- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Complete urinalysis or OAM for short is a laboratory test that is carried out in any medical institution. In the process of its implementation, the physical and chemical characteristics of urine are studied, and a microscopic examination of the sediment is also carried out. Some norms for urinalysis in adults and children are different.
General information
Urine or urine is a liquid of biological nature, which is the end product of the life process of an individual. Its formation is carried out in the kidneys in several stages. Together with it, the product of protein metabolism leaves the body - urea, uric acid, electrolytes, hormones and vitamins. By studying this biomaterial, the condition and functioning of the kidneys, organs of the digestive and cardiovascular systems are assessed. The laboratory conducts physical, chemical and microscopic types of examination of the general analysis of urine. The norms and reasons for deviations from it are discussed below.
Indications for a general urinalysis
This type of study is indicated in the following cases:
- to control ongoing therapy;
- after scarlet fever,tonsillitis and some other diseases;
- prostate diagnostics;
- to patients with chronic diseases and who are under dispensary observation in a polyclinic;
- to detect pathologies of the urinary system and kidneys;
- with suspected endocrine pathology (diabetes mellitus, pancreatitis) and neoplasms;
- passing periodic medical preventive examinations;
- medical examination.

Biological fluid is examined in several ways. The pathology and the norm will be considered below. It is best to entrust the interpretation of a general urine test to doctors for a comprehensive assessment of all the parameters obtained and a decision on further treatment tactics.
How to properly collect urine?
There are a few easy-to-follow rules that will help you get reliable results:
- eliminate products containing dyes, chocolate and alcohol-containing drinks the day before;
- collect biomaterial in the morning, on an empty stomach;
- best if the last urination was at least six hours before the morning collection;
- before collecting urine, both men and women need to perform genital hygiene using ordinary soap;
- collect an intermediate portion of urine from 50 to 100 ml, since the first contains epithelial cells of the urethral mucosa, and this will distort the results of the analysis;
- container for collecting biomaterial should be washed or sterilized, the lid to itshould fit snugly;
- a portion of urine is collected immediately in a prepared jar;
- until the biomaterial is delivered to the laboratory, it is stored in a cool place, but no more than an hour and a half.
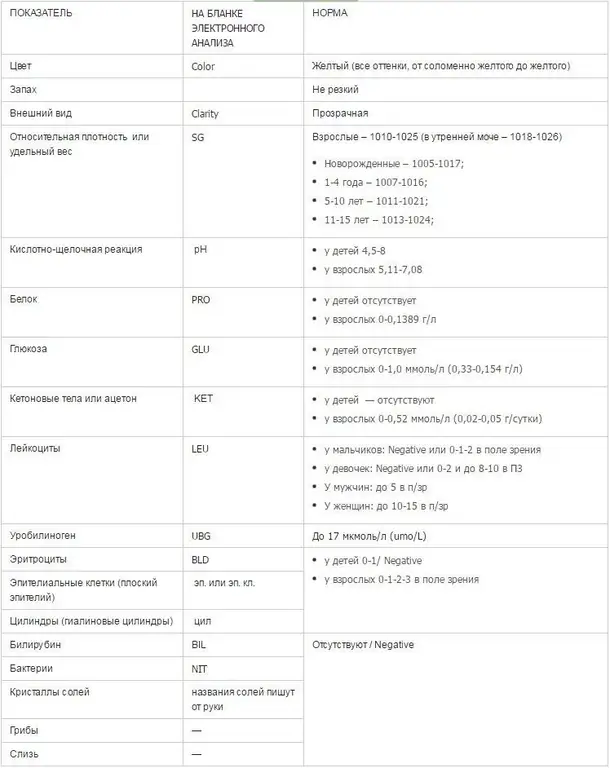
The norm and interpretation of the general urine test in adults is presented below.
PH-Wednesday
Urine is normally slightly acidic or acidic. Its changes depend on the diet and on the presence of pathological processes in the body. With diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation, renal failure, starvation - the environment is acidic. After drinking mineral alkaline water, vomiting, diarrhea, hematuria, as well as with cystitis, pyelonephritis, the urine reaction is alkaline.
Color
Depends on the pigments in the urine. The color range from light yellow to deep yellow is considered to be the norm. The result of a general urine test may be different. This indicator is influenced by the specific gravity and the allocated volume of urine. If the excreted biological fluid is bright yellow, then it usually has a high specific gravity and leaves in a small amount. Conversely, light-colored urine is excreted in a large volume and has a low specific gravity. Changing the color of urine is possible with pathology, taking certain medications or food. Let us consider in more detail the possible color of urine and what it is connected with:
- Red. It may be of various shades. Such staining indicates the presence of red blood cells in it, the appearance of which is due toinflammation of the bladder, nephropathy, lead poisoning and other pathologies. In addition, this color may appear when taking certain medications.
- Yellow-brown or yellow-greenish. This coloration results from the presence of bilirubin and bile pigments in the urine.
- Dark yellow. Means that the individual is sweating a lot or drinking little liquid. The reason may be dehydration of the body, due to high fever, vomiting or diarrhea, as well as the use of a fairly large amount of carrots, starvation and lack of milk for a baby who is breastfed. The appearance of this color indicates the pathology of the liver and heart muscle.
