- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Can a person be saved if a blood clot breaks off? This is one of the most common questions related to thromboembolism - the most dangerous condition, fraught with serious complications. The result of a detached blood clot in 80% of cases is a fatal outcome. Only a fifth of patients who have a blood clot come off manage to escape. In the article we will try to figure out why this happens and how to prevent a fatal illness.
The role of platelets in the coagulation system
In most cases, patients who are lucky enough to survive an episode of thromboembolism have to face its unpleasant consequences. Complications are associated with disorders in the work of the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. To understand the mechanism of the development of the disease, you first need to get an idea of what a blood clot is and why it comes off.
In a he althy person, the rheological properties of blood are regulated by a number of factors. One of them is the clotting system needed to stop bleeding. It includes various formed elements, including platelets, proteins and other bioactivesubstances that are produced by liver cells - hepatocytes. They produce prothrombin, an indispensable synthesized enzyme.

Normally, coagulation processes start at the slightest, even minor damage to a blood vessel, and imply the formation of a cork, a kind of patch for its torn wall. In this case, a thrombus does not form instantly. It will take several steps to form it:
- adhesion - adhesion of a platelet to the vessel wall in the area of its damage;
- aggregation - the formation of a clot (plug) from platelets that have accumulated in a significant amount;
- dissolution of a blood clot - occurs after the restoration of the integrity of the vessel.
What happens with thrombosis and thromboembolism
During the period of adhesion, part of the cells is destroyed and enzyme substances are released, under the influence of which the blood coagulation system starts - thin fibrin filaments stick to the accumulation of platelets. Once the platelets have completed their task, the clot is neutralized. However, in the presence of a number of pathological factors, this does not happen. Moreover, the clot begins to increase in size, as proteins, leukocytes and erythrocytes settle on it.
In this case we are talking about a disease of the coagulation system, called thrombophilia. If this violation of hemostasis is accompanied by the formation of clots in various parts of the circulatory system, the patient is diagnosed with thrombosis. Another name is the problem in which the lumen of the vessel is partiallyclogged, and then the clot broke off. What it is? This is a thromboembolism.

Main causes of thrombophilia
Various functional and genetic abnormalities can increase the risk of a blood clot. In particular, it refers to a gene mutation that occurred during the period of intrauterine development of the fetal egg (the first two weeks of pregnancy). Their violation causes a failure in the synthesis of blood coagulation.
In most patients, the problem is hereditary. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in patients older than 45 years. Men are most predisposed to pathology. Women suffer from thrombophilia mainly after menopause.
Doctors take every clinical case of thrombosis seriously, so the identification of causes and symptoms, and treatment are of particular importance. Broken thrombus? The consequences of the disease are inevitable, but their severity largely depends on the timeliness of the medical care provided.

What causes blood clots
The presence of a genetic abnormality or heredity does not guarantee the development of the disease by 100%. The development of thrombophilia and thrombosis requires exposure to one of a number of possible factors that negatively affect the coagulation system. These include:
- pregnancy;
- lack of motor activity against the background of immobilization (after injuries, paralysis of the body);
- liver disease;
- diabetes mellitus;
- arterial hypertension;
- slow blood flow due to arrhythmia or other heart problems;
- varicose veins, aneurysms, thrombophlebitis;
- atherosclerotic vascular disease;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- long-term use of drugs that increase blood clotting (coagulants, hormonal drugs, oral contraceptives);
- open operations on the heart, coronary vessels.
A blood clot broke off - what is it?
Blood clots attached to the venous or arterial wall completely or partially block the lumen of the vessel. With an increased blood flow velocity and an increase in blood pressure indicators, the risk of a blood clot detachment increases several times. Excessive physical activity, overstrain, excitement can lead to negative consequences. Unfortunately, it is impossible to predict whether a blood clot can come off in a particular case.
The most dangerous is the complete blockage of the blood vessel. The thrombus becomes an insurmountable barrier to normal blood circulation, which inevitably leads to the death of a person. If a blood clot in a patient has come off in the leg, this does not mean at all that it will close the lumen of the artery of the lower limb. The clot can become floating, that is, begin to freely wander through the circulatory system and at any time clog one of the vessels.

Varieties of blood clots
Blood clots can be of various types, depending on their location. By the way, it's importantdo not confuse formations on the walls of blood vessels that cannot come off and do not interfere with blood circulation in any way. Blood clots that close the lumen may be:
- Occlusive - such formations completely block the path of free blood flow.
- Floating - these bunches have a thin stem at the base, so they come off easily. Wandering blood clots are more likely than others to cause blockage of an artery in the lungs.
- Emboli - blood clots that circulate freely with the bloodstream.
Consequences
If a blood clot breaks off (the reasons for this are no longer of fundamental importance), you need to act without slowing down. The patient is threatened with such dangerous violations as:
- Stroke. The disease develops if the clot is too wide for the narrow vessels that feed the brain.
- Heart attack. Occurs against the background of the cessation of blood circulation in the coronary vessels. The death of heart muscle cells occurs due to oxygen starvation.
- Thrombosis of the veins of the legs. It is often a complication that develops against the background of varicose veins.
- Pulmonary embolism. The risk of its development is especially high in the presence of a floating blood clot. When the pulmonary artery is blocked, the patient's death occurs instantly.
Regardless of why a blood clot breaks off in a person, it is important not to waste a minute if it has already happened. About the rules of first aid and how to recognize the danger, further.

