- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
The elbow joint has a rather complex structure. The presented part of the upper limbs is formed by the radius and ulna, which are connected to the shoulder tissue. Inside the main elbow joint there are several small ones. Large nerves and blood vessels pass through the presented area, which are responsible for the mobility of the entire limb. Therefore, fractures of the bones of the elbow joint, in addition to the difficulty of motor functions and the development of a serious pain syndrome, are fraught with a whole host of complications.
What is the treatment for this type of injury? How to treat fractures of the elbow joint? What is required for rehabilitation? We will try to answer the questions presented.
Causes of injury
The elbow joint is extremely vulnerable to injury, because there is no dense muscular frame that can provide reliable support and protection of the presented part of the upper limb. This area is especially often subjected to stress in babies, who are overly active and often find themselves in situations fraught with injury.
You can get an elbow fracture as a result offall, and due to a significant shock load on this area. The most common bone tissue damage here is internal.
Types of fractures
The following types of injuries of the bone tissue of the elbow joint are distinguished:
- Closed fracture of the elbow joint is characterized by damage to the radius, its neck and head. Most often occurs as a result of excessive load when focusing on a straight limb.
- Open fractures of the elbow joint - in addition to the occurrence of cracks in the structure of the bone, soft tissues are damaged by fragments. In severe cases, the skin ruptures, a gaping wound is formed, which is accompanied by profuse blood loss.
- Fracture of the coronoid process occurs due to significant shock loads on the bone tissue. Such injuries are rare. Damage of this plan is characterized by consequences in the form of displacement and dislocation of the forearm.
Also, a fracture of the elbow joint with and without displacement is distinguished. Often with such injuries, one bone suffers.
Symptoms
The following signs may indicate a fracture of the elbow:
- The presence of a sharp steady pain that radiates to the hand and wrist.
- Limited limb mobility or its complete paralysis.
- Unhe althy, unusual for a person mobility of the arm in the area of the elbow joint, for example in the lateral direction.
- Occurrence of edema, formation of cyanotic hematoma, subcutaneous bruising.
- Neurological symptoms - numbness of the fingers and hand, tingling of the forearm.
- Injury to blood vessels, muscle tissue, skin (open fractures of the elbow joint).
A clear sign of serious damage to the elbow joint is severe pain in the back of it. Gradually, swelling and hematoma form on the front surface of the injured area. Subsequently, the ability to bend the arm is lost. The injured limb hangs limply. Muscle stiffness is felt when moving with the forearm.
After a fracture with a displacement of the bone, the ability to extend the arm remains. However, lifting the limb and rotating it laterally causes significant discomfort.
First Aid
The tactics of first aid for a fracture of the elbow joint is selected based on the specifics of the injury and its severity. Be that as it may, the primary task here is the complete immobilization of the limb. To do this, it is recommended to resort to the imposition of a tire. In this case, the arm is bent at a right angle, after which it is securely fixed. If it is necessary to eliminate unbearable pain syndrome, analgesics are used.
Conservative treatment

In the absence of an injury in an open form, they resort to conservative therapy. During the first 6-7 days after the fracture, volumetric edema usually occurs. Until the pathological manifestation disappears, a splint plaster bandage is applied to the arm. shunnedload on the injured limb for up to 3 weeks.
As the bone tissue connects, the hand is periodically freed from plaster to develop the joint. Over time, such a bandage is replaced with a rigid fixator, which has a system for adjusting the amplitude of movements.
Surgical therapy
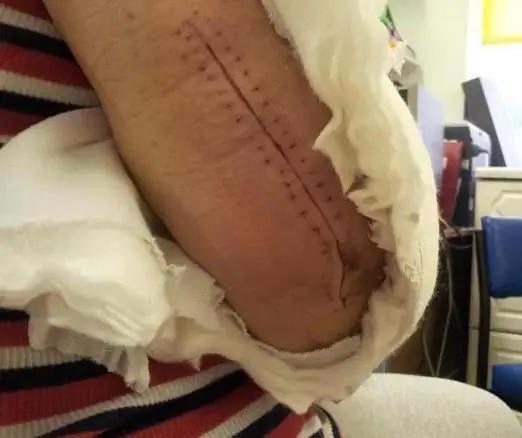
Open fractures of the elbow joint, which are characterized by displacement of fragments, require surgery. Otherwise, the ability of the forearm to bend may not be restored.
