- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes - the conjunctiva, which is caused by various infections, viruses and allergens. Let's figure out how bacterial conjunctivitis manifests itself in children. Treatment will also be detailed in this article.
Functions and structural features of the conjunctiva
Conjunctiva is a thin mucous tissue that covers the anterior part of the eye and the inner surface of both eyelids, forming a kind of pocket on the upper and lower fornix. A large number of glands in the tissues around the eyes produce tear fluid and a special protein compound - mucin. Together, they form a strong protective and moisturizing tear-like environment that provides the eyeball with visual ability and mobility.
Despite its relative thinness, the conjunctiva is a complex multi-layered organic tissue that passes into the corneal epithelium. Vessels of the eyelids and eyelashes carry out blood supply to the conjunctiva, a network of lymphatic vessels forms a layer of protective lymphoid tissue, lacrimal and ophthalmic nervesprovide the shell with high sensitivity. Thus, not only the condition of the eyes, but also visual acuity depends on the normal composition and functioning of all the tissues that make up the conjunctiva. This is why bacterial conjunctivitis is so dangerous. Symptoms and treatment in children require special attention.

The conjunctiva is the eye's first protective barrier and the most vulnerable part to various external irritants, bacteria and allergens.
In addition, the tear fluid not only descends through the nasolacrimal canal, absorbing dust and bacteria captured from the air, but also starts the reverse process when infection, viruses or allergic pathogens rise into the fornix of the eyeball and irritate the conjunctiva from the inside. Bacterial conjunctivitis occurs (you can see a photo of the manifestations of this disease in children in our article).
It is useful to know that during seasonal viral epidemics or when in contact with patients with dangerous viral infections (for example, measles or rubella), a protective mask does not help, since viruses freely enter the body through the nasolacrimal canal through the eyes.
Conjunctivitis symptoms
So, how does bacterial conjunctivitis manifest itself in children? Treatment is based on symptoms.
In a normal he althy state, the conjunctiva provides the eye with sufficient moisture, freedom of movement in the lacrimal pocket, puts a transparent protective barrier that does not reduce the visual and light-perceiving ability of the eye.
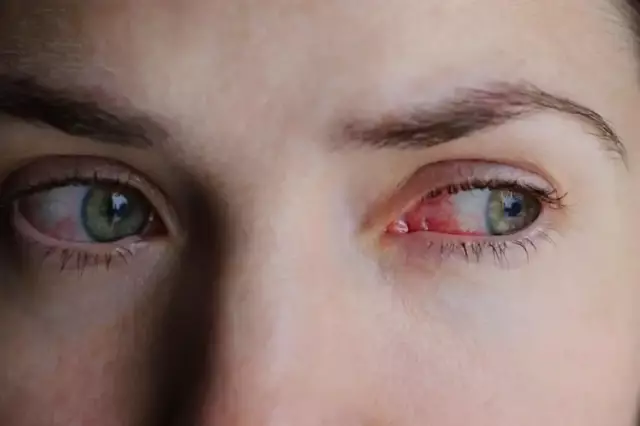
In the case when itching, burning, increased tearing begins in the eyes, a network of dilated blood vessels appears on the surface of the cornea, foreign inclusions and pain when moving the eyes are felt, the eyelids or the skin around the eyes swell, it can be concluded that passing in the eye fornix inflammatory processes. Conjunctivitis is the most common disease that affects the lining of the eye.
How to treat bacterial conjunctivitis in a child? This issue will be discussed below.
Types of conjunctivitis

Depending on the nature and source of infection, there are three types of conjunctivitis that require completely different approaches to diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
1. Bacterial conjunctivitis - caused by various bacteria such as staphylococci, chlamydia, etc. They enter the mucous membrane of the eye both from the external environment with insufficient hygiene, mechanical damage or weakening of the immune functions of the conjunctiva, and from the pathogenic microflora of the body itself during the period of infectious diseases. If bacterial conjunctivitis occurs in children, treatment should be aimed at the destruction of pathogenic microorganisms.
2. Viral conjunctivitis - affects the conjunctiva against the background of adenovirus and enterovirus infections, influenza, herpes, rubella, chickenpox. Often the viral type of inflammation is accompanied by rhinitis, pharyngitis, or a parallel bacterial form of conjunctivitis.
3. Allergicconjunctivitis accompanies almost all forms of allergic reactions of the body to chemical, food, biological allergens and is a concomitant inflammation in allergic rhinitis, dermatitis and asthma.
Bacterial conjunctivitis in children. Reasons

