- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
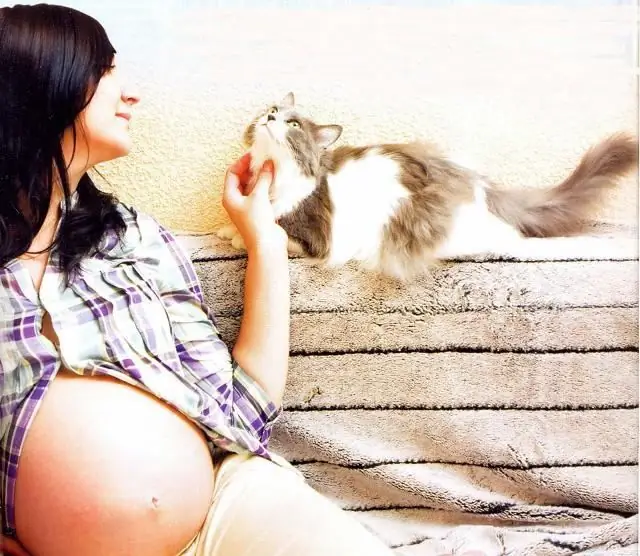
Toxoplasmosis is a pathology caused by protozoan parasites - Toxoplasma. Toxoplasmosis in humans affects the muscles, nervous system, eyes, leads to an increase in the spleen, liver and lymph nodes. The disease is very widespread and is more typical for young people. It is especially dangerous for women during pregnancy.
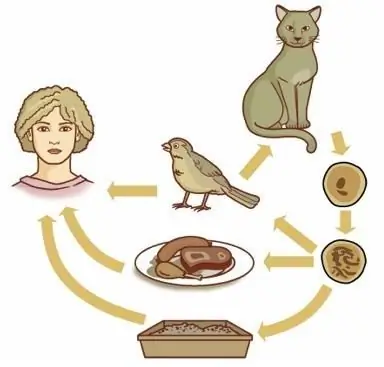
Toxoplasmosis in humans: causes
Toxoplasma can reproduce both sexually and asexually. During sexual reproduction, cysts form in the human intestine. They are highly resistant to any environmental factors: drying, low and high temperatures. Cysts leave the body along with feces and exist in the external environment, again infecting people and animals. Toxoplasmosis in humans can occur due to contact with an infected animal, because many species of both domesticated and wild mammals and birds suffer from this pathology. But the reproduction of cysts sexually can only occur in animals belonging to the cat family. So, a cat is able to secrete up to two billion cysts in two weeks of the course of the disease, whichcan live in the external environment for up to two years. In the case of asexual reproduction, persistent forms of parasites are not formed. So, you can get toxoplasmosis when:
- caring for an infected animal;
- eating undercooked meat or contact with raw meat (for example, often housewives taste raw minced meat);
- eating unwashed vegetables, herbs, fruits (they may contain cysts);
- blood transfusion or organ transplant.
Toxoplasmosis in humans: types and forms of the course of the disease
Pathology can be not only acquired, but also congenital, when the infection of the fetus occurs as a result of the disease in the mother. In general, toxoplasmosis can occur in a latent, chronic or acute form. The most severe is just a congenital pathology. And the acquired disease usually causes almost no symptoms. When it enters the human body, Toxoplasma begins to actively multiply in the intestines, and then with the blood flow it penetrates into other organs, causing inflammation in them. So, parasites affect the retina, heart muscle, liver. They can be in the body without showing activity until the impetus for this is a decrease in immunity or the impact of any adverse factors.

Toxoplasmosis in humans: symptoms
The disease manifests itself in different ways depending on the form of the current. The most severe symptoms occur in children with congenital toxoplasmosis. Moreover,if the infection of the fetus happened at an early stage of pregnancy, it dies in the womb due to the formation of deformities incompatible with life. If infection occurs in the second half of pregnancy, the baby is born with damage to all systems and organs. It can have yellowness of the skin, low muscle tone, constantly elevated temperature, swollen lymph nodes, spleen, liver, encephalomyelitis, skin rash, strabismus or blindness, an abnormally formed spinal cord or brain. With acquired toxoplasmosis, which occurs chronically or latently, symptoms do not appear, with the exception of irritability, apathy, subfebrile temperature, weakness, visual disturbances.
Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis
It is possible to detect the presence of toxoplasma in the body during the implementation of parasitological research. For this, cells are analyzed for toxoplasmosis. A positive result with a 100% guarantee will allow you to make a diagnosis. But a negative one will not always indicate the absence of a disease, since sometimes Toxoplasma in biological fluids are not detected. An enzyme immunoassay is used to detect antibodies to toxoplasmosis. To do this, take a blood test for toxoplasmosis.
Treatment
Pathology should be treated only when there are clinical manifestations. In this case, antibiotics, chemotherapeutic agents, antihistamines and sulfa drugs are prescribed. In addition, general strengthening vitamins may be indicated.






