- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
When poisons enter the body, the functioning of its organs is disrupted, which can lead to serious consequences. Poisoning is a violation of the vital functions of the body due to the ingress of toxic substances. This poses a threat to human he alth and even life. Poisoning is a common occurrence in modern life. And it is not always possible to immediately get to the doctor. Therefore, it is important to know the symptoms of poisoning and the principles of first aid.
Reasons for the prevalence of poisoning
This problem has existed at all times: a person could accidentally get poisoned by mushrooms or carbon monoxide, and a worker could be in a hazardous chemical production. However, today chemistry itself has firmly entered everyday life, and the likelihood of poisoning has increased many times over with an increase in the number of household chemicals. The use of chemicals in everyday life has become so commonplace that people do not even think about the potential dangers of all these detergents, chemical plant protection products or pest control. Sometimes these substances are stored in the home in places that are easily accessible to children. Some of them are not nowhave an odor, such as dichlorvos, used as a fly repellant.

The uncontrolled use of medicines poses the same danger. It is difficult to navigate the huge range of drugs that currently exist, and each of them has its own side reactions, which largely depend on the individual characteristics of the organism. Medicines should be prescribed by a qualified doctor after a correct diagnosis, which is not always the case.
Systematics of poisoning
A unified classification of poisonings has not been accepted due to the variety of toxic substances, their origin and chemical composition, the way they enter the body and the mechanism of action, the severity, and so on. The symptoms of administration also depend on the type of toxin, however, there are general signs by which the phenomenon of intoxication can be established - nausea, diarrhea, vomiting and fever, and others. According to the method of entry into the body, they are distinguished:
- inhalation - intake of poisons during breathing;
- oral, if poisonous substances entered through the mouth;
- percutaneous, when toxins enter through skin pores or wounds;
- injectable.
By the nature of the effect on the body of toxins are:
- acute poisoning, which is characterized by a pronounced reaction of the body with a single action of toxins;
- subacute intoxications that have less pronounced symptoms and occur with many contacts with poisonoussubstances;
- super-sharp, their consequence is the death of the victim;
- chronic poisoning occurs when poisons are gradually introduced into the body in small doses and do not have sufficiently pronounced symptoms.
By types of toxic substances, poisoning can be divided into several groups.
Carbon monoxide and lighting gas poisoning
Carbon monoxide is called carbon monoxide - it is a colorless and odorless gas, which determines its extreme danger - a person does not even feel gas poisoning, while he instantly begins his destructive work. Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin much faster than oxygen, forming carboxyhemoglobin, which blocks the flow of oxygen to cells. By binding to the protein of the heart muscle, carbon monoxide suppresses cardiac activity, and its participation in the oxidative processes of the body disrupts the biochemical balance.