The success of surgical therapy directly depends on the accuracy of the actions of the trauma surgeon, in particular, the comparison of bone fragments, their verified fixation in the anatomically correct position. The Center for Traumatology and Orthopedics is capable of providing such an operation.
In case of normal damage to the structure of the end of the ulna, therapy is aimed at tightening the tissues with a medical wire loop. Sometimes additional fixation of the bones in a static position with knitting needles is required.
If you have to treat internal fractures of the elbow joint with the formation of splinters, the therapy is based on bone grafting. In such situations, it is difficult to tighten the tissues with a loop, since this can lead to shortening of the articular surfaces. Instead, they resort to the use of dynamic compression plates.
In cases where there are signs of bone crushing, the Center for Traumatology and Orthopedics can offer the patient a replacement of bodily tissue with a special prosthesis. Implants are made fromplastic and metal. They are installed using bone cement.
Possible Complications
An unfavorable consequence of a fracture of the elbow joint can be a complete or partial loss of limb mobility. A prerequisite for this is the preservation of a feeling of discomfort or impressive pain at the end of the course of therapy. You can avoid such manifestations by exactly following the recommendations of your doctor.
To prevent the occurrence of complications in children, in particular the loss of limb functionality, treatment should be carried out under adult supervision. First of all, the injured hand must be at rest throughout the course of therapy. The child should not load the limb, perform sudden movements. Allowing such negligence can lead to a re-fracture.
Rehab
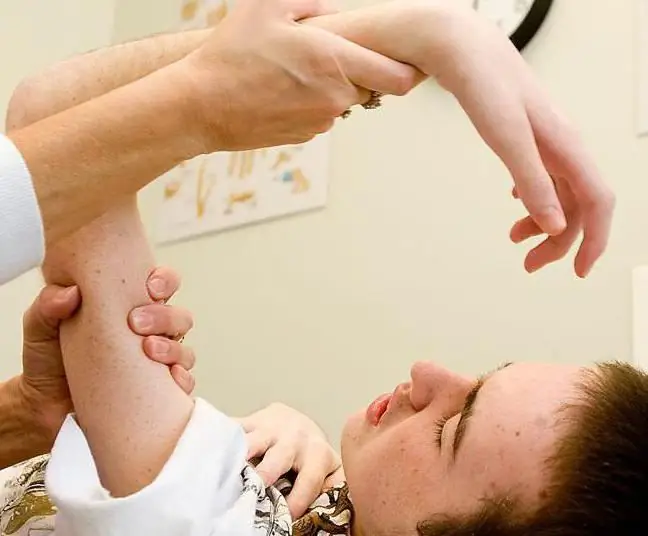
Actions aimed at restoring he althy limb functionality include:
- massage;
- therapeutic gymnastics;
- physiotherapy treatments.
The development of the joint with the help of physiotherapy exercises is possible already on the first day after fixing the limb with a plaster cast. Naturally, in this case, bending the arm at the elbow is avoided. The main emphasis is on the movement of the fingers and wrist. The victim is recommended in the prone position to start the injured limb behind the head, straining the muscles of the forearm and shoulders. Similar Solutionscontribute to the removal of puffiness as a result of activation of the outflow of lymph from the tissues.
When restoring the ability of the joint to bend, they proceed to its gradual development. To do this, the main part of the plaster cast is removed, after which measured, unsharp movements of the limb are performed. During rehabilitation with the help of therapeutic exercises, it is forbidden to bend and unbend the arm completely, as this can cause a second fracture.
Massage is resorted to only after the complete removal of the plaster cast. Moreover, the impact is exerted on the muscles of the shoulder girdle and back in a sparing mode. Regular performance of such procedures allows you to eliminate pain, strengthen atrophied muscles, stretch ligaments and, ultimately, fully restore arm mobility.
As for physiotherapeutic procedures, it is recommended to alternate them with therapeutic exercises. Here they resort to UHF methods, magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, healing mud treatment.
In closing
As a result, it is worth noting that after discharge from the hospital, the victim needs to clarify several questions for himself. You should clarify with your doctor how best to make movements in the elbow joint, when you can load the limb with weight, how to avoid relapses and complications, which you can count on in the near future.






