- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
If you suspect the development of certain diseases (usually of an infectious nature), the patient takes an analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid, which is called cerebrospinal fluid. The procedure is safe for humans. However, it has certain features and side effects. In order to draw conclusions about the features of conducting such a study, the procedure and norms of analysis will be discussed in detail below.
Cerebrospinal Fluid Functions
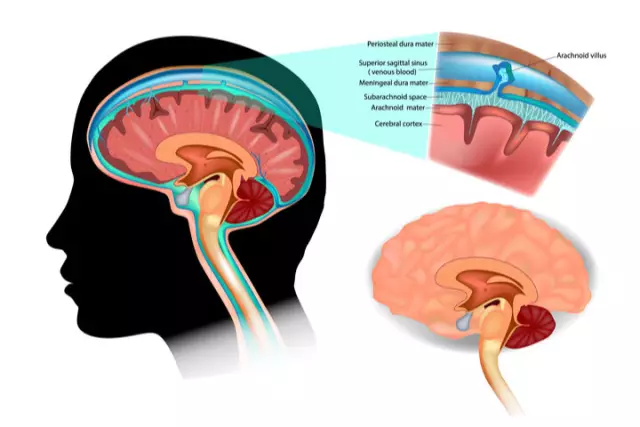
Before considering how the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid is taken, you should find out what function it performs in the body. Liquor is also called cerebrospinal fluid. This is a biological element that is constantly located and circulates in the ways allotted for it. It is concentrated in the subarachnoid membranes of the brain and spinal cord. CSF is also present in the ventricles of the brain.

Cerebrospinal fluid performs importantfunctions for the human body. It provides a balance of the components of the internal environment of the two most important parts of the body - the brain and spinal cord. Liquor protects them from impacts by absorbing mechanical shocks. With the help of it, neurons (brain cells) are saturated with essential nutrients, oxygen. Also, the liquid removes carbon dioxide, toxins and other substances used during metabolism.
Cerebrospinal fluid maintains an optimal chemical composition of the internal environment, as well as pressure inside the skull. It contains white blood cells that do not allow infection to develop inside the brain. The performance of these functions becomes possible only due to the constant flow of fluid in the paths. Liquor is constantly updated.
Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid allows you to determine the development of various pathologies. If you identify them at an early stage, treatment will be much faster and easier. It is worth noting that the amount of water that a person drinks per day affects the rate of CSF composition. In order for the body to function normally, it needs 1.5-2.5 liters of water per day. In this case, the correct pressure is maintained inside the brain. Otherwise, the person feels unwell.
Normal performance
There are certain standards for the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid. In a he althy person, the indicators should be within certain limits. If the cerebrospinal fluid does not meet the established standards, the doctor can diagnose a certain pathology. So, the cerebrospinal fluid should be transparent and colorless, similarvisually clean water. After examining the composition in appearance, they proceed directly to the analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid. The protein norm in it is up to 0.45 g / l. The cellular composition is also evaluated. 1 µl should contain 1-2 lymphocytes. Glucose should be contained in the liquid from 30 to 60%. This indicator depends on the characteristics of the patient's diet. To correctly investigate this indicator, it is compared with the data of a blood test. In this case, the pressure in the system should be 100-150 cm of water column.

In addition to microscopy, when analyzing cerebrospinal fluid, its amount is examined. It should vary between 130-160 ml. This indicator depends on the physiology of the organism.
90% CSF is water. It contains proteins, amino acids, glucose and lipids. Also in the liquid there is ammonia, traces of concentrates of nitrogen compounds and urea. The liquor contains lactic acid, as well as the remains of cells and their individual fragments.
The density of the liquid is between 1003 and 1007 g/l. The reaction of the medium is also determined during the analysis. Normal pH is 7.37-7.88 units. The composition of the liquor is alkaline. However, the indicator of environmental characteristics should not go beyond the established limits.
It is worth noting that the pressure standards may differ if the patient is sitting or lying down at the time of sampling of biological material. This phenomenon is due to the redistribution of body weight, which puts pressure on the cerebrospinal fluid in different positions.
Cytosis in the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid can range from1 to 10 µl. This indicator characterizes the number of cells in the fluid. They constantly get into the cerebrospinal fluid from tissues and blood. This is considered normal.
Indications for testing
General analysis of cerebrospinal fluid is carried out with suspicion of a number of pathologies. The doctor after the examination may prescribe a similar procedure if the patient is suspected of having a tumor. Neoplasm can be located in different parts of the body. The analysis will be able to confirm or deny its presence.