Lighting gas is a mixture of combustible gases, consisting mainly of hydrogen and methane with an admixture of carbon monoxide up to 8-14%. It is formed in production during oil or coal processing. Luminous gas until the beginning of the last century illuminated the premises. It has also been used as a fuel. Sources of the toxic substance, which is carbon monoxide, can be:
- large fires;
- production, where carbon monoxide can participate in the synthesis of many organic substances;
- highway exhaust;
- gasified premises with poor ventilation;
- home, bath stoves andclosed-column fireplaces.
Gas poisoning immediately causes a severe headache. Severe poisoning can result in death. As a PMP in case of poisoning, you need to quickly take the person to fresh air and call an ambulance, and if necessary, give artificial respiration.
Food poisoning
These include a number of diseases that are characterized by common features:
- unexpected and acute onset of illness;
- dependence between the occurrence of the disease and the use of a certain product;
- no signs of infection;
- development of the disease simultaneously in a group of individuals;
- small time interval of disease duration.
Thus, food poisoning is often an acute non-contagious disease caused by a product containing a toxic substance. Food poisoning by origin is divided into three types:
- microbial occurs when eating foods containing microorganisms or their toxins;
- non-microbial caused by plants or animals that are naturally or under certain circumstances poisonous;
- food poisoning of unknown nature.
Departure symptoms, regardless of the nature of the toxin, are chills, weakness, vomiting, fever, diarrhea.
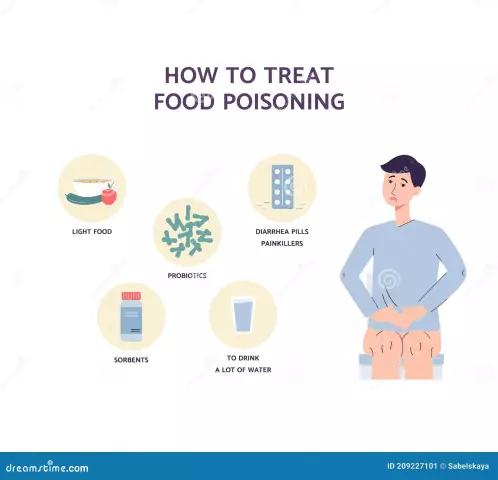
Measures to help with food poisoning
The nature of treatment for food poisoning depends on how quickly and accurately the diagnosis is made and the first measures are taken. Most of the time they are treated at home. At the first sign of malaise, the stomach should be washed. If poisoning occurs in an adult, he needs to drink about two liters of a weak solution of potassium permanganate or a solution of baking soda in order to induce vomiting and clear the stomach. For the absorption of toxins that have managed to be absorbed into the walls of the stomach, the patient should be given activated charcoal. With diarrhea, there is a danger of dehydration, so drink plenty of water. If the temperature does not subside, and diarrhea and vomiting continue, you need to take the patient to the doctor.

Food poisoning also includes botulism, which causes damage to the central nervous system. The first sign is general weakness and dizziness, as well as bloating, although there is no diarrhea and the temperature is normal. If help is not quickly provided, the disease will progress rapidly and may lead to death within a few days. First aid (PMP) for poisoning is the same as for any food poisoning. However, the patient needs to be injected with a special serum against botulism, so he must be immediately taken to the hospital.
Pesticide poisoning
Today, means of combating weeds, harmful insects, rodents, which are used both in agriculture and in everyday life, have become very widespread. These substances are accompanied by instructions for use, which spell out the rules for their storage and use. However, the systematic violation of these rules, the manifestation of negligence when working with them periodically lead to severe poisoning both at work and at home, where dangerous pesticides are oftenstored in the house, without thinking about the likelihood of dire consequences.
Pesticides are organic compounds of chlorine, phosphorus, mercury, copper compounds or carbamic acid derivatives. These substances can affect the internal organs through a different mechanism, however, in any case, the consequences will be the most severe. Chemical poisoning gives such first signs as sweating, increased salivation, and an excited state. Then spasms, vomiting can begin. The victim should be immediately taken to a doctor, and before that, first aid measures should be provided. If the poison has got on the skin, it is necessary to rinse this place with a stream of water. If a poisonous substance enters the body, a gastric lavage should be done (provided that the person is conscious). The intestines can be cleansed with enemas. And to prevent the absorption of poison into the body, it is necessary to give the victim sorbents - activated carbon and enveloping substances, for example, Almagel, in its absence - starch.

Further measures to neutralize the poison should be taken already in the hospital, since the victim needs to be injected with an antidote, the choice of which depends on the type of poisonous substance. Chemical poisoning is a very dangerous phenomenon, so when working with pesticides, one should not forget about safety rules and protective equipment.
Acid poisoning
If acid comes into contact with the skin, it is necessary to quickly rinse the area with a stream of cold water. Acid ingestion burns the oral mucosacavity, larynx, stomach and immediately there is acute pain. Usually poisoning with 80% acetic acid occurs, the symptoms of which are hoarseness, pulmonary edema and suffocation. In addition to the burn, the poisonous substance is absorbed and affects the internal organs. In more severe cases, there is vomiting and fever, severe stomach pain that can cause shock, and there is a risk of kidney failure and death.
First aid measures for the victim before the arrival of the ambulance are gastric lavage. It is necessary to carefully, in small portions, give him cold water to drink, you can also swallow ice in small pieces, put it on his stomach. You can wash the stomach with milk or water with egg whites - twelve proteins should be added to one liter of milk. Washing with a two percent suspension of burnt magnesia is suitable, but in no case should a solution of baking soda be given - a chemical reaction will occur between acid and soda with the formation of gases, the pressure of which on the walls of a damaged stomach can even lead to its rupture.