- Green color of urine in the analysis (the norm is given above) means the presence of pus in the biomaterial.
- White. This shade is formed when the content of fats, lymph or phosphates in urine, which appear as a result of oncology of the urinary system, damage to the kidneys by a tubercle bacillus.
- Urine acquires a dark or black-brown color due to the presence of the following pathologies in an individual: melanomosarcoma, nocturnal paroxysmal hemoglobinuria, melanoma, hematglobinuria.
- Pink. Such an unusual shade acquires a biological fluid when phenolphthalein is excreted by the kidneys.
- Transparent. Urine of a pale color indicates a violation in the work of the kidneys, the presence of diabetes insipidus. In addition, this color appears when taking a large amount of liquid or taking diuretic drugs.
- A greenish-brown hue is detected inpatients on certain drugs, such as indomethacin or amitriptyline.
- Yellowish orange. This color is different from the norm. In the general analysis of urine, it appears due to the intake of multivitamin complexes or foods high in beta-carotene, as well as vitamins C and B.
Smell, specific gravity
Urine has its own special smell, but in the presence of some pathologies it changes. For example, with inflammation in the genital or urinary system, ammonia appears, and a smell reminiscent of pickled apples or acetone indicates diabetes mellitus.
In a he althy individual, the specific gravity during the day can change, but at the same time fit into the norm. Interpretation of the results of urinalysis showed hypostenuria, i.e., a decrease in specific gravity below the acceptable minimum limit. The reason is an increased output of biological fluid, a decrease in the concentration ability of the kidneys, as well as heavy drinking. Hyperstenuria or an increase in specific gravity in excess of the maximum allowable values indicates large fluid losses due to vomiting, diarrhea, and toxicosis in pregnant women; diseases of the heart and blood vessels, the presence of acute glomerulonephritis. In all these cases, a small amount of urine is excreted. The reason for fluctuations in specific gravity is associated with fluid loss, food intake and exhaled air. Substances dissolved in urine, such as s alts, creatinine, uric acid, urea also affect this indicator.
Transparency
Urine should betransparent is normal. The results of the urine test showed turbidity - this means that it contains microorganisms, erythrocytes, epithelial cells, leukocytes, mucus, s alts, precipitated, fat drops. In addition, improper storage temperature of urine also affects this indicator. If turbidity is detected, it is determined when it acquired such a consistency: immediately after excretion from the body or as a result of storage.
Protein
In the analysis of urine (norm 0) it should not be. Its appearance in urine is caused by the following reasons.
Physiological:
- against the background of the use of a large amount of foods enriched with protein substances;
- as a result of stress;
- epilepsy attacks;
- emotional overload;
- great physical activity.
Functional. They are associated with an acute violation of regional and systemic hemodynamics against the background of:
- high temperature;
- emotional stress;
- arterial hypertension;
- heart failure;
- hypothermia
Pathological, which are divided into:
- Extrarenal. The admixture of protein substances in urine appears due to prostatitis, pyelitis, cystitis, vulvovaginitis and urethritis.
- Renal. The cause is glomerulonephritis, chronic or acute pyelonephritis, nephropathy of pregnancy, severe heart failure, hemorrhagic fever or vasculitis, renal amyloidosis, hypertension, lipoid nephrosis, tuberculosiskidneys.
When using medical devices (test strips), there may be a false positive result, the cause of which is severe hematuria, increased density and alkaline urine.
Glucose
This parameter should not be present normally. Interpretation of a urine test in adults showed the presence of glucose, what is the reason? Its appearance can be caused by various factors. Distinguish glucosuria:
- Pathological. It has a different occurrence: Ishchenko-Cushing's syndrome is pituitary, diabetes mellitus is pancreatic, hemochromatosis is hepatic. For a reliable assessment, the concentration of glucose is determined in daily urine.
- Physiological. Appears after emotional stress, consumption of a fairly large number of carbohydrates or after taking some hormonal drugs, with poisoning with chloroform, phosphorus and narcotic morphine-like analgesics.
Bilirubin and hemoglobin
Bilirubin should not be present normally in adults. The interpretation of the urine test revealed it in the urine - this indicates a violation of the liver, outflow of bile, hemolytic anemia, alcohol poisoning.

