- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
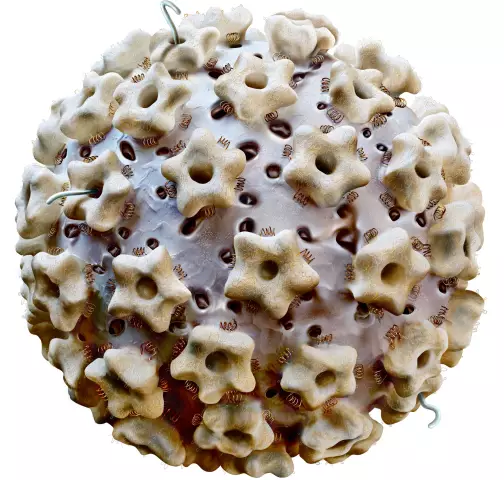
Recently, papillomavirus has become widespread. Perhaps he began to mutate, like many viruses that attack humans. They evolve, adapt to antiviral drugs. Before you start treating papillomavirus, you need to find out what it is.

Papillomavirus, or HPV, belongs to the category of living only in the body of Homo sapiens. Accordingly, it is transmitted only from person to person. Scientists have counted as many as a hundred of its varieties. Forty of them are sexually transmitted and live on the genital mucosa. This virus manifests itself in the form of peculiar genital warts and codylomas. 50% of varieties can serve as provocateurs of oncological diseases. Infection occurs not only through sexual contact. A variety of HPV, found in the form of warts, is transmitted by household means and through damage to the skin. Some types, such as non-oncogenic HPV, enter the human body mainly in childhood or in youth, agingorganisms are not attracted to them. They show up

flat warts, but there are also vulgar ones (I wonder who came up with such a name). The virus may not manifest itself for a long time. In principle, compared to others, it is not persistent, it can disappear on its own. But if HPV has firmly established itself in the body, it is not so easy to deal with it. Therefore, it is worth taking seriously such a phenomenon as human papillomavirus. Treating it is hard work. You need to start with the correct definition of its variety. For example, a type called "papillomavirus 16" is quite widespread. Treatment of this dangerous species cannot be carried out independently. This type of HPV provokes the occurrence of oncological tumors, it is parasitic on the mucous membranes of the genital organs and is the cause of cervical cancer. So all actions must be performed only under the close supervision of specialists.

What are the warning signs? For starters, the appearance of formations on the genitals, similar to warts. Treatment of papillomavirus in the dormant stage (in carriers) is not carried out, there are no technologies. Although some paid clinics may offer to vaccinate against HPV. Be vigilant, such a vaccination has a narrow focus. It is put on girls from 9 years old and women up to 26 years old. But only if they are not infected with the virus. Otherwise, the consequences are simply catastrophic, HPV begins to develop at a breakneck pace, and there is a high probability of developing oncology. you for your money(from 20 thousand) get a problem for life. There are quite a few precedents.
Treatment of papillomavirus in the active stage is carried out by several methods. The most common - surgical - removal of papillomas and warts. Then ointments come in popularity. They have a composition that inhibits the development of the virus. Next in the rating are methods such as burning with electric current, a mixture of acids, and exposure to radio waves. But all these types of treatment are used only under medical supervision. And none of these methods gives a guarantee of getting rid of HPV. You must decide for yourself whether you need papillomavirus treatment, how much it threatens your he alth.