With traumatic brain injuries, a similar study is also required. If you suspect the development of a heart attack or stroke of the brain or diseases that accompany them, the doctor may prescribe a similar procedure. One of the groups of indications is an infection in the lining of the brain. Therefore, an analysis of cerebrospinal fluid is almost always prescribed for meningitis, meningoencephalitis, etc.
Indications for examination may be the presence of an intervertebral hernia, epilepsy or brain hematoma. In the presence of such diseases, the analysis will be able to detect the presence of pathology.
The sampling of biological material is carried out by taking a puncture. The procedure can be performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Sometimes, in the process of such a puncture, an antibiotic is introduced into the body. It should be noted that this procedure is completely safe. It does not lead to disorders in the spine. Therefore, you should not be afraid that complications will arise after the collection of cerebrospinal fluid. There is a certain technique for taking biological material.
In specialized clinics, based on the examination, the doctor will be able to diagnose a number of diseases that are dangerous to human he alth and life. Comparing the indicators with the standards, you can determine the deviation. Next, its cause is established. This allows you to draw conclusions about the processes occurring in the patient's body.
How is the analysis done?
Many patients are interested in how the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid is done. This procedure is special. For its implementation, a doctor of appropriate qualification makes a lumbar puncture. A special needle is inserted into the tissue. In some cases, the patient is indicated for an atlanto-occipital puncture.

The doctor puts the first drop on a napkin. This avoids getting blood into the material. Its presence can significantly affect the result. Considering how the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid is done, it is worth noting that at the slightest suspicion that travel blood has entered the test tube, the puncture is redone. Use a new needle each time.
Due to some circumstances, it is impossible to take a puncture in some patients due to the ingress of travel blood into the material. If three attempts were unsuccessful, the fourth puncture is not carried out. This can lead to the development of various complications.
Liquor is not collected in glass test tubes. In this case, there is a possibility that white blood cells will stick to the glass.
To take the required amount of liquid, make a puncture in the arealoins. It is safe to take a puncture here. Penetration of the needle into the sheath of the spinal cord will not harm a person. Here the nerve fibers move freely in the CSF. It is impossible to pierce them with a needle. However, after the puncture, the person feels constant discomfort in the lumbar region. Headaches may also occur. Unpleasant symptoms go away on their own after a couple of days.
Cerebrospinal fluid test results will vary depending on the policy of the clinic where the test is performed. The material is delivered to the laboratory no later than one hour after the puncture. Usually the patient receives the result of the examination the next day.
Assay kit
To perform such an analysis, a set of reagents for the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid is used. It includes a number of components that interact with biological material. The cost of such sets varies from 1200 to 1500 rubles. By default, it can be used to define the following:
- cytosis;
- quantity and quality of protein indicators;
- qualitative indicator of globulin.
Samson's reagent is used to prevent cell cytosis for several hours. It is included in almost every kit for the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid. The reagent contains acetic acid. It dissolves red blood cells. The reagent also contains fuchsin, which stains cell nuclei red. In this case, it is much easier for the laboratory assistant to count their number in the biological material. It is also possible to perform cell differentiation without any problems.
Qualitative protein analysis is carried out using the Pandey reaction. Cerebrospinal fluid clinical test kit contains phenol. It reacts with protein. As a result, the liquid becomes cloudy. The more intense this process, the correspondingly more of a certain protein is contained in the cerebrospinal fluid. In a similar way, determine the amount of it in the composition. Only in this case, sulfosalicylic acid and sodium sulfate are used. The cloudier the composition, the more protein it contains.
To check the composition of globulins, the None-Apelt reaction is used. Biological substances react with ammonium sulfate. When using such kits, it is possible to determine how certain processes in the body proceed, whether there is any pathology. An experienced doctor of the appropriate qualification is engaged in decoding.
Liquid color

It is worth noting that the decoding of the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid is carried out in a complex manner. Compare the indicators obtained during the study of blood, urine, as well as some instrumental procedures. Patient complaints are also taken into account. One of the important indicators is the color of the liquor. If the liquid has ceased to be transparent, an increased viscosity is determined in it, this indicates the development of the disease. By the color of the liquid, we can talk about the development of certain pathologies:
- Red. In the subarachnoid space, hemorrhage is determined. This is where high blood pressure comes into play. This state speaks ofpre-stroke condition.
- Light green. The liquid may also have a yellowish tinge. This color indicates the development of meningitis or brain abscess. A similar situation occurs with complications of an inflammatory nature.
- Opalescent or diffuse. Talks about the development of the pathological process. It develops in the membranes of the brain. May also be present in bacterial meningitis.
- Yellow. It's called xanthochromic. The shade indicates a brain hematoma or the possible development of oncology in this department.
If the liquid becomes cloudy, this indicates a high content of cells in it. This may include bacteria. A serious inflammatory process develops in the body. An increased density of CSF indicates the presence of a traumatic brain injury or inflammation. Too low density is also a pathology. This condition is called hydrocephalus.
Cytosis, protein concentration
In the course of deciphering the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid, such an indicator as cytosis is necessarily examined. The increase in the concentration of cells in the biological material should not exceed certain limits. If the cytosis is increased, exceeds the allowable value, this may indicate the following:
- complications in the development of a stroke or cerebral infarction;
- allergy;
- appearance of oncological neoplasms;
- meningitis;
- organic lesions of the meninges.
Also be sure to control the level of protein in the analysis. An increased concentration is indicative ofoccurrence of serious pathologies. For example, it can be meningitis, benign or malignant neoplasms, hernia (protrusion) of the intervertebral discs, encephalitis. Also, a similar situation may indicate compression of neurons located in the spinal column.

