- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
To assess the state of he alth of the body, including the functioning of all organs and systems, a reliable method is used - a biochemical blood test. Thanks to this study, the doctor evaluates carbohydrate, mineral, lipid and protein metabolism, as well as the active work of enzyme substances. Deviation of indicators from the norm indicates a failure in organs and systems. Only a doctor can reliably assess the condition of an individual and correctly decipher the results.
General information
The blood circulating in the body, thanks to an extensive vascular system, penetrates into all cells and tissues. Its volume depends on body weight and is about seven percent of it. The composition of blood includes plasma and shaped particles. The quantitative content of the latter is studied based on the results of a general analysis. Plasma is ninety percent water, in addition, it containsamino acids, s alts, proteins, breakdown products of protein substances. A biochemical blood test shows that a malfunction has occurred in the work of one or another organ, or, conversely, all organs and systems are functioning normally.

In the blood, in addition to nutrients, there are waste products of cellular tissue that leave the body through the sweat glands, kidneys, liver, gastrointestinal tract, as well as substances formed as a result of the pathological process. Changes in the blood occur much earlier than the first symptoms of the disease appear. This type of research provides invaluable assistance in diagnosing many diseases, including their early detection.
Preparing for a biochemical blood test in adults
For any kind of examinations, including blood biochemistry, one must carefully prepare. To do this, follow a few simple recommendations:
- For three days, give up fatty, spicy, spicy, sweet foods, canned food and pickles, strong tea and coffee drinks.
- After the last meal, at least twelve hours must pass before the delivery of the biomaterial.
- For a day, refuse to visit the sauna or bath, physical activity, and, if possible, eliminate emotional stress.
- Do not take alcohol-containing drinks for the day.
- One hour before the procedure - smoking.
- On the day of the test, neither drink nor eat. Blood sampling is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Physiotherapeutic manipulations, massage, medication should be rescheduled (according toagreement with the doctor). You can perform them after donating blood.
The results of the biochemical blood test will be ready in a day or two.
Indications for blood biochemistry
The study is indicated during a preventive examination, dispensary observation, registration in a antenatal clinic due to pregnancy, complaints of an individual about a deterioration in well-being when contacting a clinic. Blood biochemistry is also prescribed in the following cases:
- past strokes, heart attacks;
- cerebral ischemia;
- IHD;
- hypercholesterolemia;
- pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- gastric ulcer;
- enteritis;
- gastritis;
- menstrual irregularity;
- myoma;
- inflammatory process in the uterus;
- endometriosis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- obesity;
- neoplasm in the pituitary gland;
- and more.
In some cases, additional examinations are required to confirm the diagnosis.
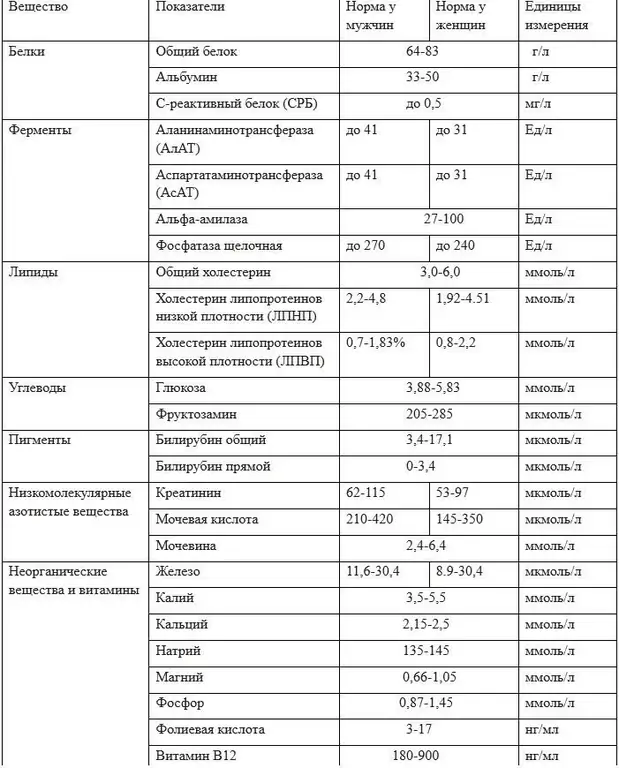
Indicators of blood biochemistry in adults
With this analysis, you can explore a fairly large number of indicators. In each case, the necessary set is determined by the attending doctor. The results obtained are compared with the norm. Deciphering a biochemical blood test in adults involves assessing and comparing the following parameters:
- Glucose, fructosamine are indispensable for assessing carbohydrate metabolism.
