- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
The periodontium is the collection of tissues that surround the tooth. Each component of this complex complex performs certain functions, thereby holding the teeth in the bone, as well as maintaining their integrity. What is the peculiarity of its structure?

Classification of periodontium
Do not forget that this is a complex of tissues. What is the periodontium made of? This is a set of tissues that provide not only nutrition, but maintain the integrity of the teeth. This set includes:
- gingiva,
- alveolar bone tissue (together with periosteum),
- periodontium,
- tooth (cement, root dentin, pulp).
To understand the structure of the periodontium, you should carefully consider each of the tissues.
What is gum
First of all, the gum is the tissue that includes the periodontium. It affects the he alth and condition of the teeth. The gum belongs to the group of masticatory mucous membranes. Such tissues surround the surface of the teeth and represent a kind of barrier that does not allow all kinds of infections to penetrate inside.
The top layer of the gums is a layer of squamous keratinized epithelium. Whattouches the inner part, then it represents a transition to the shell. It is often called the marginal zone of the hard palate. Outside, the gum is in contact with the mucous membrane that covers the alveolar process of the jaw. This feature of the structure of this part of the periodontium allows you to quickly restore tissue after chemical, physical or mechanical damage.
The gum is attached to the underlying bone. These periodontal tissues are immobile and have a large number of ligaments capable of performing many functions.
Bone tissue
Periodontal tissues perform many functions. The complex also includes the alveolar process of the jaw. It is based on a bone substance that covers the inner and outer walls in layers, like plates. Between them, in turn, is a substance with a spongy structure. It hides many vessels, nerves and channels.
It is worth noting that such a bone base of the teeth performs important functions and provides the periodontal tissues with the necessary substances. In addition, the alveolar process of the jaw is interconnected with other components of the periodontium.

Periodont, cement, tooth enamel
The periodontium is one of the connective tissues that make up the periodontium. These are specific fibers and cells, blood and lymphatic vessels, as well as nerves. The periodontium is located between the alveolar process of the jaw and the teeth. This fabric allows you to adjust the load on the teeth.
As for the cement, it is the tissue of the teeth, which in its own waystructure is very similar to bone. Its main difference lies in the absence of some cell elements. The main function of cement is the binding action of all tooth tissues.
Enamel is one of the most durable parts. It is she who takes on the main load when chewing and grinding food. The high strength of this fabric is achieved due to specific enamel prisms, which consist of a connective fiber and hydroxyapatite.
Dentine and pulp
Dentin is another component of the periodontium. It is a fabric with a solid structure. Dentin is covered with tooth enamel and cementum. It is worth noting that this tissue contains less minerals. Therefore, dentin is inferior to tooth enamel in hardness. Inside this tissue is the pulp.
What is this? The pulp is soft tissue. It feeds the teeth. The pulp consists, as a rule, of connecting elements, vessels and nerves. It is she who protects against the reproduction of periodontal microorganisms. This is another function that the pulp performs. It is worth noting that this tissue is involved in the formation of dentin.
What are the functions of the periodontium
Periodontal tissues perform a variety of functions, among which it is worth highlighting:
- plastic;
- trophic;
- barrier;
- shock-absorbing.

Plastic function
Due to this function, periodontal tissues have the property of systematic recovery. In addition to this, cellsupdated regularly. Similar processes are carried out thanks to fibroblasts, osteoblasts, cementoblasts and other elements.
Trophic function
In this case we are talking about reflex regulation of pressure when grinding food. This is due to the specific structure of the periodontium. The extent to which this ability of tissues will be developed depends directly on the capillaries and nerve receptors, which intertwine and create something like networks.
Barrier function
According to experts, the effectiveness of this function is affected by the condition of the periodontium, as well as the presence of certain diseases of the gums and other tissues. The protective effect can reduce the low antibacterial properties of the epithelium, as well as its ability to keratinize. In addition, the structure of the gums also affects the ability to perform this function.
It is worth noting that human saliva also minimizes the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the body. After all, it contains a variety of biologically active components of various spectrums of action and origin. These substances include white blood cells, enzymes, and immunoglobulin.
Shock-absorbing function
Pathology of the periodontium can reduce the effectiveness of this function. It is worth noting that in the process of chewing food, the neurovascular ligaments, as well as the alveoli, are constantly exposed to minor damage. The periodontal complex can significantly reduce the load. This is achieved thanks to the cells and crevices that are located between the tissues.
Periodontal integrityplays an important role. The he alth of the organism as a whole depends on the state of this system. It is for this reason that it is necessary to visit the dentist regularly and monitor the condition of the teeth.

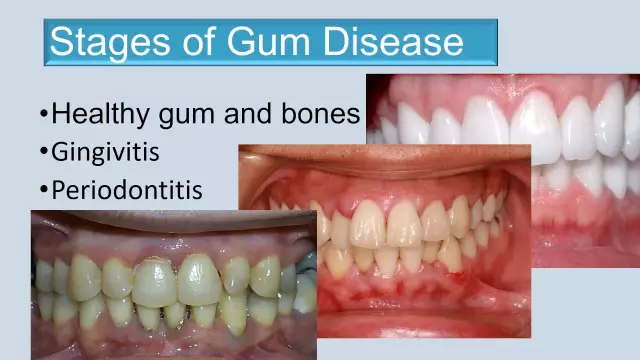
Periodontitis and gingivitis
Periodontal disease is quite common. In this case, the pathological process can have a tumor, inflammatory or dystrophic character. The most common diseases are periodontitis and gingivitis. These are inflammatory processes that occur in periodontal tissues. Their main difference is in localization. In the case of gingivitis, the inflammatory process affects only the tissues of the gingival margin, affecting only the upper gum tissues. As for periodontitis, it involves all the structures of the periodontium. A similar disease is characterized by progressive destruction of the alveolar processes of the jaws and destruction of the periodontal connective tissues.
In fact, these ailments are interrelated forms of one disease. After all, initially inflammation begins in the tissues of the gums. Only after some time, the cells of the alveolar process and the periodontal ligaments are affected.
Prepubertal periodontitis
Similar periodontal diseases occur in childhood in the presence of not only permanent, but also milk teeth. The reason for the rather rapid and early development of the disease is a defect in general immunity. Treatment of this disease is usually reduced to careful antimicrobial control. However, as practice shows, to achieve a positiveThe result can be eliminated by eliminating the defect in immunity by taking certain medications.