Conjunctivitis in children is a very common disease and up to 5 years of age is diagnosed in 30% of cases of all eye pathologies. This is due to the peculiarities of the child's body and the immune system, which is actively formed and does not effectively protect the body from the effects of adverse factors. Of no small importance is the specificity of children's groups and living conditions.
High risk of infection on the mucous membrane of the child's eyes, which still attaches little importance to hygiene and basic sanitary standards, activity of children during the incubation period, when a sick child continues to communicate with peers and becomes a source of further spread of infection, psychophysical features of life young children - all this contributes to the frequent occurrence of infectious inflammation, including the eyes. This is how bacterial conjunctivitis occurs in children.
In newborns, a special place is occupied by conjunctivitis, which occurred during the passage through the birth canal of a mother with untreated sexually transmitted diseases - gonorrhea or chlamydia. This conjunctivitis appears within days of birth and can have serious consequences, including blindness and loss of an eye ifdo not provide appropriate treatment in time.
With age, the indicator of eye pathologies in children begins to shift towards various refractive disorders, such as myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism.
Diagnosis of bacterial conjunctivitis in children
The methods of diagnosing, treating and hygiene of various diseases in children from the famous pediatrician Evgeny Olegovich Komarovsky are very popular today. His school, which has television and print versions, has received wide recognition from the audience and all responsible parents. The simple, understandable, confidential manner of presenting information and the effectiveness of the methods of the famous doctor help to raise the conscious and cultural level of the population educating the younger generation.

The scientific approach to explaining the most common children's he alth problems and the availability of solutions offered give parents the opportunity to independently examine all aspects of complex medical reports and assess the need for professional help.
The spread, activity and periods of exacerbation of bacterial conjunctivitis in children are difficult to accurately fix, since the frequency of processes, the relative ease in most cases of getting rid of inflammation, the positive experience of previous treatments - these factors lead to rare visits to doctors.
Diagnosis depends on how bacterial conjunctivitis presents in children. Symptoms can vary.
It is usually possible to diagnose bacterial conjunctivitis without appropriate qualifications, since its course is nonspecific and the main difference from other types is the presence of mucopurulent or purulent discharge along the edges of the eyelids or frequent dried crusts on the eyes. Concomitant signs may also be redness of the eyelids and corneas of the eyes, swelling of the skin, increased tearing, itching.
Children complain of a burning sensation in their eyes, often begin to rub their eyes with their hands, become lethargic, whiny. Perhaps a slight increase in body temperature. These signs, already in the early stages of the development of inflammation, give signals to attentive parents and allow you to quickly and independently stop the spread of the infection.
If, with other unpleasant symptoms, there are no characteristic signs of a bacterial variety of conjunctivitis, all circumstances under which the child could get inflammation should be analyzed.

For example, going to mass events, new food, animal hair, dirty toys, washing powder, swimming in the pool, long walks that caused hypothermia or getting a lot of dust in the eyes - these factors will help identify signs of allergic or viral conjunctivitis.
In case of more dangerous symptoms (pain in the eyes, photophobia, blurred vision, blisters on the eyelids), contacting a pediatrician or family doctor will allow you to start treatment faster and avoid irreversible consequences. To establish an accurate diagnosis, the doctor finds out all the possible circumstances and symptoms of the course of the disease, examines the organs of vision, skin and mucous membranes, and, if necessary, gives a referral to a narrow specialist - an ophthalmologist.
Taking a smear from the conjunctiva for cytological examination and biomicroscopy allow you to make an unambiguous conclusion and select the drugs necessary for treatment.
There are also specific research methods - for example, the Gram and Giemsa methods, which with a high degree of probability will attribute inflammation to one of the varieties of conjunctivitis. Thus, the revealed neutrophilia in the mucosal scraping indicates the bacterial nature of inflammation, lymphocytosis will unequivocally confirm the viral nature of conjunctivitis, and eosinophilic inclusions - allergic.
So, the child has bacterial conjunctivitis. Komarovsky advises treating children under the supervision of specialists.
Varieties of bacterial conjunctivitis
Recent studies prove that the formation of the microflora of the mucous membrane of the eye occurs after birth, and not during the passage of the birth canal, as previously thought. In addition to the bacteria characteristic of the normal microflora, a certain number of pathogenic microorganisms, such as staphylococci and diphtheroids, are present in the eye.
Despite the fact that the lacrimal fluid contains numerous protective components (immunoglobulins, lysozyme, lactoferrin), Staphylococcus aureus successfully adapted to overcome such a barrier andstably present in the conjunctival mucosa. The result is bacterial conjunctivitis. Komarovsky recommends treating children with antibiotics.
Treatment
The use of broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs - ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, gentamicin - in most cases gives quick positive results. However, the frequent occurrence of allergic reactions and strains resistant to such antibiotics is an argument for a more accurate isolation of the microorganism that caused conjunctival inflammation and the selection of a drug with a narrower spectrum of action. This is how serious bacterial conjunctivitis can be in a child. Treatment reviews are positive.
Diphtheria and gonococcal varieties of conjunctivitis require specific topical therapy. Antibiotics-fluoroquinolones are now becoming widespread, which have proven effective in combating bacterial varieties of conjunctivitis, except for streptococcal and pneumococcal. It should be noted that the resistance of a number of bacteria to these drugs is also rapidly increasing. This is such a difficult treatment for the diagnosis of "bacterial conjunctivitis in children". Drops in therapy are used quite often, more on this below.
Using drops
An effective system for suppressing inflammation is the combined use of polymyxin-B in the form of drops and ointments. Drops are prescribed at intervals of 2-3 hours, 2-3 drops in each eye, ointments - 3-4 times a day, and are used until the child is completely recovered, that is, for 5-7up to 10-14 days.

