- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Disorders of the pituitary gland are diseases that in recent years have been diagnosed more often than before. Each person needs to imagine such problems in general terms in order to consult a doctor for a detailed diagnosis at the first symptoms. It must be understood that diseases associated with impaired activity of the pituitary gland are dangerous - this is not only a decrease in the quality of life, but also a high probability of various complications.

What is it about?
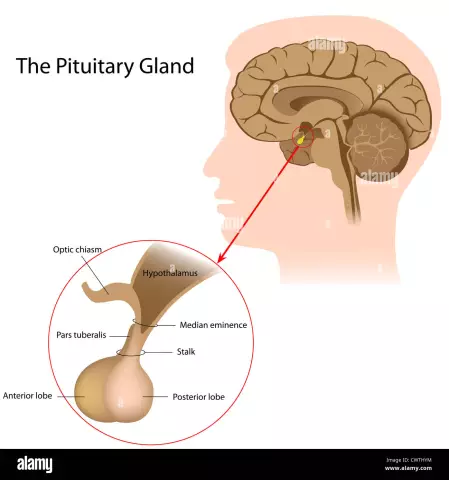
The pituitary gland is indispensable for the endocrine system. This term refers to a small gland located in the brain, in its lower half. The gland is located near the saddle-shaped cranial bones and produces hormones that ensure the possibility of normal life, regulating human growth, metabolism and reproductive ability.
If the hormonal background is disturbed, then it is likely that this condition was provoked by diseasespituitary. They affect women and men equally, they affect people of different ages, social status, leading different lifestyles.
Where does trouble come from?
As a rule, a symptom of pituitary gland disease is an abnormal level of hormones produced by this gland in the human blood. Both an overabundance and too little concentration are possible. In any of the options, the entire endocrine system suffers greatly.

Typically, the lack of production of hormonal compounds is provoked by incorrect blood supply or brain injury. In some cases, diseases associated with the pituitary gland are observed against the background of hemorrhage, inflammation, and problems in the vascular system. It may also be a consequence of exposure.
Diseases of the pituitary gland, in which the level of activity of the gland is overestimated, are often associated with a benign neoplasm. This pathology in medicine is called adenoma. The disease is quite widespread, its development can be provoked by trauma or infection of the brain. In some cases, an adenoma (pituitary disease) develops against the background of long-term use of oral contraceptives.
How to suspect a problem
Diseases of the pituitary gland manifest themselves in a number of symptoms characteristic only of them. In addition, there are manifestations characteristic of some other diseases, which can make diagnosis more difficult.
So, if the pathology developed before birth, then it is quite easy to notice it - you can see a disproportionate addition, unhe althyappearance. If hormonal activity is insufficient, growth slows down, and such a person will be below average for life. But excessive activity of the gland leads to gigantism - growth does not stop throughout life.
With pituitary disease, some patients grow truly enormous in height, which is accompanied by acromegaly - the limbs increase, the voice coarsens, the posture deteriorates, the internal systems and organs are deformed.

If the disease of the pituitary gland is characterized by an incorrect, too weak process of producing growth hormone, this leads to disturbances in the functioning of the genitourinary system. A blood test for biochemistry can reveal a lack of sodium, glucose, somatotropin. There is also an unnatural response to insulin.
What else happens?
If the lack of hormones develops in a secondary form, patients are diagnosed with hypothyroidism. In some cases, Graves' disease affects the pituitary gland. Quite rarely, but still, pituitary dwarfism occurs - such a pathology more often affects the male half of humanity than the female. What is good, modern medicine knows quite effective methods for eliminating pathology.
Hypothyroidism
If the thyroid gland does not produce the amount of hormones necessary for the normal functioning of the body, this causes hypothyroidism. Usually this is observed when the functioning of this organ is insufficient or with a pathological effect on the processes that control the hormonal background.
Primary (thyroid) hypothyroidism is usually triggered by a lack of iodine in the body. In some cases, it is caused by mechanical injuries of the thyroid gland, provoked by radiation therapy, surgery, etc.
Secondary hypothyroidism is a disease in which the body does not have enough hormones produced by the thyroid gland. With this disorder, the hypothalamus cannot generate thyroliberin, which affects the work of the pituitary gland - the processes of creating thyroid-stimulating hormone stop.
Central hypothyroidism
Tertiary hypothyroidism in modern medicine is often also called central. This form is narrowly distributed and is characterized by the inability of the thyroid gland to cope with the functions assigned to it. In some cases, this is triggered by the pituitary gland, but sometimes the hypothalamus plays a role.