- Bile acids, bilirubin.
- Triglycerides, cholesterol, apoliproprotein are indicators of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism.
- Protein. Assessment of protein metabolism is based on the analysis of total protein, urea, albumin, creatinine and uric acid. Among specific proteins, transferrin, myoglobin, troponin, ferritin, C-reactive protein are checked.
- Phosphotase, lipase, amylase.
- Micronutrients.
- Vitamins.
Deviation of indicators from acceptable values in one direction or another indicates a pathological process. Correct interpretation of a biochemical blood test in adults helps in making a diagnosis, and also allows you to prescribe timely treatment. Below we consider in more detail the reasons for the deviation of some indicators from acceptable values.
Total protein (unit - g/L)
In an adult individual, the level of total protein is normal up to 83 in both men and women. This indicator indicates the total amount of protein substances in the blood, which are involved in many biochemical processes:
- act as catalysts for various chemical transformations;
- protect the body from infections;
- carry out the transport function.
The most common causes of increased protein in the blood:
- oncology;
- joint inflammation;
- rheumatic diseases.
Low levels of total protein in a biochemical blood test in adults indicate diseases of the liver, kidneys, intestinal pathology and the presence of malignantneoplasms.

Albumin is the main protein in plasma produced by the liver. Its low level is found in cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, heart failure, sepsis, drug poisoning. A high concentration is characteristic of dehydration, extensive burns and prolonged diarrhea.
Glucose (unit mmol/L)
The norm in an adult is from 3.8 to 5.8. An overestimated level of this indicator of a biochemical blood test is observed when:
- diabetes;
- cystic fibrosis;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- a neoplasm in the pancreas.
Short-term excess is possible with overeating, stress and consumption of sweets in large quantities. Under the following pathological conditions, low blood glucose levels are observed:
- cancer of the adrenal glands, stomach;
- hypothyroidism;
- poisoning with alcohol and drugs;
- liver disease;
- inflammatory diseases of the pancreas.
Cholesterol (unit mmol/l)
This substance is an important component of lipid metabolism, which is actively involved in the production of vitamin D and various steroid hormones by the adrenal glands, the formation of cell membranes. Define:
- total cholesterol, the norm of which is the same for both sexes and ranges from 3 to 6;
- HDL and LDL, their allowable levels are different for women and men in a biochemical blood test.
High cholesterol present at:
- obstructive jaundice;
- atherosclerosis;
- hepatitis in the chronic stage;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- hypothyroidism.
Low concentration is a consequence:
- prolonged fasting;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- lung disease (COPD);
- malignant neoplasms in the liver;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- metabolic failure.
Bilirubin (unit µmol/L)
This substance is a red-yellow pigment, which is formed as a result of the breakdown of hemoglobin in the bone marrow, liver and spleen. The reasons for the high level of bilirubin in a biochemical blood test, the norm of which is from 3.4 to 17.1 for men and women, are:
- gallstone disease;
- liver cancer;
- acute cholecystitis;
- cholangitis.
Low bilirubin levels are common in drug poisoning, acute or toxic hepatitis, liver disease due to bacterial infection.
Minerals: sodium
This element maintains the osmotic pressure in cells and tissues in the body of the individual, as well as the physiological level of acidity. Its level is controlled by the hormonal substance of the adrenal cortex. With edema, heart failure, diabetes mellitus, the use of a large amount of diuretics, a low sodium content in the blood is observed. An elevated level is present at the followingstates:
- diabetes insipidus;
- pathology of the hypothalamus;
- prolonged diarrhea;
- vomit;
- coma.
Biochemical analysis of blood in women
Women and men have different blood biochemistry values.
First of all, this is due to hormonal instability in different life periods in women. In the process of research in the laboratory, more than forty blood parameters are detected, which help to identify violations in the functioning of organs and systems. The following indicators are analyzed:
- Total protein. A low amount indicates insufficient intake with food. A change in this value from the norm indicates the occurrence of pathological processes in the liver, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys or connective tissue.
- Ferritin. A low level indicates infection, neoplasm, rheumatism.
- Transferrin. In violation of liver function, this indicator undergoes changes.
