- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
To date, medicine has studied almost every centimeter of the human body. The purpose and functions of each organ and cell are determined. However, for a long time, one of the mysteries of the human body was the so-called appendix of the caecum. Physicians struggled over the definition of its functions for more than a decade. Despite all the “mysteriousness” of this process, one of the most common inflammatory processes in the human peritoneal cavity is associated with it.
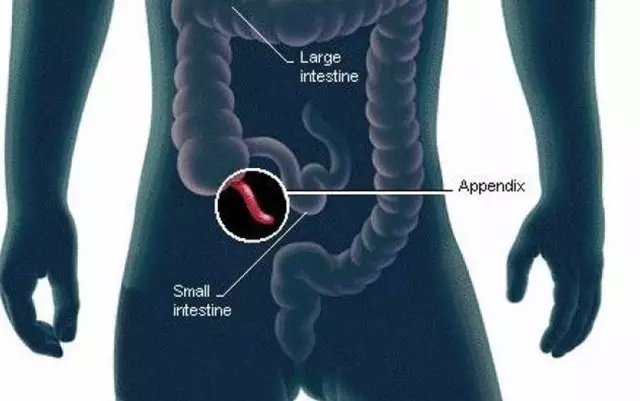
Anatomy of the appendix and caecum
The caecum is the first section of the large intestine. It is presented as a sac-like formation, which is located under the ileoceral valve (the place where the small and large intestines are separated). Depending on the human body, its length can vary between 3-8 cm. A appendix extends from the caecum. It is also called the appendage of the caecum.
Despite thisstrange name, most people know what the appendix is called. They call it the appendix.
This is the name of a rudimentary human organ that has lost its digestive function over the course of evolution. It is located at the confluence of the ileum with the large intestine: on the right side of the peritoneum.
On average, its length reaches 8-10 cm, although there are cases when it was 50 cm.
What is the appendix of the cecum used for
Until the middle of the twentieth century, doctors had no idea why a person needs an appendix. It got to the point that after the birth of the child, it was immediately removed, since it was believed that nothing but harm could be expected from this organ. However, such drastic measures brought unexpected results: children who had their appendix cut out were significantly behind their peers in development. In addition, a person without an appendix was more likely to suffer from gastrointestinal diseases.

With the development of medicine, the question of the need for the appendix of the caecum in humans has disappeared, since its main function has been clarified. Despite the fact that it does not take a direct part in the process of digestion, its main function is to breed bacteria that a person needs.
Since there are lymphoid accumulations in the appendix, which are responsible for delivering immune cells to the intestines, it is involved in eliminating the processes of inflammation of the intestines and the entire gastrointestinal tract.
Inflammation
Everyone knows the name of inflammationappendix of the caecum, and what it is. It's appendicitis.
There are two clinical and anatomical forms of the disease: acute and chronic.

Acute appendicitis is an inflammation in the appendix of the caecum, which develops against the background of a change in the biological ratio between the human body and microbes. Acute appendicitis is one of the most common diseases in the abdominal cavity and requires immediate surgical intervention.
Chronic appendicitis is rare. It is considered a complication of previously unoperated inflammation of the appendix. The process of inflammation is thus delayed.
According to the classification of Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Vasily Ivanovich Kolesov, both acute and chronic inflammation, in turn, are divided into subspecies.
Types of acute appendicitis:
- Catarrhal - only the serous membrane of the process becomes inflamed.
- Destructive - inflammation spreads in the thickness of the appendix, can be phlegmous, gangrenous or perforated.
- Complicated - there is sepsis, abscesses of the peritoneal cavity, local or widespread peritonitis.
Types of chronic appendicitis:
- Primary-chronic - the development of inflammation stops at the initial stage and does not turn into an acute form.
- Recurrent - attacks of acute appendicitis periodically recur, but their form is more blurred.
- Residual - occurs as a result ofattack of acute appendicitis, which was stopped without medical intervention.
Causes of Appendicitis
At the risk of appendicitis are older people, as well as women 20-40 years old. The development of inflammation of the appendix of the caecum can cause a number of reasons. These include:
- Congenital kink of the process or its excessive mobility.
- Clogged appendix with undigested food particles.
- Abdominal injury.
- Various infectious diseases (typhoid fever, tuberculosis, etc.).
- Supersensitivity of the appendix due to the restructuring of the immune system.
- Diseases caused by parasites (ascariasis, opisthorchiasis, etc.).
- Intestinal diseases associated with tumors.
- Inflammatory processes in the walls of blood vessels.
Stages in the development of appendicitis
The first stage of inflammation of the appendix of the caecum is a simple appendicitis. Rezi at this stage may not be strong, so patients often do not seek help from doctors. As a result, further development of the inflammatory process.
Simple appendicitis flows into a phlegmous form. It is accompanied by the filling of the process with pus, the formation of ulcers on its walls and the spread of inflammation to the tissues that surround the appendix.
In severe cases, there is a transition from phlegmous to gangrenous form of appendicitis. From the process filled with pus, inflammation spreads throughout the abdominal cavity. At this stage, the pain goes away,because there was a death of the nerve cells of the inflamed appendix. Instead, a general deterioration in the human condition begins against the background of intoxication of the body.
If the patient is not given medical care at this time, the appendix may burst and all the pus will spill into the abdominal cavity, resulting in a general infection of the blood. Failure to provide assistance to the patient can result in death.
Symptoms of inflammation of the appendix
Appendicitis has many symptoms, but the pain is on the right side first. Depending on the position of the process, the pain can be felt in different places. So, if it is located normally, pains are felt in the right iliac region, if it is high, then it hurts almost under the ribs, if it is bent back - in the lumbar region, goes down - pain occurs in the pelvic region. The pains are also aggravated by laughing and coughing.
In addition to pain, symptoms of appendicitis include:
- Feeling nauseated.
- Gagging.
- Constipation or diarrhea.
- Rise in body temperature.
- Jumps in blood pressure.
- Increased heart rate.
- Lack of appetite.
- Inflation of the abdomen.