Features of pathology
It is rather difficult to suspect hypothyroidism at the very beginning of the development of the disease, since its course is hidden and has no clear symptoms. Most often, pathology is detected during a blood test to identify the characteristics of the hormonal background. With a congenital form, a child has bloating, an umbilical hernia, a disproportionate tongue, and thyroid glands. Over time, the baby loses its appetite, normal development is disturbed, the weight goes beyond the prescribed, the digestive tract is disturbed - constipation appears.
If you start treating the disease on time, you can restore the functionality of all body systems to the fullest. Also, the growth process will be normal.baby.
When the form is advanced in an adult, the pathology can be suspected by the appearance of the patient - the skin on the face is yellowish, the face swells, since the fluid is not excreted from the body in the normal way. A person feels weak, his hair and eyebrows are actively falling out, his skin dries, his muscles hurt.
Usually a rather lethargic person who speaks in a hoarse voice and is rather hard of hearing. Further development of the disease is associated with disruption of the nervous system, which negatively affects memory, the ability to concentrate, and intelligence. There are problems with sleep, the patient's condition is depressed. Hemoglobin drops in the blood, cholesterol rises.
Hyperprolactinemia
Prolactin is a hormone that is normally actively involved in the formation of the required amount of breast milk for a nursing mother. Hyperprolactinemia can develop in one of three forms. The natural variant is the physiological form due to childbirth and growth. Pathological is usually provoked by an adenoma or other internal disorders. With long-term use of certain groups of medicines, a pharmacological form of the disease may appear.

Clinical symptoms can occur in patients of different ages and genders. At the same time, women note:
- excretion of breast milk;
- menstrual irregularity;
- inability to get pregnant;
- lower sex drive;
- pain during intercourse.
Men oftenimpotence develops, vision loss is possible. In patients at a young age, the reproductive system develops with a delay. Hyperprolactinemia provokes metabolic problems, acne. Patients feel constant weakness, sleep is disturbed. Often the disease provokes diabetes.
Adenoma
There are two types of pituitary adenoma - active and inactive hormonally. Usually, the pathology develops rather slowly, the neoplasm is benign. Depending on the size, they speak of a microscopic, macroadenoma.
At an early stage of development, the adenoma practically does not manifest itself, which significantly complicates the diagnosis. Over time, the tumor provokes the endocrine-metabolic syndrome. At the same time, the thyroid gland grows in size, excess weight, warts appear. Most patients note that the skin becomes oily. Many people are diagnosed with diabetes. Often, an adenoma also has symptoms of hypothyroidism, hyperprolactinemia.
How else to notice an adenoma
The development of adenoma is associated with an ophthalmic, neurological syndrome. In this case, the patient's visual field is distorted, and he suffers from headaches. As a rule, vision is greatly reduced, there are violations of eye movements. Doctors explain this by the fact that the neoplasm compresses the Turkish saddle, cranial nerves.

Often with pituitary adenoma, patients become depressed and suffer from nervous disorders. Continuous growth of neoplasm provokes mental disorders.
How to identifydisease
If symptoms characteristic of adenoma are observed, there is at least the slightest suspicion of this disease, you need to make an appointment with a local therapist who will redirect you to an endocrinologist. When using the services of a private clinic, you can immediately go to an endocrinologist for a detailed diagnosis of the state of the body.
The doctor will choose the most applicable instrumental methods of analysis, control the content of hormones in the urine, blood, and make an analysis for biochemistry. If there is an assumption that the cause is nodular hypothyroidism, an additional ultrasound diagnosis is performed.
To determine the type of tumor, you need to undergo a CT scan or MRI. This also allows you to accurately determine the size of the neoplasm, to understand how much the Turkish saddle has suffered and what the nature of the damage is. An ophthalmological examination also evaluates the condition of the cranial nerves.
What to do?
Treatment of diseases of the pituitary gland is determined by the characteristics of a particular diagnosis. First you need to choose drugs that allow you to return the hormonal background to normal. The patient is also prescribed medications that stimulate the production of the necessary hormones by the internal systems of the body. In addition, they carry out general strengthening activities and choose a diet that is optimal for the pathology.

If an adenoma is established, radiation therapy can give a good result, eliminating the neoplasm. With a macroadenoma, surgical removal of the tumor is possible.
Lack of hormonesin the blood must be replenished with external sources, accompanied by mineral components and vitamin therapy. In the treatment of young patients, hormones are administered in minimal doses. With a well-chosen program, well-being soon returns to normal, children's growth normalizes.