- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Diseases of the spinal column are very dangerous. After all, they affect a vital structure - the spinal cord. One of these pathologies is a sequestered hernia. The disease negatively affects the entire body and can lead to a number of severe consequences.

Characteristics of the disease
What is a sequestered disc herniation? This is a pathology in which the nucleus pulposus (jelly-like contents) is squeezed out through a rupture or crack in the disc membrane and completely separated from it.
Such a fragment begins to put pressure on the adjacent spinal nerves. As a result, the patient experiences pain, numbness, a tingling sensation in the area where the nerve is pinched. Sometimes a detached piece of disc is able to penetrate into the epidural space. In such situations, there is simply unbearable pain. It can be felt not only in the back, but also in the limbs.
Severe condition is characterized by the development of cauda equina syndrome. With this course of the disease, the patient mayLose control over defecation and urination. In addition, there is numbness in the legs and inguinal region. This form of the disease is an indication for immediate surgical intervention. Otherwise, irreversible damage to the nervous tissue is possible.
The detached fragment in some cases may break down and then be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Sources of pathology
The destruction of the intervertebral disc is caused by excessive tension of the paravertebral muscles. This triggers the development of dystrophic processes. As a result, the fibrous ring is damaged.
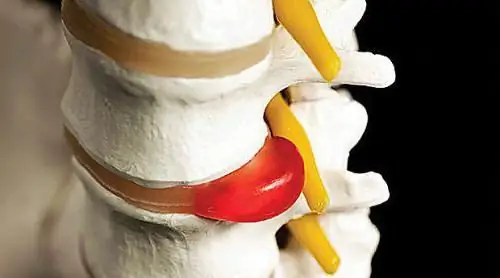
The higher the load experienced by the disk, the more likely it is to develop this hernia. In this regard, sequestered hernia is most often formed in the lumbar region.
Predisposing factors to the appearance of the disease are the following points:
- malformations;
- osteochondrosis;
- excessive weight;
- deficiency in cartilage tissues of minerals;
- work that puts a heavy load on the spine (loader, builder).
Most often the disease begins to develop on the background of:
- stress;
- weight lifting;
- wrong bending, squats;
- hypothermia.
Symptoms of the disease
Sequestered hernia in some cases can develop almost imperceptibly. In this case, the patient periodically experiences back pain. But people get used to such phenomena. The formation of a sequester is perceived assick like another attack.
Symptoms of the disease depend on the location of the hernia. That is why it is necessary to consider them separately.
The following signs indicate the development of pathology in the cervical region:
- frequent headache attacks;
- periodically numbness appears in the neck, hands;
- pain syndrome in the neck area;
- discomfort is permanent intense;
- pain gets worse after exercise;
- muscle tissue on the upper limbs is gradually depleted;
- weakness in the muscles appears in the area of shoulders, neck, arms;
- gait changes;
- paralysis of the limbs gradually begins to develop.

If sequestration has developed between the thoracic vertebrae, then the patient has the following symptoms:
- severe chest pain;
- discomfort can be given in the shoulder blades, abdomen, ribs;
- pain intensifies even after minor exertion;
- leg paralysis develops;
- feeling of numbness can cover the chest, abdomen, back;
- muscle tissue gradually weakens, sometimes complete atrophy is observed.
The following signs indicate the pathology of the lumbosacral zone:
- intense pain attacks occur in the lumbar area;
- discomfort is permanent, pronounced;
- the slightest load leads to increased pain;
- discomfort can be given in the lower extremities, buttocks;
- tendon reflexes are lost;
- leg muscles are depleted;
- toes, feet periodically go numb;
- the process of urination or defecation may be disturbed;
- weakness and impotence appear in the legs;
- feeling stiff in the lower back;
- Sometimes leg paralysis develops.
Diagnosis of disease
In the case of the above symptoms, the patient should consult a neurologist. The doctor will listen to the patient's complaints, assess his neurological and physical status. If a hernia is suspected, an additional examination will be required.
Unfortunately, x-rays are in most cases an uninformative diagnostic method. It is not able to reliably show the presence of fractures, bone growths, displacement of the joints.
Sequestered spinal herniation is most accurately visualized with MRI. This study allows you to determine the position, size of the pathology. In addition, MRI gives an idea of the state of muscles, ligaments, and nerves.
Treatment methods
To fight the disease is used:
- conservative therapy;
- surgical intervention.

