- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
One of the most vulnerable parts of the spine is the cervical region. The reason for this phenomenon is a weak muscular corset and the proximity of the vertebrae. Therefore, this zone is most susceptible to various deformations and injuries, as a result of which the blood supply to the brain is disrupted and motor activity is reduced. Preliminary diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis is the study and analysis of the clinical manifestations of pathology. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor uses instrumental research methods.
General information
There are eight nerve roots and seven vertebrae in the cervical region. The first nerve is located between the beginning of the skull and the first vertebra, the second - between the first and second, and so on. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a rather serious disease, which is accompanied not only by a strong pain syndrome, but also by such pathological conditions as:
- dizziness;
- vomit;
- migraine;
- angina;
- nausea.
With cervical osteochondrosis, intervertebral discs are destroyed, as a result, arteries, vessels and nerve roots in the neck are compressed. The reason lies in the degenerative-dystrophic processes. Basically, this disease affects people over 35 years of age. The disease provokes hypothermia, neck injuries and a sedentary lifestyle. Among the main signs are pain in the chest and cervical region, weakness, migraine, dizziness. With osteochondrosis, the first seven vertebrae of the cervical region suffer. Timely detection of the disease is especially important, since subsequent therapy depends on it.

The main stages in the diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis are:
- Collecting anamnesis.
- Inspection.
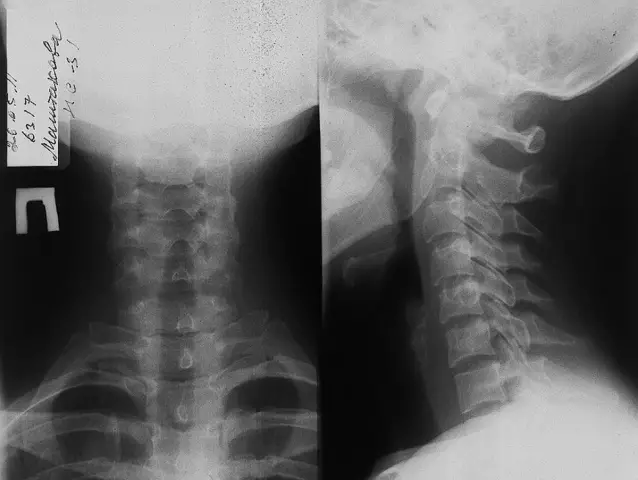
- X-ray. On the pictures you can see bone growths, narrowing of the intervertebral holes and cracks.
- Doppler ultrasound of the vertebral and carotid arteries in order to detect a failure of the blood supply to the spinal cord and brain, as well as vasospasm.
- Duplex scanning of head vessels.
- Audiography - to identify hearing impairments.
- MRI and CT of the cervical and head to identify the extent and localization of the process, compression of blood vessels and spinal cord, displacement of the intervertebral discs.
- Ultrasound.
- Blood tests.
If the disease has appeared recently, then it can be detected only by chance during an MRI. Diagnosticscervical osteochondrosis is difficult, as its symptoms are similar to pulmonary and cardiac anomalies. Therefore, patients often first of all seek help from a general practitioner or cardiologist, and only then, if treatment is ineffective, to a neurologist. If the disease is detected at a late stage, treatment will be aimed at eliminating the signs of pathology. The disease most often affects the weaker sex at the age of thirty-five. Due to the weakness of the muscular corset and thinner bone tissue, degenerative-dystrophic processes in the fair sex develop faster and are more pronounced. Methods for diagnosing cervical osteochondrosis in women do not differ from those in men, adolescents and children, these are:
- gathering anamnesis;
- inspection;
- radiological examination;
- CT;
- MRI and others.
History taking and examination of the patient
During the conversation, doctor:
- listens to complaints;
- reveals the symptoms of the disease;
- asking about previous treatments and their effectiveness;
- learns about bad habits, working conditions, hereditary factor, existing diseases.
When examining a patient, the doctor evaluates the stiffness of movements, the position of the neck relative to the body. Examines the skin for external visible changes. Palpates the neck for lumps. Sensitivity to pain is checked with a special needle, which makes a slight tingling of the cervical region. The next step in the diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis are instrumental methodsresearch.
X-ray of the cervical spine
You can diagnose osteochondrosis, as well as sprain or bruise, using x-rays. This method is easy to perform, accessible and informative. Equipment for the study is available in any medical institution. Doctor recommends it for the following conditions:
- neck injury;
- numbness in hands;
- headaches of unknown origin;
- discomfort and discomfort when turning the head;
- etc.
Among the contraindications are:
- pregnancy;
- body weight over 120 kg - image quality suffers.