- Abdominal tension.
- The presence of a white or brownish coating on the tongue.
Diagnosis of appendicitis
First of all, the doctor takes a complete medical history. The hallmark of appendicitis is an increase inpain in the appendix area during palpation: the doctor abruptly releases his hands after pressing on the peritoneum in the appendix area.

In addition, there are a number of activities aimed at diagnosing appendicitis:
- Carrying out a clinical blood test. The level of leukocytes is checked, since an increase in their number in the blood indicates the presence of infectious processes in the body.
- Conducting a clinical analysis of urine in order to detect red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria in urine, and then draw conclusions accordingly.
- X-ray examination of the abdominal organs: although rare, fecal matter can be detected, which can lead to inflammation of the appendix of the caecum.
- Examination of the abdominal cavity with ultrasound provides an opportunity to see the full picture of what is happening, however, the identification of signs of inflammation of the appendix is possible only in 50% of cases.
- Computed tomography examination is the most reliable and painless way to diagnose inflammation and exclude other possible diseases similar to it in terms of symptoms.
- Laparoscopy is a surgical intervention using a microvideo camera that gives a three-dimensional image of the abdominal cavity.

To date, there is no way that makes it possible to diagnose inflammation of the appendix with 100% certainty. That is why, in case of suspected appendicitis, the doctor uses the entirerange of diagnostic tools available.
Treatment
When a patient is taken to a medical facility, first of all, he will have to go through the above points, namely, a blood test, urine test, and an x-ray of the abdominal cavity. This is necessary because the symptoms of appendicitis may be hiding another disease.
If, after all the examinations, the doctor diagnoses "acute appendicitis", then the patient will have surgery to remove the appendix.

There are two ways to remove the process: traditional and endoscopic.
During a traditional operation, a surgeon makes an incision 8-10 cm long and removes the appendix, suturing the place where it was attached to the intestine.
Endoscopic surgery is performed using a thin tube with a camera. It is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a small hole and gives an image of the operation on the monitor. The advantage of endoscopic surgery is a short postoperative period.
The possibilities of modern medicine make it possible to discharge a patient with appendicitis the next day after surgery. If the appendix ruptures, the patient will be kept in the hospital for a week, during which they will be given antibiotics to help fight the infection.
Prevention
Following the following rules will help prevent the development of inflammation of the appendix of the caecum:
- Prevent constipation, as the result may be the death of the microflora of not only the large intestine, but also the appendix.
- Do not neglect the basic rules of personal hygiene. According to doctors, the most common cause of appendicitis is infection, which can be avoided by following the simplest rules.
- Do morning exercises. Exercise will help set the intestines and the appendix itself to work.
- Sudden getting out of bed is not recommended.
- Periodically massage the abdomen. This will improve the blood supply to the process of the caecum and speed up the movement of food in the intestines.

In addition, another element of appendicitis prevention is a he althy and active lifestyle. Fresh air, jogging, swimming, exercising and other attributes of an active life provide normal blood supply to the gastrointestinal tract and the appendix in particular.