- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
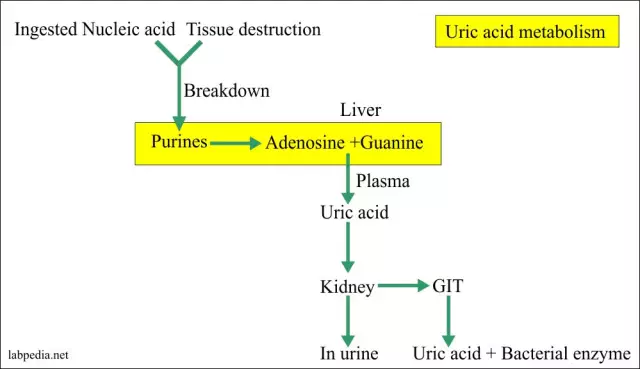
Uric acid is produced by the liver to remove excess nitrogen from the body. This component is present in the blood in the form of a sodium s alt and is the end product of protein metabolism. In case of violations of the kidneys, an increase in the concentration of this substance occurs, which leads to various damage to tissues and organs. Often, elevated uric acid provokes the development of kidney stones and kidney failure, and its excess is deposited in cartilage and joints, leading to painful inflammatory processes.
Norms of uric acid in the body

With a normal lifestyle and a balanced diet, the human body should produce up to 600 g of uric acid daily. A third of this amount is excreted through the intestines, and the rest is excreted in the urine. In men, the concentration of uric acid is considered to be within 55 mg per liter, and in women this mark should not exceed 40 mg, but the onset of menopause may slightly increase this figure. It should be noted that hyperuricemia is more common in mencause of non-compliance with the rules of he althy eating.
Blood chemistry
Uric acid is a very important indicator of a person's he alth, so its study is currently used quite widely by specialists of various profiles.

However, for more reliable indicators, the patient must follow some rules before taking biological material. For 12 hours before a uric acid test, you should refrain from eating, completely eliminate all drinks except water, and also give up alcohol and cigarettes. In addition, for 2-3 days it is necessary to follow a diet that contains a minimum amount of purine. This means that the patient should avoid legumes, coffee, chocolate, red meat, liver, kidneys and tongue. Blood sampling is carried out on an empty stomach, and elevated uric acid is determined by the enzymatic method, which is quite simple, reliable and convenient.
Causes of illness
Elevated uric acid can be detected even in the body of a he althy person with prolonged fasting, physical exertion or eating purine-rich foods.

In addition, pregnant women suffering from severe toxicosis may also experience hyperuricemia. A pathological increase in the amount of uric acid is a sign of gout, a disease in which the kidneys excrete only part of this substance, and the rest crystallizes anddeposited in the eyes, skin, joints, kidneys, heart and intestines. As a rule, this disease is inherited, in other cases it develops as a result of malnutrition. Often, elevated uric acid is observed in obesity, heart failure, blood diseases, hepatitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis, psoriasis, eczema, and pathologies of the biliary tract.
You can reduce the concentration of this substance with the help of medications, otherwise complications such as the development of gout, the deposition of stones, increased blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances, the development of angina pectoris and even myocardial infarction are possible.