Special preparation for the procedure is not required, the patient takes off all jewelry, metal objects and undresses to the waist. For the diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis, an x-ray is done with functional tests. With the help of a conventional x-ray, the mobility of the vertebrae and their displacement are revealed. When they are detected, the doctor preliminarily diagnoses osteochondrosis. To confirm it, an x-ray is performed with functional tests, during which the degree of damage and displacement of the vertebrae is assessed, and in addition, it is clarified how deformed the anterior wall of the vertebral region is. During the procedure, the individual takes different positions of the body for greater clarity and information content of the images. Based on the change in the height of the anterior sections of the spine compared to the posterior ones, which is quite clearly seen on the pictures, the radiologist prepares a conclusion aboutthe severity and nature of the pathology. Next, the neurologist makes a final diagnosis and selects a course of therapy.
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography
MRI in the diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis is considered one of the informative ways. With its help, they reveal:
- directly the disease and the degree of its development;
- causes of pain;
- evaluate the deformation and load on the intervertebral discs;
- hernia, it is a frequent companion of this anomaly.

In addition, MRI can also distinguish the structure of the nucleus pulposus. The duration of the study is about thirty minutes. Contraindications for this procedure:
- pregnancy;
- claustrophobia;
- individual has a pacemaker or insulin pump.
The advantage of this type of research is:
- no exposure;
- possibility to determine various changes in the structure of the spinal column and discs.
The only drawback is its high cost.
The next method for diagnosing osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is CT. During the procedure, a person is in a tomograph, which can be both open and closed, the scanner moves around the patient's body and takes pictures. Computed tomography can be done using a contrast agent.
Duration of manipulation is about ten minutes, so the exposure is minimal. The procedure is contraindicated:
- pregnant and lactatingwomen;
- children. Before making a decision on the appointment of a CT scan for the younger generation, the doctor evaluates the risks and benefits;
- with oncopathology.
Re-CT can be performed no earlier than a year later.
Which of the two methods to use in the diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis, the doctor decides individually for each patient. CT and MRI are two high-precision methods that allow you to take high-resolution images.
Ultrasound examination of the cervical spine
The main objective of this type of study is to examine and analyze the state of the spinal canal, intervertebral discs and nerves of the spinal cord. Special preparation for the procedure is not required. During its implementation, a person takes a lying and sitting position. In addition, if osteochondrosis, trauma, hernia or instability of the motor segments is suspected, a study is carried out with functional tests - flexion and extension (the patient flexes and extends the neck as much as possible). This allows you to better see the displacement of the vertebrae. In adult individuals, for the detection of cervical osteochondrosis, ultrasound diagnostics is considered a particularly effective method. Ultrasound examination has a number of advantages:
- No exposure.
- Informativeness of the obtained results.
- Harmless for babies and expectant mothers.
- You can perform the procedure multiple times.
- Low research cost.
- Availability - available in any medical facility.
Diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis
In neurosciencefor the diagnosis of this pathology, the presence of the following syndromes matters:
- Root - manifested by intense pain under the shoulder blade, in the neck, larynx, collarbone. It intensifies when moving. In addition, the work of the masticatory muscles is disrupted, hiccups, numbness of the tongue, paralysis and paresis, impaired sensitivity of the hands appear.
- Vertebral artery - there is a whole range of symptoms: pressure surges, nausea, headache, tinnitus, weakness, depression, loss of consciousness with sudden head turns, dizziness.
- Cardiac - there is shortness of breath, pain in the region of the heart, tachycardia.
- Vertebral - neck mobility is disturbed, there are pains in the cervical region.
To clarify the diagnosis, differential diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis is carried out in women, men and the younger generation. It is necessary to identify and exclude such pathological conditions as:
- oncology;
- angina;
- gastric ulcer;
- old injuries and fractures;
- disturbances in the work of nerve endings;
- and others.
For these purposes, doctors recommend the following types of studies:
- Ultrasound of the chest and heart;
- ECG;
- doppler ultrasound;
- gastric endoscopy;
- duplex vascular scanning;
- blood test for heart markers.

For the diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis, it is important to know some features of the pain syndrome inthe left side of the chest to determine if the heart hurts or is it a symptom of osteochondrosis:
- Pain in the heart appears with any load, such as walking or stress. In addition, it is accompanied by a frequent pulse and a change in complexion. It turns red or pale. With cervical osteochondrosis, shortness of breath and some stiffness in the limbs form.
- With heart problems, the individual has difficulty breathing and a feeling of compression of the sternum. With osteochondrosis, the pain intensifies with each breath and heart medications do not help.
- With cardiovascular anomalies, the pain is short-term and lasts no more than two minutes, and with cervical osteochondrosis - up to two or more days.
- Heart failure pain is felt in the left side of the chest, back of the head, neck, shoulders and arm. With osteochondrosis, it is felt in all parts of the spine.
Signs of osteochondrosis
For the timely diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis, the symptoms listed below are a reason for an immediate visit to the doctor:
- hearing and vision loss;
- deposition of s alts in the neck;
- numbness of the tongue;
- heart pain that does not go away after taking Nitroglycerin;
- blackout in the eyes, dizziness and fainting when turning the head sharply;
- a state of constant tension in the muscles of the neck;
- limited mobility of the lower and upper limbs;
- throbbing pain in the occipital area, radiating to the crown and temples;
- shoulder pain aggravated byturning or tilting;
- neck stiffness and difficulty turning head in the morning;
- pain syndrome in the cervical region, radiating to the eyes, ears, shoulders, which manifests itself even during sleep;
- feeling of pressure in the sternum;
- intensification of pain in the cervical region during exercise or movement and its decrease after rest;
- shortness of breath and shortness of breath.