How to understand whatblood clot broke off
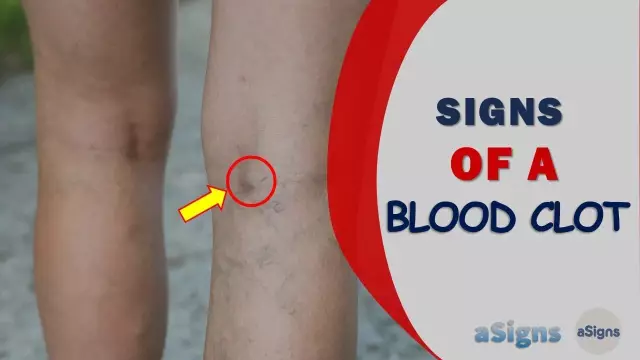
Symptoms of a detached blood clot in all patients are different and depend on the location of the blockage. If the thrombus has closed the lumen of the vessels of the brain, the patient may experience all the signs of an ischemic stroke, which can be considered an indirect confirmation of thromboembolism. The external manifestations of the disease include impaired speech, swallowing, immobility of one side of the body. With partial blockage of the vessel, signs of a detached blood clot may be a headache, discomfort in the neck, loss of visual acuity.
If a blood clot has entered the coronary artery and interferes with blood flow, the patient will feel a pressing and sharp pain in the sternum. Sometimes the pain radiates to the chin, the internal organs of the abdominal cavity, the neck, the left arm and the space between the shoulder blades. Patients in whom a blood clot has come off (symptoms are almost identical to a pre-infarction condition) should urgently call an ambulance team.

The most optimistic prognosis is the blockage of the veins of the lower extremities. Thrombosis may be indicated by blueness, a decrease in temperature in the injured limb, swelling and severe pain. Treatment is carried out mainly by surgery. But with a pulmonary embolism, in some cases, even emergency resuscitation measures do not help. If a blood clot breaks off in a person, the symptoms are as follows:
- blue skin;
- pronounced oxygen starvation;
- severe shortness of breath;
- stop breathing and heartbeat.
Rulesfirst aid
If the patient has signs of a detached blood clot, you need to do the following:
- help the victim to take a comfortable horizontal position;
- call a team of specialists;
- apply an ice compress to the supposedly damaged area.
In no case should the place of separation of the platelet clot be warmed. Before the doctors arrive, the patient can be given painkillers or antispasmodics. By the way, in patients with a confirmed diagnosis of "thrombosis", such funds should always be present in the home first aid kit.
It is impossible to help a person who has already had a blood clot and a blockage of the pulmonary artery at home. The only thing you can do, knowing about the predisposition to thrombophilia, is to follow the rules of prevention and take anticoagulants as prescribed by your doctor.
Medication treatment
When diagnosed with thrombosis, the patient is prescribed appropriate medications. Patients who underwent surgery on the heart and blood vessels are also forced to take drugs regularly. The most effective means include:
- Xarelto.
- Rivaroxaban.
- Eliquis.
- Apixaban.
- Pradaxa.
- Dabigatran.
In order to strengthen the walls of arteries and veins, specialists prescribe drugs such as Ascorutin, Detralex, Venoruton. In complicated cases, to prevent blockage of the vessel by a floating thrombus, a cava is placed in its lumen.a filter designed to trap blood clots.

How to prevent a blood clot breakaway
Speaking of the prevention of thromboembolism, it would be better to start with the prevention of blood clots. It is not possible for any doctor to say exactly whether a blood clot can come off in a patient. To prevent the development of serious complications, a person at risk should adhere to a number of conditions, first of all:
- Refuse cholesterol-rich foods.
- Meals should only be steamed or in the oven, no fried foods at all.
- Include citrus fruits, broccoli, cherries more often in the diet, drink green tea - these products are classified as natural anticoagulants.
- If you have a predisposition to thickening of the blood, take anticoagulants, the most popular and inexpensive of which is aspirin. Taking the drug must be agreed with the attending physician.
- Keep an active lifestyle, play sports, but avoid excessive physical exertion. This is necessary to thin the blood, strengthen the myocardium, and accelerate blood circulation.
The consequences of a blood clot in the heart and lungs can be the most deplorable, so you need to visit a doctor regularly and not self-medicate.