- Albumin. With its help, diseases of the liver and kidneys are determined.
- Myoglobin. With injuries, burns or convulsions, an overestimated amount of it is detected.
- Ceruloplasmin. An increase above the norm indicates the presence of tumors of a malignant nature, inflammation and myocardial infarction.
- Rheumatoid factor. Changes in this parameter are observed in mononucleosis, tuberculosis, infective endocarditis, rheumatoid arthritis.
- C-reactive protein. When inflammatory processes occur in the body, thisparameter increases.
- Lipid spectrum: LDL, HDL, triglycerides, total cholesterol. Interpretation of the results of a biochemical blood test allows you to identify cardiac pathologies.
- Enzyme group helps to detect failure in the functioning of the liver and pancreas: ALT, AST, A-amylase, lipase, cholinesterase, creatinine kinase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, lactate dehydrogenase, alkaline phosphatase.
- Glucose. Diabetes mellitus is detected by this parameter.
- Bilirubin. Its deviation from normal values occurs in various hepatitis, anemia, cholelithiasis, tumors in the pancreas and liver, diseases of the biliary tract.
- Creatinine. With its fluctuations, diabetes mellitus, damage to the adrenal glands, kidneys and liver are suspected.
- Urea. This parameter helps to identify diseases of the digestive system, kidney failure and liver pathology.
- Microelements, vitamins, acids.
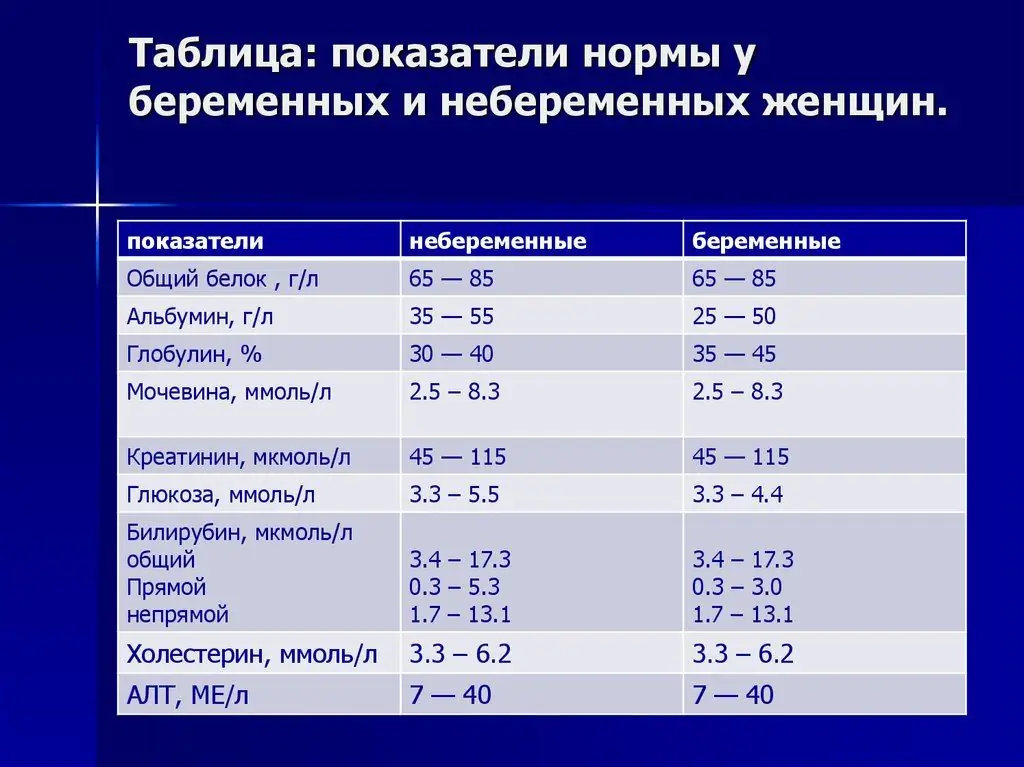
Blood biochemistry during pregnancy
Carrying out this type of study allows you to get an idea about the water-electrolyte, carbohydrate metabolic process, as well as the number of trace elements. A biochemical blood test helps to determine the functional state of all body systems in a pregnant woman. During this period, a huge load is placed on the endocrine system, heart, kidneys and liver, so monitoring the activity of these organs is very important.
