- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
What is the first thing most people think about today? What do they think is the most important thing in life? Of course, he alth. In the 21st century, cardiovascular diseases are the most common, for their full treatment it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis, including examination of arteries and veins.
The article describes how ultrasound of vessels is done, what this procedure shows, which vessels are examined using ultrasound.
Definition
Vascular ultrasound is a study of the arteries and veins of the body using an ultrasound method. The examination ranks second in frequency of appointments after echocardiography.
Diagnosis of vascular diseases has advanced dramatically after the introduction of ultrasound machines into medical institutions. It became possible to examine the vessels from the inside, without violating the integrity. With the development of new research methods (one-dimensional, two-dimensional, Doppler), the quality of visualization and diagnostic accuracy is getting higher.

How do they do it?
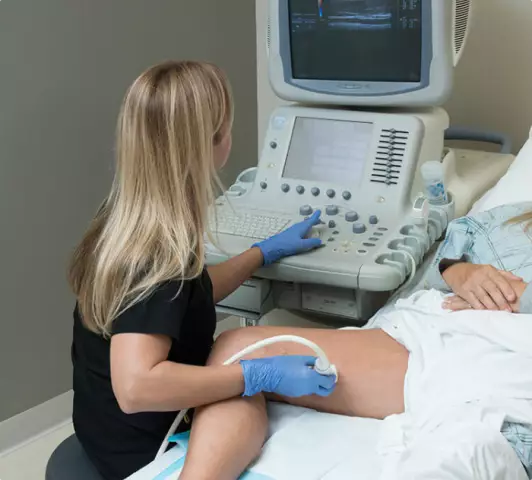
The procedure takes place in a darkenedindoors, the person should be in a prone position. Ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities is performed when the patient lies on his stomach. In all other cases, you need to lie on your back.
To improve skin contact, the transducer is lubricated with a gel that conducts ultrasound. Without it, air trapped between the skin and the transducer dramatically reduces the visibility of structures.
Examination is always carried out on both sides - left and right. In this way, the degree and symmetry of the lesion is assessed.
Rendering issues
As soon as the doctor puts the sensor on the skin, he starts looking for the vessels necessary for the examination. The specialist sees their layered structure, evaluates the size, blood flow velocity, looks for the presence of pathological elements: atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, separation of the inner layer of the vascular wall.
It is possible to consider all of the above only if visibility is good. But there are situations when there are difficulties for visualization during vascular ultrasound:
- Thick layer of subcutaneous fat. In this case, ultrasound simply cannot reach the depth at which the vessel lies.
- The short neck creates certain difficulties in the study. In this case, the vessels are not straight. They are in different planes. For a quality diagnosis, the doctor will need a little more time.
- Severe swelling in the legs also reduces the ability to visualize the vessels, as in the first case.
- The presence of an open wound at the projection point forces the doctor to look for other places fordetection of arteries or veins in this area.
Each person is individual, and everyone needs to adapt to conduct a full-fledged examination that best answers the questions of the attending physician.
Types of examinations
There are a huge number of vessels in the human body: arteries and veins of various diameters, arterioles, venules, capillaries. They penetrate every organ, structure, delivering useful substances with the blood and taking the waste products of cells.
Unfortunately, not all of them can be seen on ultrasound. Only vessels of large and medium diameter are subject to this examination. Capillaries and the venules and arterioles preceding them cannot be visualized by the device.
Most often, doctors prescribe an examination:
- Neck.
- Heads.
- Lower limbs.
- Hearts (much rarer).
Ultrasound of neck vessels
The patient is asked to lie on his back and slightly raise his chin, sometimes turn his head to the side. The doctor examines in order:
- Common carotid artery (CCA).
- Its bifurcation (the place of division into internal and external carotid arteries). It is in this place that an atherosclerotic plaque is most often found.
- External carotid artery.
- Internal carotid artery to the point of entry into the skull.
- The vertebral artery (VA) in the first two segments - before its entry into the spine and in the processes of the vertebrae.
- Subclavian artery.
- Locations of the common carotid and vertebral arteries on the left.
- The brachycephalic trunk on the right and itsbifurcation into OCA and PA.
- Jugular veins.

Of course, if pathology is detected during ultrasound of the vessels of the neck in its lower part, the examination can be extended to the upper limbs.
Ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels
It is always carried out together with the previous one. It allows you to assess the blood flow in the brain, the structure of the circle of Willis - a system of arteries that form sidings of blood flow to the brain. Even if one artery fails, nothing will happen to the brain, because the others compensate in full. It is this system of arteries that specialists are trying to visualize.
For ultrasound of the vessels of the brain, an access point with the thinnest bone plate is used - the temple, and the smallest sensor is a sector one. During the study, the doctor displays the complete circle of Willis or the main arteries in turn, if they are not in the same plane.

