- Author Curtis Blomfield [email protected].
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
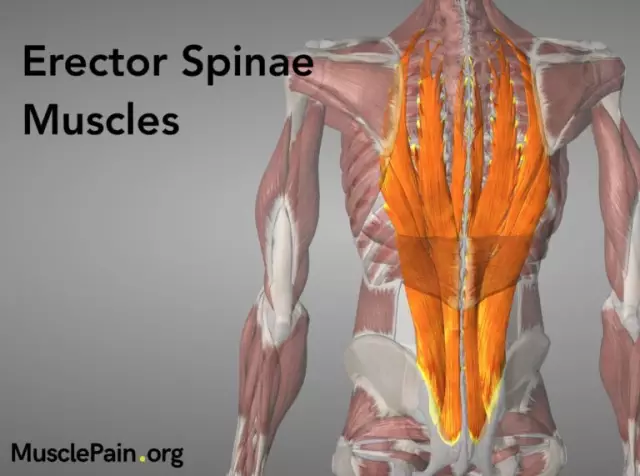
The erector spinae muscle is the most powerful and longest muscle on the back. It fills the entire space on the sides from the spinous processes to the ribs. And in length it runs along the entire length of the spine. It starts from the sacrum and extends to the very base of the skull. She takes part in turning the head and lowering the ribs. But the main function of the muscle that straightens the spine is to keep the body in a straight position. In the process of evolution, thanks to upright posture, it has become the strongest among the muscles of the body.
Anatomy of the muscular corset of the spine
The body in the correct position is held by many muscles of the back, abdominals and chest. They make up a muscular corset that protects the spine and internal organs. Some of these muscles are more significant, others perform auxiliary functions. Human he alth depends on the state of the spinal column, so strong back muscles are very important, sincethey hold the vertebrae in place. Their significance is great, as they are involved in almost all movements.
The erectors of the spine are deep muscles. They do the job of protecting and moving the spine. They also include the belt muscle of the back, which runs from the thoracic to the cervical vertebrae and is involved in turning and tilting the head. Many small muscle bundles make up the transversospinous muscle of the back.
On top of these are superficial: trapezius, latissimus dorsi, rhomboid, serratus superior and inferior.

Building
The deep muscles of the back, which are combined under one name "straightening the spine muscle", are located along the entire spinal column. They are several small and large bundles of muscle tissue that are attached to the pelvic bones, ribs and transverse processes of the vertebrae. It is divided into three parts at the level of the upper lumbar vertebrae.
In the lumbar region, the largest muscle bundles extend from the bones of the pelvis and sacrum. In this place, the extensor function is performed by the muscle that straightens the spine. Attachment of its lumbar in the upper part is carried out to the ribs and transverse processes of the vertebrae. Therefore, this part is also called the iliocostal muscle.
The longissimus dorsi muscle attaches to the transverse processes of the vertebrae. It is often considered as a single unit with the iliocostal, but it is located medially.
Spinalis dorsi attaches tospinous processes of the thoracic and cervical vertebrae.

Functions
It is also called the extensor or rectifier of the spine. The posture of a person, gait, and the he alth of the spine depend on the degree of development of this muscle. It is involved in torso tilts, turns, and balance. It tenses when coughing, moving the diaphragm and during defecation. But besides this, the erector spinae muscle performs a static function. It supports the body in a straight position and ensures the stability of the spinal column during any movements. It is these muscles that protect the spine from any damage, keep it in the correct position.
The contraction of individual parts of this muscle allows you to tilt your head back, unbend various sections of the spine, lower the ribs. With its unilateral contraction, the body tilts to the sides.

Meaning of the erector spinae muscle
It is on her work that the posture and he alth of the spine depend. If this muscle is weak or diseased, any movement of the person causes pain. It is problematic even just to keep the body upright. If the spine is bent, the volume of the chest and abdominal cavity changes, which leads to various diseases of the internal organs.

Problems arising in its functioning
The erector spinae often becomessubject to patient complaints. Throughout her life, she withstands a huge load. After all, it must maintain the stability of the spine during any movements. And if there are any problems in its functioning, the spine loses mobility, is affected by various diseases. This usually occurs with increased load, frequent weight lifting, hypothermia. Myositis, myalgia, lumbago may develop. Pain also occurs with osteochondrosis, displacement of the vertebrae, intervertebral hernia.
If, due to overwork, the muscle that straightens the spine is weakened, the stability of the vertebrae is disturbed. Pain may occur due to its spasm or due to infringement of the nerve roots. Especially often it occurs in the lumbar spine. Therefore, people who spend a long time in one position or subject the lower back to increased stress need to perform special exercises.

The erectors of the spine: how to exercise and relax
The peculiarity of these muscles is their slow recovery. Therefore, straining them is often not recommended. Training with strength exercises is best done no more than 2 times a week. The rest of the time, classes should include exercises to relax and stretch these muscles. This will help relieve their spasm:
- The easiest exercise to relax the back muscles is hanging on the horizontal bar. It is recommended to be in this position for several minutes 2-3 times a day.
- Sit on a chair, legs spread wide, handslower. Exhaling slowly, alternately bend the spine in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar regions, drawing in the stomach. While inhaling, straighten up, unbending your back in the reverse order.
- Lie on your back, wrap your arms around the knees of your bent legs. While inhaling, press your feet on your hands, as if trying to unbend them, exhale - bring your knees closer to your head.

How to strengthen muscles
The erector spinae muscle performs the main task of keeping the body in a straight position. Therefore, it is very important to strengthen the muscular corset of the spine. Many diseases of the musculoskeletal system appear due to the fact that the muscle that straightens the spine is very weak. Exercise will help strengthen it:
- You can start with the usual torso tilts from a standing position. Then weights are added to increase the load.
- Lie on your stomach on the couch, legs in weight. While inhaling, raise your legs, straining your buttocks, linger for 5-8 seconds, while exhaling, lower them below the level of the couch.
- This exercise is performed when the upper body is on weight. Hands behind the head or on the belt, raise the body, lingering in the upper position for 5-8 seconds.
- Lying on your stomach, hands behind your head. Raise the upper body, straightening the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine in succession. Hold this position for 5-8 seconds.
- The starting position is the same. Stretch your arms forward and, while inhaling, raise your upper body and legs at the same time.
So that the back muscles do theirtasks to protect the spine and keep it in the correct position, they need to be strengthened. For this, regular exercise, sleeping on a pillow-top mattress and frequent breaks from sedentary work are important.