- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Down syndrome, also called trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder that leads to cognitive impairment. Pathology occurs in an average of one in eight hundred newborns. Signs of Down syndrome are manifested in developmental delay, which can be mild or moderate, the formation of characteristic facial features, low muscle tone. People suffering from pathology often have gastrointestinal diseases, heart defects and other problems.

Causes of Down syndrome
The name of the pathology is given in honor of Langdon Down, the doctor who first described this disorder in 1866. The doctor was able to name his fundamental symptoms, but he failed to correctly determine the cause of the pathology. This happened only in 1959, when scientists found out that Down syndrome has a genetic origin. Each human cell includes 23 pairs of chromosomes that carry the genes necessary for the normal development of the organism. 23 chromosomes are inherited through the egg from the mother, and pairs of them make up 23 chromosomes inherited throughfather's sperm. But it happens that a child from one of the parents inherits additional chromosomes. When he receives two from his mother instead of one 21st chromosome, in total (taking into account the 21st chromosome received from his father) there are three of them. This is what causes Down syndrome.

Signs of Down Syndrome
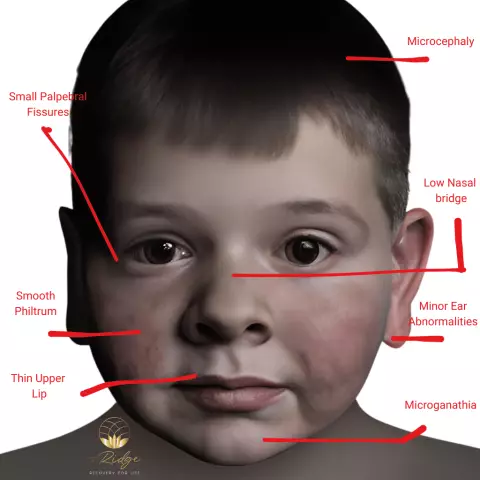
The manifestation of the disorder can vary from mild to severe forms, but most people with pathology have pronounced external features. So, the outward signs of Down syndrome include:
- flattened face, small mouth, small ears, short neck, slanted eyes;
- wide and short hands with short fingers;
- arched sky, crooked teeth, flat nose bridge;
- chest curvature, etc.
Cognitive Impairment
Children with this disorder have communication problems. This is manifested in the fact that they are hardly given training. Moreover, this problem persists throughout life. It is still not entirely clear exactly how an extra chromosome 21 can affect cognitive development. The brain of a person with Down syndrome is almost the same size as the brain of a he althy person. But the structure of its separate areas - the cerebellum and the hippocampus - is somewhat changed. This is especially true for the hippocampus, which is responsible for memory.

Heart defects and gastrointestinal diseases
The signs of Down syndrome listed above are abouthalf of the children are also accompanied by congenital heart defects. In some cases, in order to correct defects, surgery is required immediately after birth. In addition, many gastrointestinal diseases are characteristic of children with this disorder, especially tracheoesophageal fistula and esophageal atresia.
Other violations
Children with a pathology are predisposed to diseases such as:
- hypothyroidism;
- infantile spasms, seizures;
- otitis media;
- hearing and visual impairments;
- instability of the spine in the neck;
- obesity;
- hyperreactivity and attention deficit;
- depression.
Down syndrome treatment
To date, there is no cure for the disorder. It is only possible to carry out therapy for concomitant disorders, for example, heart disease or gastrointestinal diseases. But the quality of life of children with this pathology can still be improved. Various methods are used for this, including speech therapy, physical therapy, occupational therapy.