Basically, specialists examine the anterior, middle and posterior cerebral arteries and the anterior, posterior communicating arteries. In each, the blood flow velocity in all segments and the index of resistance to blood flow are evaluated. The doctor also draws attention to the symmetry of the indicators on both sides.
Sometimes a specialist cannot remove a single artery. This is not due to his low professionalism. This happens due to the special properties of bone tissue. In this case, he tries to visualize them from the opposite side, but this is not always possible due to the great depth.occurrence of vessels.
In the brain, it is also important to trace the course of the vertebral arteries, which merge into the main artery. The suboccipital fossa is used as a "window". Ultrasound of the vessels of the brain is carried out first lying down, then standing. The same indicators are evaluated as in the study from the temporal access and changes in blood flow during the verticalization of the patient.
Indications
Since the two methods described above are always performed in pairs, the indications for their use are the same:
- headaches;
- dizziness;
- tinnitus;
- migraine;
- high blood pressure;
- stroke;
- transient ischemic attack;
- convulsions (suspected epilepsy);
- vestibular disorders;
- cerebral ischemia;
- vertebrobasilar insufficiency;
- ischemic heart disease;
- atherosclerosis of any location;
- soft tissue injury of the neck;
- sudden blindness.
Examination of vessels of the lower extremities
Diseases of peripheral arteries and veins stand a little apart, but have an enormous frequency of occurrence in the population. The reason for this is the absence or insufficiency of the prevention of this pathology. Ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities allows you to determine the cause of symptoms associated mainly with walking.
Immediately before the examination, whether it be veins or arteries, it is necessary to remove all clothing below the waist, including socks, except for underwear. Next, the patient lies on his back and follows all instructions.doctor.
During the study, the specialist assesses the condition of the arteries and veins. Arteries are examined for atherosclerosis, thrombosis. When a vessel is blocked already in the region of the inguinal fold, to search for the upper border of the lesion, the study moves to the abdomen, so the aorta or inferior vena cava may be affected.

The blood flow is checked without fail. If atherosclerosis of the arteries is suspected, the doctor will need to measure the pressure on the legs to determine the ankle-brachial index (ABI). A cuff is placed on the lower part of the thigh or upper part of the leg, into which air is pumped. At this time, the doctor monitors the blood flow with a sensor. When the pulsation stops, it remembers the corresponding number on the tonometer and starts measuring on the next artery. So the doctor should calculate the ABI at least 4 times on both legs - according to the number of arteries in the lower leg.
If vein thrombosis is suspected, ultrasound is performed very carefully. In their normal state, it is necessary to compress the vessels with a sensor and conduct a test with holding the breath and subsequent straining. This checks the functionality of the vein valves. If there are signs of thrombosis with an isolated apex in the lumen, then such a diagnosis cannot be carried out, since there is a possibility of detachment of a part of the thrombus with subsequent pulmonary embolism.
Indications for ultrasound of the arteries of the lower extremities:
- cold lower limbs;
- pallor of the skin on the legs;
- lack of arterial pulsation onfoot;
- pain in the calf muscles when walking;
- weakness in legs;
- diabetes mellitus;
- long-term non-healing wounds, leg ulcers;
- blackening of the skin on the foot;
- long smoking history;
- high blood cholesterol.
Indications for vein examination:
- massive swelling on the legs, often asymmetric;
- local reddening of the skin on the legs;
- presence of brown pigmentation and coarsening of the skin in the shins;
- suppuration on the leg;
- leg pain at rest;
- feeling of fullness in the leg;
- dilated saphenous veins.
Vessels of the heart
For normal functioning, the heart needs an uninterrupted supply of blood, for which the coronary or coronary arteries are responsible.

In addition, large vessels depart from the heart: the pulmonary trunk, aorta, inferior and superior vena cava, pulmonary veins. There are 2 ways to conduct an ultrasound of the vessels of the heart:
Transthoracic - through the chest. Combined with ultrasound of the heart. During the procedure, the specialist examines the main trunks extending from him and carrying blood to him. These are the aorta, pulmonary trunk, vena cava and pulmonary veins
Intravascular ultrasound allows you to examine the inside of the coronary arteries that feed the heart muscle. Diagnosis is carried out in conjunction with coronary angiography. A miniature ultrasonic sensor is inserted along the conductor and advanced to the coronaries under the control of the X-ray machine. The survey allows in the smalleststudy the walls of the vessel in detail, determine the shape of the plaque, its composition. In addition, this is the best method of visualization and control during stenting or balloon dilatation (methods for expanding the lumen of the arteries affected by the pathological process). This method is actively used all over the world by cardiac surgeons, roentgen angiosurgeons. Not so common in our country yet

Indications for ultrasound of the vessels of the heart (intravascular diagnostics):
- assessment of arterial stenosis;
- assessment of shunt performance;
- control of endovascular operations.
Results
After ultrasound of the vessels, the specialist fills in the examination protocol. There should be sizes, speeds, indexes. The detected pathology is described in as much detail as possible to determine the dynamics after treatment. What does vascular ultrasound show and what conclusions can be seen in the protocol?
In the arteries of any diameter, atherosclerotic changes of varying degrees are detected. It can be just a thickening of the IMT (middle and inner wall layer) or a plaque. In the presence of the latter, the degree of stenosis is necessarily measured as a percentage and the change in blood flow is indicated before and after narrowing of the lumen.

When vein thrombosis is detected, the upper limit is determined, the mobility of the top of the thrombus is assessed. Particular attention is paid to the structure of the thrombus, homogeneous or not, whether there are signs of blood flow inside the vessel. Thus, with some degree of probability, it is possible to determine the prescriptionprocess and treatment prognosis.
Where to diagnose?
Ultrasound is a very common way to detect various diseases, including blood vessels. Ultrasound can be done in the direction of the attending physician free of charge at any clinic. But most likely you will have to wait your turn for several days or weeks.
If there is a suspicion of venous thrombosis, then the patient is urgently hospitalized in a hospital, where they will carry out all the necessary diagnostics.
But where to do an ultrasound of the vessels without wasting time and nerves? In any private medical center there is an opportunity to be examined on the same day. You do not need to ask for a referral from your doctor for this. Naturally, the procedure will be paid.
After the study, the specialist will tell you who to contact if you have a pathology, what to expect. In exceptional cases, the doctor calls an ambulance to deliver the patient to the hospital for treatment.