- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
The branch of anatomy that studies the structure and physiology of human and animal tissues is called "histology". What does this mean for modern medicine? In fact, a lot. Medical histology puts among its priorities such as:
- studying the causes of the transformation of normal cells into atypical ones;
- tracking the processes of occurrence of malignant and benign tumors;
- identifying natural mechanisms to fight cancer.
Of course, these are far from all the tasks that histology solves. It is closely related to modern medicine and the diagnosis of diseases in particular. Histological studies are widely used in therapy, surgery, gynecology, endocrinology.
Histology - what is it?

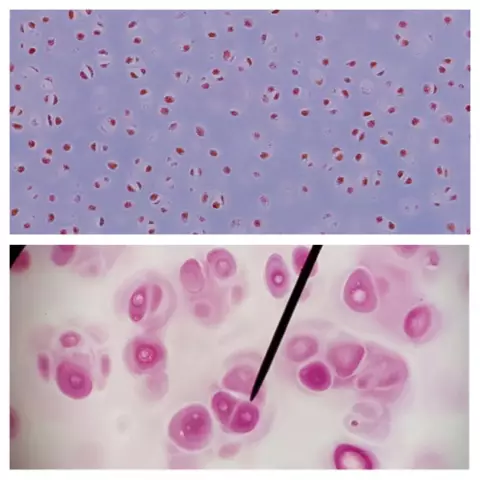
Histology is often referred to as microscopic anatomy. This name is quite justified, since it studies the structure of tissues and entire systems.organs at the microscopic level. The object of the study are the thinnest sections fixed on a glass slide. Histology is primarily a descriptive science. Its main task is to monitor the changes occurring in tissue cultures, both in normal and pathological processes. The histologist must know everything about the formation and subsequent embryonic development of tissue - about what changes it undergoes in the postembryonic period, what is the norm and what is pathology. Histology interacts closely with sciences such as cytology and embryology.
History of the development of science

The development of histology is associated with the creation of the first microscope. Malpighi is the father of microscopic anatomy. But, of course, many scientists participated in the formation of science. They enriched histology with observations, found new research methods, and painstakingly described their results. The terminology testifies to the contributions of great scientists. She immortalized their names in the names of tissue structures and research methods: for example, staining according to Giemsa, Malpighian layer, islets of Langerhans, staining according to Maximov, Lieberkühn's glands. For more than 400 years, science has existed as an independent, separate from anatomy. Her main interests lie in the field of veterinary medicine and medicine. Currently, the most widely used methods of histological research, allowing you to study individual cells in detail. This is done by making temporary preparations on a glass slide. These modern methods includetissue culture, frozen section technique, histochemical analysis, phase contrast and electron microscopy. In addition, the latter allows you to study in detail not only the structure of an individual cell, but also its organelles. Using electron microscopy, it was possible to recreate a three-dimensional tissue model.
Histology sections
Like any science, microscopic anatomy is divided into sections. General histology deals with the study of the structure, properties and functions of tissues as a single organism as a whole and their interaction. And the study of specific organs and structures is devoted to private microscopic anatomy. Histology is also divided into normal and pathological. The first specializes in the study of tissues in a he althy body, and the second examines the nature of their morphological and physiological changes in connection with a particular disease.

Pathological histology also deals with the description of the influence of bacteriological and viral agents on the functioning of tissues and individual cells. What does this mean for modern medicine? First of all, information about the stages of development of oncological diseases. In addition, the study of tissue changes can further help to cope with many malformations of organs, primarily congenital.
Histology - what is it: a descriptive science or a branch of medicine?

It is impossible to overestimate the role of histology in modern medicine. It's hard to find an industry it hasn't penetrated yet. Histological studies are relevant intherapy, pediatrics, gynecology, urology, endocrinology, dermatology. And the diagnosis and subsequent treatment of many diseases is completely impossible without it. So what is histological examination? This is the study of the morphological structure of human tissues, which involves a biopsy and examination of the surgical material. Most often it is carried out for diagnostic purposes. A biopsy is a study of microscopic pieces of tissue that are taken from a patient during an examination procedure. Such a pathomorphological examination is paramount in the diagnosis of almost all oncological neoplasms. It is also indispensable for assessing the quality and effectiveness of drug treatment.
How a histological analysis is done

While examining tissue samples, a pathologist makes a microscopic description of its structures. The sizes, a consistence, color, characteristic changes are considered. As a result of such a thorough clinical and anatomical analysis, a conclusion is given. The results of histology can indicate both the presence of pathology, and its absence. Such an indicative answer may serve as a reason for further examination in order to identify a range of possible diseases. The results of histological analysis cannot serve as a reason for making a final diagnosis. They only indicate a developing disease in a particular organ or system. Based on them, further diagnostics are carried out. Often a histological examination reveals a state of precancerous changes in structures. In thatcase, atypical cells can be traced in the material. This is a clear reason for the preventive treatment of the patient in order to strengthen the immune system. The presence of atypical cells does not indicate developing oncology, but it clearly indicates a high risk of such diseases.