- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
The fourth ventricle of the brain - what is it? Where is it located and what functions does it perform? What can be pathological changes? You can find the answers to all these questions, as well as the causes and methods of treating diseases associated with it, in this article.
Ventricles of the brain
The ventricles of the brain are cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid. There are only four of them: paired temporal, third and fourth ventricles of the brain. The latter is located between the cerebellum and the medulla oblongata. Its shape is somewhat reminiscent of a tent, which is divided into a roof (cerebellum) and a bottom (medulla oblongata).
What are the functions of the fourth ventricle of the brain? The thing is that in the ventricular complex there is constantly liquor (cerebrospinal fluid), which, by the way, plays an important role in protecting the central nervous system. From the ventricles, it enters the subarachnoid space, from where it drains into the venous system, and from there into the lymphatic system.

Pathologies of the fourth ventricle of the brain
The ventricles of the brain can suffer from pathologies as well as all organs and systems of the human body. Problems can be due to various reasons: from inflammation to the presence of parasites. In this article, we will consider only two situations: a tumor and an expansion of the ventricle.
Tumor of the fourth ventricle of the brain
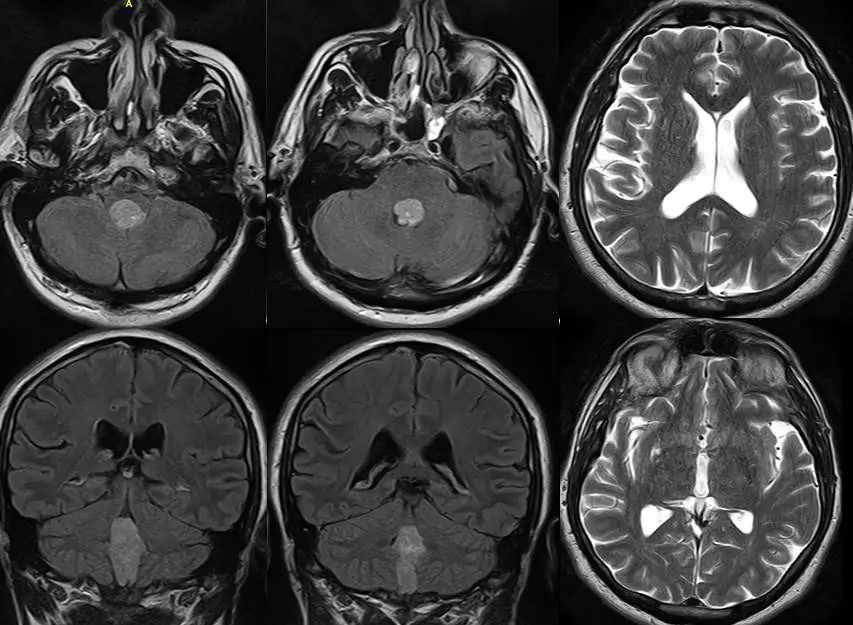
The development of a tumor in this part of the brain prevents an adequate outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which causes the following symptoms:
- headache combined with vomiting;
- dizziness;
- disturbances in the work of the heart and breathing (lymph outflow from the fourth ventricle goes to the medulla oblongata, which is responsible for involuntary cardiac and respiratory activity);
- unsteady gait;
- nystagmus (twitching of the eyeballs);
- discoordination;
- often accompanied by hydrocephalus (accumulation of large amounts of cerebrospinal fluid).
To diagnose this disease, consultations of several doctors are required, at least a general practitioner and a neurologist. To make a final diagnosis, the results of additional research methods are needed: CT or MRI of the brain.
Surgical treatment. Before removing the tumor, it is often necessary to extract excess fluid from the skull. In most cases, after excision of the tumor, dropsy still remains and bypass surgery is performed. In the malignant course of the disease, in combination withsurgical treatment is chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
Headache and vomiting in combination with each other are cerebral signs (brain), as these are symptoms of increased intracranial pressure. If available, it is recommended to consult a doctor and undergo an examination for the purpose of diagnosis.
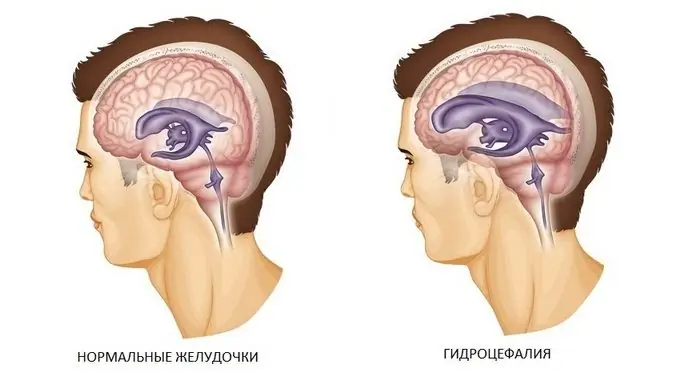
Hydrocephalus
Expansion of the fourth ventricle of the brain or the entire ventricular complex is called hydrocephalus, and in the common people - dropsy. By definition, it is an excess of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles, which causes their increase. Very often this condition occurs in children and is congenital. But not always the expansion of the ventricles indicates the presence of pathological changes. They can only talk about physiological features - a large head. But the final verdict is put by the doctor after a complex of studies. The cause of this pathology is still unknown.
How does this state manifest itself?
- nausea, vomiting, dizziness (with acute hydrocephalus);
- rolling eyes down (a symptom of the setting sun);
- skull enlargement, sometimes excessive;
- apathy;
- unsteady gait;
- involuntary urination and defecation;
- impaired consciousness when turning the torso and head.
Causes of hydrocephalus:
- infectious lesions of the brain (including meningitis);
- traumatic brain injury;
- stroke;
- tuberculosis;
- alcoholism/drug addiction.
At the initial stage of the development of this condition, it is possible to use conservative treatment, if it has already developed - only surgical intervention in order to remove excess cerebrospinal fluid and reduce intracranial pressure.
Both of these diseases require a doctor's consultation, individualized treatment and a thorough examination. All ailments are much easier to cure at an early stage, so experts recommend not to delay visiting a doctor. Stay he althy!