The decision on the necessary measures is taken only by the doctor. Very often, patients believe that only with the help of surgical intervention it is possible to fight such a disease as a sequestered hernia. Conservative treatment can be no less effective method. But you should strictly follow all the appointments and recommendations of the doctor.
Drug therapy
It should be reminded once again that the treatment of a sequestered hernia without surgery is possible only on the recommendation of a doctor. It is strictly forbidden to fight such a pathology on your own. Indeed, in most cases this is the path to disability.
Conservative treatment involves keeping the sequester from falling out completely until the tissue of this fragment completely dies. This will allow bone growths to form, covering the formed holes.
Medication is prescribed to improve the patient's condition:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Such drugs relieve pain, reduce the severity of the inflammatory process. Medications may be recommended to the patient: Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Nimesil.
- Diuretics. Such drugs are prescribed in short courses. They perfectly relieve puffiness provoked by tissue compression. Therapy may include such drugs: "Furosemide", "Hypothiazid".
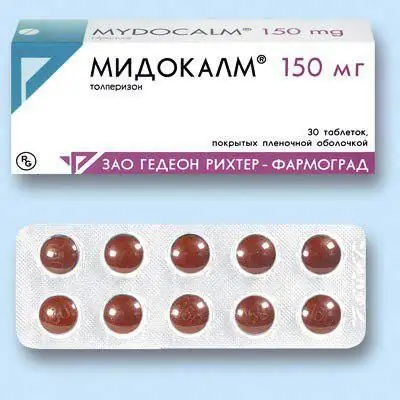
- Muscle relaxants. These drugs relieve muscle spasms. One of the effective muscle relaxants prescribed for this disease is the drug Mydocalm.
- Vitamins of group B. They are prescribed to improve the conduction of impulses. These are the following medicines: "Thiamin", "Pyridoxine".
- Chondroprotectors. These are drugs that provide improved nutrition to cartilage tissues. The most commonly prescribed drug is Chondroitin Sulfate.
- Anticonvulsants. This group of drugs is able to eliminate neuropathicpain. The following remedies are recommended for patients: Carbamazepine, Finlepsin, Convulsofin.
- Other medicines. To improve tissue trophism, stimulate microcirculation, medications may be included in the treatment: Actovegin, Trental.
If necessary, resort to novocaine blockades.
Additional methods of conservative therapy
Sequestered hernia is treated without surgery, not only with drugs.
The patient is prescribed a range of physiotherapy treatments to improve well-being:
- diadynamic currents;
- magnetotherapy;
- stretch;
- ultrasound;
- Darsonval currents.
In addition, the patient is recommended physical therapy classes, a massage course is prescribed.
With positive dynamics, improvements are noticed already at 2-3 weeks of conservative therapy.
When surgery is required
But, unfortunately, there are situations when a sequestered hernia cannot be treated conservatively. Surgery is the only way to restore he alth.

The need for surgery occurs in the following cases:
- The course of the disease is characterized by a sharp deterioration. There may be periods of improvement. They quickly turn into deterioration.
- The size of the sequester is quite large (more than 10 mm).
- There is a strong weakening in the nerve root zonemuscle tissues.
- Limbs go numb all the time.
- Conservative therapy, carried out for six months, did not give positive dynamics.
- There is a progression of the pathology, despite the observance of all doctor's prescriptions.
- A patient is diagnosed with an autoimmune disease.
Surgery
As noted above, conservative treatment of a sequestered hernia does not always give positive results.
The operation can be carried out in several ways:
- Microdiscectomy. With the help of microsurgery, a sequestered hernia is removed. This allows the patient to relieve the pressure exerted by this fragment on the roots of the brain.
- Endoscopic removal.
- Percutaneous nucleoplasty. During the operation, the disc is sclerosed using cold plasma and an electrode.
- Removal of a prosthetic disc. Replace the damaged prosthesis with the bone of the patient himself or with a titanium prosthesis.
- Autotransplantation of cartilage. The necessary tissues are taken from the patient and propagated in a test tube. After 3-4 months, such cartilage is transplanted to the patient.
- The part of the vertebra that compresses the spinal cord is removed. These operations are: laminotomy, foraminotomy.
Rehabilitation and prevention
If a sequestered hernia has been operated on, then the patient must follow certain rules recommended by the doctor.
During rehabilitation it is important:
- do not lift heavy;
- take everything prescribed by the doctordrugs;
- avoid strenuous exercise.
When the body recovers from surgery, the patient should proceed to the prevention of recurrent hernias.
To protect against recurrence of pathology, it is recommended:
- do physical therapy regularly;
- follow a special diet;
- go to the pool (swimming is very useful for such an ailment);
- watch your posture;
- treat periodically in a sanatorium.
Strict adherence to all medical recommendations will defeat the pathology and protect against its recurrence.