When the causative agent of pneumococcal infection is established, washing with a solution of boric acid is prescribed, since these bacteria multiply in an alkaline environment, so acidification of the microflora of the eye will stop the development of pathological bacteria. Some types of bacilli are affected by 0.25%-0.5% solutions of zinc sulfate, which are applied 4-6 times during the day. This is the treatment for a diagnosis of bacterial conjunctivitis in children.
An effective way to treat chronic forms of conjunctivitis is the combination of a steroid and an antibiotic. But given the high percentage of complications after the use of such drugs, they are prescribed only for severe inflammation, and in case of acute conjunctivitis they are not used. In any case, if within 2-3 days the clinical picture from the use of drugs does not change for the better, treatment should be stopped and hidden causes of negative consequences should be looked for.
Bacterial conjunctivitis caused by other purulent-septic diseases such as otitis media, tonsillitis, pyoderma, in addition to local treatment, of course, requires treatment of the infections that provoked this type of conjunctivitis, and usually goes away with its end.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky

When bacterial conjunctivitis is diagnosed, symptoms and treatment are linked in children.
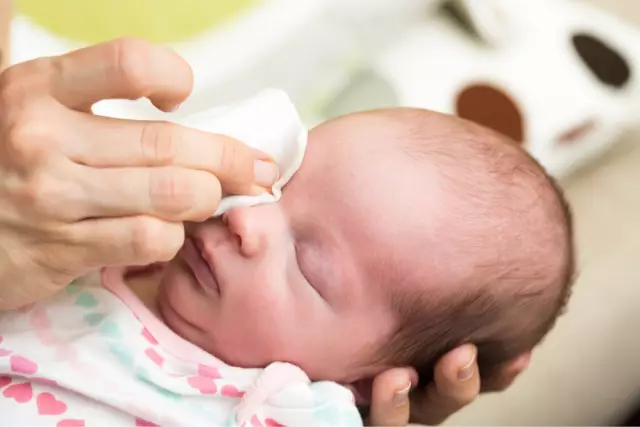
At the first signs of conjunctivitis, the child must be isolated fromother children, refuse to attend children's educational institutions. After the appointment by an ophthalmologist or pediatrician of treatment, follow the recipe and method of using the drugs as accurately as possible. Do not apply bandages or prolonged compresses to the eyes, as this prevents normal blinking, which means washing the mucous membrane with tears and removing purulent deposits from the tissues around the eyes.
Eye washing with infusions of chamomile, calendula, solutions of boric acid or furacilin is carried out 5-8 times during the day, with cotton pads different for each eye, abundantly moistened. Wipe should be from the outer edge of the eye to the inner. It is advisable to apply drip solutions with a rounded pipette, without touching the eyelid or cornea of the eye, in order to avoid infection in the pipette.
Also, without contact, you should put the ointment prescribed for treatment under the lower eyelid. For bacterial conjunctivitis, drops with chloramphenicol, albucid, tetracycline or erythromycin ointment are prescribed.
Since almost all types of bacterial conjunctivitis are accompanied by dry eye syndrome, dry skin around the eyes, which only intensify with the use of antimicrobials, it is useful to use tear substitutes, such as Systein and Vidisik, to maintain stable moisture in the mucous membrane of inflamed eyes. . So you can defeat bacterial conjunctivitis in a child of 6 years. Treatment, of course, must be agreed with the pediatrician.
Prevention of conjunctivitis in children
Most efficientprevention of an unpleasant disease is the constant teaching of children to personal hygiene. Frequent hand washing for babies, cleaning toys and interiors to disinfect surfaces, a food culture explaining the importance of pre-treatment of fruits and vegetables, cutlery during meals will help get rid of frequent recurrences of eye infections.
It is useful to teach older children to bury their eyes and apply ointment on their own, as children are intolerant of any impact on painful areas, especially the eyes, so the child's personal participation in the treatment will speed up the recovery process. You need to be attentive to activities aimed at a general increase in immunity: walking, playing sports, balanced nutrition, taking vitamins when immunity is weakened, hardening procedures.
Expectant mothers should be examined for urogenital infections before delivery and, if necessary, undergo treatment with antiseptic treatment of the birth canal, take care of the examination and special treatment of the baby's eyes immediately after birth.