza
As mentioned above, an acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI) does not have a big impact on the development and he alth of the fetus. But when a cold turns into the flu, there is a danger of developing complications that can cause an abortion. This is especially true for a severe form of the disease in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, as it has a teratogenic effect onfruit.
Measles rubella
Prevention of extragenital pathology in the form of rubella should be carried out even before pregnancy. It consists in mandatory routine vaccination, which is carried out even in childhood or adolescence.
The measles rubella virus is able to cross the placenta and have an embryotoxic and teratogenic effect on the fetus for up to 16 weeks. At the same time, congenital malformations can be observed even in children of those mothers who did not get sick, but simply had contact with people with rubella.
The disease is characterized by the following symptoms: swollen lymph nodes, prolonged fever, thrombocytopenia, articular syndrome, hepatomegaly.
Measles rubella in the first trimester of pregnancy is an indication for its mandatory termination.
Herpes
HSV (herpes simplex virus) is able to cross the placenta and cause damage to the central nervous system, heart and liver of the fetus. As a result, a born child may lag behind in mental development or have calcifications in the brain, microcephaly.
The virus is most dangerous in the first trimester, as it has an irreparable effect on the unborn child, and the pregnancy must be terminated. Herpes in the third trimester becomes a prerequisite for emergency delivery by caesarean section.
Treatment of extragenital pathology in pregnant women
As we have already found out, the concept of extragenital pathology includes many diseases. Therefore, it becomes clear that there is no single way to treat it.exist. All necessary therapy is carried out based on the type of disease, its severity, the presence or absence of exacerbations in any of the trimesters, and so on.

What medications should be taken if extragenital pathology is observed? For miscarriage, some drugs are prescribed, for infectious, viral, inflammatory diseases, completely different ones. In no case should you self-medicate. Only a responsible doctor (gynecologist, internist, endocrinologist and others) has the right to make a decision and prescribe the intake of a particular drug.
Prevention of EGP
Prevention of extragenital pathology is primarily to identify possible chronic diseases. At a time when some are well aware of all he alth problems, for others, an exacerbation of a disease during pregnancy can come as a real surprise. That is why many obstetrician-gynecologists advise to undergo a complete medical examination even during the planning period.
The next moment is the pregnancy itself. In the presence of extragenital pathology, it can be resolved or contraindicated. In both the first and second cases (if the woman refused to terminate the pregnancy), it is necessary to register with the relevant specialist and visit him at least once a month. This will help to notice the appearance of possible complications in time and eliminate them.
In addition, a pregnant woman may be offered plannedhospitalizations. You should not refuse them in order to protect yourself and your unborn baby from negative consequences.
Easy pregnancy to you, be he althy!