In the normal course of pregnancy, expectant mothers hand overthis analysis twice:
- When registering at the antenatal clinic. During the initial examination, changes that occurred in the body before conception are revealed.
- After 30 weeks after the previous analysis, he is prescribed again, with a preventive purpose.
In addition, a biochemical blood test is indicated in the following cases:
- assessment of therapy in the presence of complications during the period of gestation;
- control of existing comorbidities;
- dispensary observation in a day or round-the-clock hospital.
Biomaterial is taken from a vein. The number of indicators that need to be analyzed, the doctor determines individually. It must be remembered that the permissible values of individual blood characteristics depend on the period of pregnancy and differ from the norm of a non-pregnant woman. The table shows the norms of a biochemical blood test in a pregnant woman in different trimesters.
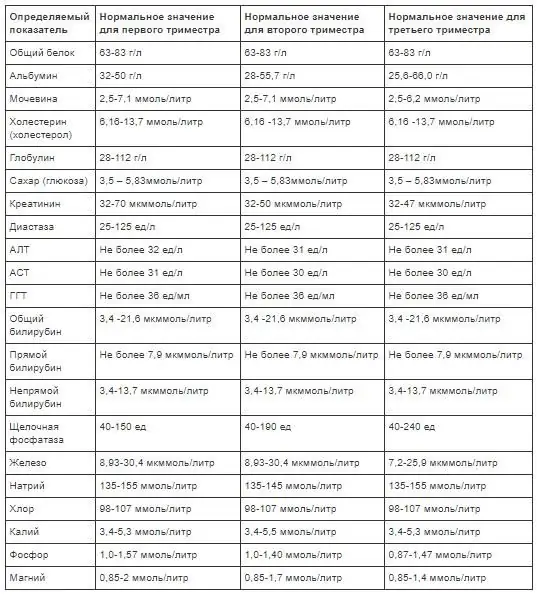
Let's look at some of them in more detail:
- Total protein - shows the amount of proteins in the blood serum. Throughout pregnancy, its level should be at the same level. The detection of low values indicates that the expectant mother is malnourished, and at high values, an additional examination of the liver will be required.
- Glucose. Monitoring it allows you not to miss the gestational diabetes mellitus that occurs during pregnancy.
- Cholesterol -participates in the synthesis of female sex hormones. High rates can provoke pathological changes in the fetal cardiovascular system. At values almost two times lower than normal, it is recommended to change the diet of a pregnant woman.
- AST and ALT. An increase in the level of these enzymes signals hemolytic anemia, obesity, or problems with the liver, heart.
- Urea. This indicator is analyzed together with creatinine. Together, they show the work of the excretory system. The reason for the increase in urea in excess of the permissible values in the first trimester is toxicosis. In addition, an increase in this indicator is observed when eating a large amount of food rich in proteins.
- Bilirubin - formed by the breakdown of hemoglobin. The increase in this indicator in the third trimester is due to the pressure of the uterus on nearby organs. This phenomenon is not considered a pathology, and the level of bilirubin returns to normal soon after delivery.
- Uric acid. As a result of an increase in the volume of circulating fluid in the first two trimesters, a decrease in the level of this indicator is observed. In recent months, the amount of uric acid has increased, which is associated with the development and growth of the fetus.
- Creatinine - provides energy to muscle tissue. In the first and second trimester, this figure decreases slightly. The reason is the increased load on the kidneys due to the increased volume of circulating blood. Low levels are present in lean women and those who prefer a vegetarian diet. The doctor in these cases recommends a specialdiet.
- Minerals - magnesium, calcium, chlorine, iron, potassium, phosphorus. These substances take an active part in the metabolism and are necessary for the fetus and the pregnant woman. The value of these indicators is evaluated together with other results of biochemistry.
Diagnosis of possible violations
Biochemical and general blood tests are prescribed in outpatient and inpatient settings with the aim of:
- monitoring treatment outcomes;
- detection of the pathological process.
Information obtained from the results of a biochemical study helps to form an idea about autoimmune reactions, about the functioning of systems and internal organs, about the water-alkaline balance of an individual. In addition, this analysis is indicated for in-depth diagnosis when:
- disturbances in the digestive tract;
- hormonal failures;
- damage to the kidneys, heart, liver;
- blood diseases;
- pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.

Deviations of the parameters of a biochemical blood test in adults from the norm are a signal of problems in the body of an individual. It is an integral part in identifying the pathology of internal organs.






