- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Higher nervous activity (HNA), types and balance - this is the balance of excitation and inhibition, that is, the ratio between these forces. Taking into account the ratio of the forces of the inhibitory and excitatory processes, balanced and unbalanced types can be distinguished, that is, the processes can either be equally strong, or one will prevail over the other.

Nervous processes
Nervous processes are as mobile as how quickly the cells of the cerebral cortex change from the process of excitation to the process of inhibition and vice versa. That is, the higher activity of the nervous system can be labile (mobile) or inert (sedentary).
Types of GNI according to Pavlov
Pavlov I. P., on the basis of studies on animals and humans, was able to identify four clearly manifested types of activity of the nervous system:
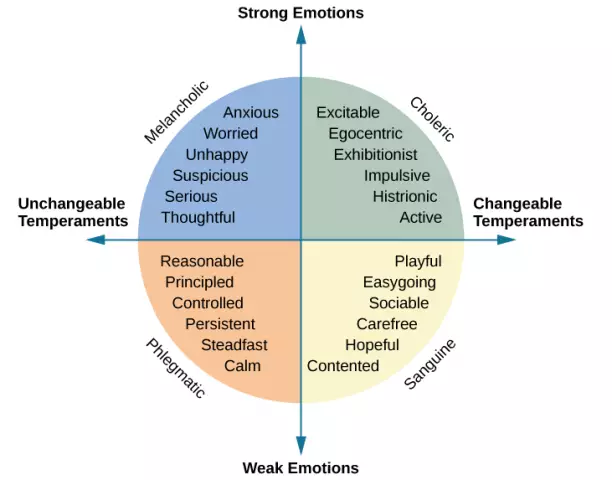
1. Choleric type - strong, unbalanced, excitable.
2. Sanguine - strong, agile, balanced.
3. phlegmatic - stronginert, balanced.
4. Melancholy - Weak.
Information obtained from experiments on animals applies to humans. But it is worth noting that the physiologist Pavlov studied the types of higher nervous activity in humans in clinical conditions.

Temperament according to Pavlov
Restraint and dynamism of nervous processes characterizes the types of activity of the nervous system of people, which are the physical basis of their temperaments. Specifically, higher nervous activity (types of temperament) is manifested in behavior. And this is not only the manner of human behavior, but also aspects of the psyche that make themselves felt in cognitive activity, in the actions and feelings of a person.
Higher nervous activity (types of temperament) are also manifested in the functioning of signaling systems and their interaction. But at the same time, human behavior can be diverse not only due to the physiological basis, but also due to the system of conditional, temporary connections that are formed in the course of human activity.
Higher nervous activity (types of temperament) affects only the behavior and activities of people. In addition, the type of human nervous system can change in the course of life, since it depends on the influences to which a person is exposed. Also, types depend on training and education. Temperament often changes with age.

Personality
Any type of nervous activity, like any temperament, canconfer socially important personality traits. Types cannot be evaluated positively or negatively, since each of them has its pros and cons. For example, a choleric person is more energetic than a phlegmatic person in actions and reaction speed, but at the same time, a phlegmatic person is more restrained and cold-blooded. For an example of the positive qualities of various temperaments, one can cite the responsiveness of a sanguine person, the slowness of a phlegmatic person, the energy of a choleric person, and the stability of a melancholic person.
But on the other hand, higher nervous activity, temperament types are often undesirable properties for a person. Sanguine temperament, for example, under certain conditions can lead to a tendency to "scatter", phlegmatic - can determine indifference and indifference to the environment, and so on. Therefore, you need to understand the negative and positive aspects of temperament and be able to manage them, which is the main goal of education.