Alkali poisoning
In case of alkali poisoning, there is a strong thirst, profuse salivation and vomiting. Since they have a greater penetrating power, the burns are stronger and deeper. In severe cases, stomach bleeding or kidney failure may occur. In case of poisoning with ammonia, damage to the respiratory tract and, as a result, pulmonary edema can also occur. Assistance with alkali poisoning consists in washingstomach with a large volume of water. Only a doctor can provide further assistance, so the victim should be taken to the hospital as soon as possible. In stationary conditions, washing is carried out using a probe with water or milk with egg whites. This solution will neutralize the alkali. Can also be washed with weak solutions of citric or acetic acid.
Drug poisoning
Drugs designed to cure a disease and restore a person's he alth can themselves cause severe intoxication. This poisoning will occur if a person has exceeded the dose indicated by the doctor, or mixed up the medicines. Often people start taking drugs on their own, doing self-medication. It happens that the medicine gives a strong allergic reaction.
In all these cases, acute intoxication occurs, the severity and consequences of which depend on the type of medicine, the state of he alth of the victim, the dose taken and the time of exposure to the substance on the body. The first signs of poisoning are dizziness, abdominal pain, vomiting and fever. Then diarrhea, loss of consciousness may begin, then the condition of the victim will only worsen, unpredictable consequences are possible.

The answer to the question of what to do if poisoned with drugs depends on the active substance that caused the poisoning, since an antidote is required. Professional help can only be provided by a doctor, therefore, an ambulance should be called immediately. However, there are some urgent steps you can take before she arrives:
- if poisoning occurs, give the patient a few glasses of warm water to drink;
- should artificially induce vomiting;
- if required, repeat gastric lavage;
- after cleansing the stomach, give the victim a few tablets of activated charcoal;
- should give the victim plenty of fluids, you can two percent solution of baking soda.
A doctor should be called even if it seems that the poisoning is mild, as the condition of the victim may suddenly deteriorate sharply.
Alcohol poisoning
Alcohol poisoning is a toxic effect on the body of ethyl alcohol and its decay products. You can also get poisoned by other alcohols - methyl, isopropyl and others, which are strong poisons, but this will already be chemical poisoning. Ethanol intoxication occurs gradually, as its concentration in the body increases, and at home it is impossible to determine the degree of its severity, therefore, they usually focus on the stage of human intoxication, which are distinguished by three.
- The first stage is characterized by mild intoxication, in which the concentration of ethyl alcohol in the human blood reaches two percent. Nevertheless, the initial symptoms of the effects of alcohol on the central nervous system are already noticeable - euphoria sets in, the pupils are dilated, and speech becomes a little confused.
- The second stage begins at two to three percent ethanol in the blood. A person is no longer able to control his speech and movements, and in the morning he feels nausea,weakness and other signs of poisoning, including vomiting.
- The third stage is the most severe, the concentration of alcohol in the blood rises above three percent, which can lead to dangerous intoxication. In this state, respiratory failure, convulsions, up to cardiac arrest can occur. It all depends on the amount drunk and the body's defenses.

Alcohol intoxication is a very common phenomenon, and everyone should know what to do if they are poisoned by ethyl alcohol. If the condition is moderate, then it is necessary to induce vomiting, and then rinse the stomach with plenty of clean water without manganese or soda. After that, you should take any sorbents - you can take several tablets of coal at once.
In case of severe poisoning, the measures of assistance will be completely different - in no case should you induce vomiting so that the victim does not choke in it, gastric lavage is also excluded. It is urgent to call an ambulance, and while she arrives, provide the patient with all possible assistance - lay him on his side, clean the oral cavity of saliva, mucus, if necessary, make artificial respiration. Other necessary actions can only be carried out in a hospital.
Most of the poisoning occurs due to negligence in the storage or use of various toxic substances or food hygiene standards. To prevent poisoning, first of all, sanitary education of the population and control over the implementation of sanitary instructions is necessary.