Juvenile focal periodontitis
This is a specific disease of periodontal tissues, in which there is only a partial lesion of the supporting apparatus of the first permanent teeth. This disease is caused by microorganisms called Actinomycetes comitans. These bacteria are actinomycins. Most often, juvenile focal periodontitis occurs in children whose parents are carriers of these microorganisms.
This disease is often accompanied by a minimal inflammatory process. It is worth noting that the microorganisms that cause the disease are able to suppress the protective reactions of the immune system. Antibodies in such situations simply do not have time to form. Despite this, the disease rarely accompanies a person throughout life. The destruction of permanent teeth in children is rare, as specific antibodies gradually accumulate and have time to fully form.
What therapy is given
Treatment of periodontal tissues in juvenile focal periodontitis is carried out by taking antibiotics. Such therapy lasts for 3 weeks, but no more. In this case, local intervention is carried out. Taking antibiotics in this case is simply necessary, since pathogens initially inhabit the periodontal groove, and eventually the periodontal pocket. In addition, bacteria penetrate deep into bone structures and soft tissues, where their resistance to drugsrising.

Drug-resistant and rapidly progressive periodontitis
These periodontal diseases are caused by certain microflora Actinomycetes comitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis or Prevotella intermedia. However, most often there is a combination of several. In such situations, microorganisms only reinforce each other's actions, thereby causing not only tissue destruction, but also suppression of the protective functions of the immune system.
Treatment of these ailments is reduced to careful treatment of periodontal pockets, as well as antimicrobial therapy, which lasts from 3 to 4 weeks. At the end, patchwork operations are performed. This type of surgical therapy is carried out only after a full course of antibiotics. Otherwise, the treatment will be ineffective.
You can verify the correctness of the prescribed therapy only by doing a microbiological analysis of tissue biopsy specimens and the contents of the periodontal pocket.
What is periodontal disease
Timely diagnosis of periodontal disease allows you to identify many diseases at an early stage. Many people suffer from a disease such as periodontal disease. This disease is based on atrophic-destructive processes occurring in soft tissues. In this case, the disease proceeds quite slowly and has few symptoms. The underlying cause of periodontal disease has not yet been identified.
What happens to tissues? With such a disease, a cosmetic defect occurs: exposure of the roots of the tooth. Most often, patients complain that the gums insome places have begun to subside. At the same time, the teeth visually become longer. Often, patients are worried about itching in the gums. There may also be pain in the necks of the teeth.
How is periodontal disease treated
At the moment, there is no etiotropic therapy for this disease, since the main reason for its development has not been established. Most often, doctors eliminate only the symptoms of the disease. This is done with the help of special tools. This allows you to eliminate the increased sensitivity of tissues and reduce inflammation. In addition, patients with such an ailment are prescribed auto-massage or a simple gum massage, darsonvalization, which allows correcting trophic disorders. Sometimes splinting is used. Finally, wedge-shaped defects are filled.
In some cases, a vestibuloplasty operation is performed. However, the effect of such interventions is short-lived.
Tumor-like and tumor tissue lesions
Such periodontal lesions are difficult to predict. Such diseases appear only in those who are prone to such processes. In this case, the impetus for the development of tumor and tumor-like ailments is hormonal failure. Most often, the main reason is the accumulation of a large amount of growth hormone, not only during pregnancy, but also during puberty.
However, as practice shows, these are only factors that can provoke the development of such lesions in individuals predisposed to oncological processes. There are other reasons as well. scientists wasAnother factor has been established that can provoke the development of such a pathology. This is due to the use of anabolics in professional sports and bodybuilding.

Method of treatment
Treatment of tumor and tumor-like lesions is reduced to the elimination of trauma and inflammation. Often, overgrown tissue is removed. Most often this is required for interradicular granuloma, epulis, hypertrophic gingivitis, gingival fibrosis, and so on.
Patients suffering from these ailments should carefully monitor oral hygiene, using not only special antiseptic solutions, but also antibacterial rinses.
Disease prevention
Periodontal prevention is of particular importance. Such measures can prevent the development of a particular disease, as well as avoid negative consequences. Prevention of periodontal diseases is reduced to the following rules:
- Proper and rational nutrition, saturated not only with vitamins, but also with minerals.
- The use of various drugs that contain fluoride.
- Elimination of malocclusion, as well as abnormal location and structure of certain organs and soft tissues of the oral cavity. In this case, it is necessary to get rid of selective functional grinding and suprocontacts. After all, these pathologies can lead to periodontal trauma and the development of certain diseases.
- Defects in orthodontic treatment, prosthetics andfillings.
- Go to the dentist's office on time.
- Keep dental and oral hygiene.
- Eliminate violations of the architectonics of tissue attachment of the vestibule of the oral cavity.
- Comorbidities need to be treated.
Finally
The periodontium is a complex of different tissues, each of which performs certain functions. With the wrong approach to oral hygiene, all kinds of diseases can develop. And this is not only inflammation of the periodontium, but also the formation of tumors. In the presence of any disease, you should immediately seek help from specialists. This will help avoid more serious complications.