Reducing the amount of protein in the cerebrospinal fluid is not a pathology. Fluctuations of this indicator in the negative direction are a physiological state. This cannot be regarded as a symptom of a disease.
Protein penetrates into the cerebrospinal fluid from the blood plasma. With its increase, the blood-brain barrier becomes permeable. Through it, the protein enters the cerebrospinal fluid. This indicates the development of serious pathologies in the body. To make a correct diagnosis, an analysis of the protein content in the blood serum is carried out. Based on the information received, an albumin index is obtained. For this, the protein index in the cerebrospinal fluid is divided by the same value in the blood plasma.
Next, the degree of damage to the blood-brain barrier is assessed. If the index is less than 9, no violations were found. If the indicator is in the range from 9 to 14 units, the lesion is regarded as moderate. Noticeable disorders are diagnosed in the presence of an albumin index at the level of 15-31 units. Severe lesion is defined in the range of 31-100. Above 101 units, the barrier function is completely impaired.
To determine the amount of protein, the biological material is mixed with sulfosalicylic acid, sodium sulfate. As a resultthe liquid becomes cloudy. The intensity of this process is determined by the photometric method. For this, special equipment is used. The result is evaluated at a wavelength of 400-480 nm.
Glucose and chlorides
During the clinical analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid, the glucose level is also determined. Both an excess and a decrease in sugar in the cerebrospinal fluid are considered a negative phenomenon. If the norm is exceeded, we can talk about the development of various diseases. It can be epilepsy, concussion, oncological neoplasms. In addition, an increase in glucose may indicate the development of type 2 or type 1 diabetes.
Low sugar in the cerebrospinal fluid indicates the development of the inflammatory process. Including it may have a tuberculous nature. Meningitis is also characterized by similar symptoms.
The analysis also determines the concentration of chlorides. It is unacceptable to increase or decrease this indicator. If the concentration of chlorides in the biological material is exceeded, an additional examination is required. A similar situation may indicate the development of renal or heart failure, as well as oncological neoplasms.

If the concentration of chlorides is reduced, this may indicate the development of meningitis. Also, a similar situation is observed with the appearance of a tumor. At the same time, a set of indicators is necessarily investigated. The doctor cannot make a diagnosis only on the basis of the deviation of one indicator. A comprehensive examination allowsget the correct result.
Microscopy
Cerebrospinal fluid analysis can count the number of cells and create a cytogram in smears. To do this, they are stained according to Nokht or Romanovsky-Giemsa with the help of azure-eosin. However, in addition to the number, the composition of the cells is also studied. For this, microscopy of biological material is carried out.
In the normal state, only monocytes and lymphocytes enter the CSF. However, due to various reasons, diseases, other cells may also be included in the composition. It should be noted that normal cerebrospinal fluid contains up to 10 lymphocytes. Their number increases with the development of tumors in the central nervous system. Also, their level rises in the presence of an inflammatory process in the membranes of the brain.
Other cells
If blood plasma cells are detected in the biological material, this indicates the development of an inflammatory process in the brain for a long time with encephalitis, meningitis, and a number of other similar diseases. A similar situation is observed in the postoperative period.
If tissue monocytes are present in the CSF, this also indicates the development of a chronic inflammatory process in the central nervous system. Single inclusions of these cells in the cerebrospinal fluid are allowed. If there are a lot of them, this indicates an active tissue reaction during wound healing.
Macrophages should also not be found in CSF. They appear in the cerebrospinal fluid only after bleeding or inflammation. It is considered normal if such cells are found in biological material collected for research, inpostoperative process. This indicates the process of purification of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Neutrophils should also not be present in the cerebrospinal fluid. If they are present here, this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process. If there are enough neutrophils in an altered form, then this process is already fading.
Eosinophils are present in the analysis in the presence of subarachnoid bleeding, brain tumors and meningitis. Very rarely, epithelial cells are observed in the collected material. This is a sign of the development of a tumor or an inflammatory process.
Having considered the features of conducting and interpreting the results of the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid, you can expand the knowledge about this procedure.