Symptoms of osteochondrosis depend on which cervical vertebra and nerve is affected:
- first - sensitivity decreases in the occipital region;
- first - second - pain in the back of the head and crown;
- second - third - numbness of the tongue, speech problems, rare;
- third - fourth - weakening of the neck muscles, numbness and pain in the shoulder blade and shoulder;
- fourth - hiccups, heart pain, breathing difficulties, occurs infrequently;
- fourth - fifth - sensitivity in the shoulders decreases, pain appears;
- fifth - sixth - pain reaches the thumb of the upper limb;
- sixth - seventh - pain from the cervical region moves to the shoulder and shoulder blades, and also reaches the fingers, in addition, loss of sensitivity is noted in these areas;
- in case of pinching of the nerve between the first thoracic and the eighth cervical vertebrae, pain and numbness extends from the neck to the little finger.
After an accurate diagnosis is established, troubleshooting should begin.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
In the treatment, as well as in the diagnosis of cervicalosteochondrosis, there are several methods:
- conservative;
- surgical;
- mixed.
With their help, they remove the pain syndrome, relieve the inflammatory process, prevent complications and improve the condition of the individual for a certain period. It is impossible to completely cure the disease. When choosing a method of treatment, the doctor focuses on the clinic, stage and form of the disease. With a conservative method, the following medicines are used:
- "Sirdalud", "Baclofen", "Mydocalm" - muscle relaxants.
- Chondroxide, Teraflex, Alflutop, Artron, Chondroitin are chondoprotectors.
- "Diclofenac", "Ketorol", "Meloxicam", "Nimesulide", "Prednisolone", "Hydrocortisone" - with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Furosemide, Veroshpiron are diuretics.
- "Milgamma", "Ascorbic acid", "Tocopherol acetate" - vitamins.
In addition to tablet dosage forms, medicines in the form of patches, ointments or gels are widely used.

Among non-drug remedies, they have proven themselves:
- massage in the neck area;
- therapeutic exercise under the guidance of an experienced doctor;
- acupuncture;
- wearing a special Shants collar;
- self-massage;
- vibration massage;
- application of Kuznetsov's applicator;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- magnetotherapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- electrophoresis;
- balneotherapy;
- use of orthopedic mattresses and pillows.
Surgical interventions are resorted to with severe radicular syndrome, spinal cord compression, increasing problems with sensitivity and motor activity of the upper limbs.
It is important to remember that high-quality diagnosis and treatment of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis depend on the qualifications of the doctor. For women, when choosing a method of therapy, the first place is given to the use of non-drug means, and especially gymnastics. In addition, the treatment of the disease in women is based on some specifics of the endocrine and cardiovascular systems. Therefore, the methods are somewhat different from the methods of treating the opposite sex. For which the basis is medicines, and in addition massage, physiotherapy, gymnastics, etc.
Therapy of cervical osteochondrosis at home
Treatment of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis at home:
- gymnastics;
- self-massage;
- rational nutrition, which contains foods enriched with trace elements and vitamins;
- he althy sleep - implies the use of a hard or semi-hard mattress for sleeping, a small pillow of medium hardness;
- proper organization of the workspace - a chair and a table should be chosen according to height, you should sit straight, after every hour of work do a little warm-up;
- various anesthetic compresses using medicinal herbal raw materials;
- taking the medicine recommended by the doctor.
All of the above measures can also be used as a prevention of the disease, and since the disease is getting younger, its prevention should be de alt with from childhood. It is desirable that physical activity (swimming, running, yoga, Pilates, walking) be your constant companion. For example, the benefits of gymnastics in the treatment of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis at home are as follows:
- improving brain nutrition;
- increased mobility of the cervical spine;
- reduce pain;
- strengthening plasticity;
- normalization of blood flow in problem areas;
- development of the muscles of the cervical zone.

The result will depend on the regularity of the exercises. Contraindications, which are mostly temporary, can be consulted with your doctor.
Diagnosis and medical rehabilitation of cervical osteochondrosis
Pain in the neck is a frequent companion of passive pastime. This problem is faced by most individuals of all ages. One of the causes of pain is cervical osteochondrosis. However, to confirm the diagnosis, you should contact a he althcare institution, where they will conduct the necessary types of examination and prescribe treatment, after which it is desirable to undergo a full course of medical rehabilitation.

What is this? This is a set of measures aimed at restoring working capacity and physical he alth. Doctors-rehabilitologists have developed for thisspecial programs. The nature of the measures for cervical osteochondrosis is determined by the stage of the disease and clinical manifestations. For each individual, an individual rehabilitation program is selected. Thus, in order to prevent complications leading to disability, after the diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis, treatment should be started immediately.