The appearance of hemoglobin in the urine is an alarming sign, it signals such serious pathologies as sepsis, burns, intoxication with chemicals, hemolytic anemia. In addition, myoglobin is detected in the analysis during high physical exertion, muscle tissue damage, myocardial infarction, myopathy.
Ketone bodies
These include acetoacetate,acetone and 3-hydroxybutyrate. In a practically he althy individual, they are not found in a urine test (normal 0). Their appearance is provoked by alcohol poisoning, starvation, diabetes mellitus, and in babies with diarrhea, vomiting, diathesis, neuro-arthritic, severe infectious process.
Nitrites
Normally they are absent. When urine is in the bladder for more than four hours, it is affected by the bacteria that it contains. This situation is observed with the progression of infections of the genitourinary system. The detection of nitrites indicates bacteriuria.
Microscopic examination
It is carried out after the chemical and physical properties of urine have been determined. The precipitate obtained as a result of centrifugation is divided into:
- Organized, in which white and red blood cells, epithelium, casts are found.
- Unorganized - mucus, s alt crystals, tyrosine, cystine, lecithin. The precipitation of s alts depends on the acidity, as well as on the properties of urine. This indicator is important for diagnosis.
In addition, the residue may contain fungi of different species, microorganisms, spermatozoa.
Leukocytes in urine analysis: norm and interpretation
Normally they should not be detected, but one-time values are acceptable. If more than five leukocytes are found in the field of view, infectious processes in the urinary system are suspected, as well as amyloidosis, glomerulonephritis, kidney transplant rejection, interstitial nephritis in the chronic stage. The presence of ten or more bodies in the sediment is a sign of severeinflammatory process in the urinary system. The detection of active white blood cells, which are normally absent, signals an inflammation of the urinary system.
Epithelium in urine analysis: norm and interpretation
It is subdivided into:
- Flat. In women, they are found in large numbers. In men with prostatitis and urethritis, it increases.
- Transitional. An increase in the quantitative composition of these cells is associated with acute inflammatory processes in the renal pelvis, bladder, urolithiasis, intoxication, tumors of the urinary tract.
- Renal. Appears in case of poisoning, nephritis, circulatory failure. The reasons for the presence of a large number of such cells are necrotizing nephrosis, which is caused by intoxication with antifreeze, mercury and other substances.

Single fragments of the first two types are allowed in the field of view, the latter should not be.
Erythrocytes
According to the results of studies of the general analysis of urine in an adult, they should normally not be present. The detection of red blood cells is associated with pathologies of organic, autoimmune, infectious genesis. When red blood cells are detected in any even the most minimal values, additional types of examinations, medical supervision and re-testing are required.
Cylinders, bacteria
Distinguish cylinders:
- hyaline;
- cylindroids;
- grainy;
- leukocyte;
- waxy;
- epithelial;
- erythrocyte;
Normally, the first type can occur sporadically. All others must be absent. Comparison of the interpretation of the general analysis of urine and the norm of this indicator revealed that there are cylinders in the biomaterial - this indicates intoxication, infection or impaired renal function.
Normally, bacteria are absent or their number is minimal and not more than two thousand cells in one milliliter. The results of the general analysis indicate only the presence of microbes in the urine.
In an alkaline environment, phosphates, ammonium urate, tripel phosphates are detected. In acidic - oxalates (calcium carbonate and oxalate), urate s alts of calcium, sodium, magnesium, potassium and uric acid.
Children's urine test
The same indicators are determined in urine as in adults.

Let's take a closer look at the norms for urine analysis in children:
- The color should be straw yellow. However, in the first months in children, it may be colorless. A change in the color of urine occurs when taking certain foods, as well as medications. Dark-colored urine indicates kidney damage.
- Acidity. Permissible rate from slightly acidic to slightly alkaline environment. Deviations are observed when the child has vomiting, intestinal infection, inflammation of the urinary tract and some other pathologies. For example, in diabetes, the environment is acidic.
- Transparency. If there is an infection in the body, a violation of metabolic processes, the urine becomes cloudy. Normal urine is clear.
- Specific gravity. The rate depends on the age of the child. A decrease in this indicator occurs with kidney disease. An increase - with dehydration of the body or the presence of glucose or protein in the biological fluid.
- Leukocytes. An increase in excess of the allowable values (more than 2) indicates pyelonephritis, cystitis and problems with the genitals.
- Erythrocytes in urinalysis. Normally 0 to 1 per field of view.
- Epithelium. An increase in the number of these cells occurs during inflammatory processes in the urinary tract.
- Protein. It shouldn't exist.
- Ketone or acetone bodies. Normally absent. Their presence occurs with severe dehydration, starvation and diabetes.
- Glucose. The presence of this indicator indicates diabetes.
- And also, according to the results of a urine test, children should normally be free of bacteria, fungi and s alts.
Conclusion
With the help of such a simple analysis, various diseases of the kidneys, prostate gland, bladder, pyelonephritis, neoplasms and other pathological conditions are diagnosed at the earliest stages, that is, when the clinic is still missing. Although urine is produced by the kidneys and is the end product, it serves as an indicator of all diseases.

With its help, the doctor receives the necessary information about the state of the organs and systems of the body of the individual. Correct interpretation of the results of a general urine test and the norm makes it possible to detect even the smallest malfunctions in the body. And only a doctor can correctly compare all the parameters. That's whyfor any deviations from the norm, you should consult a doctor.






