- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
In the human body there are not only blood vessels, but also the so-called "white" vessels. They were known for a long time, and in the middle of the 18th century, knowledge about the lymphatic system became more extensive. Unfortunately, lymphoproliferative diseases are not uncommon, and they can occur in any organ.
Lymphatic system
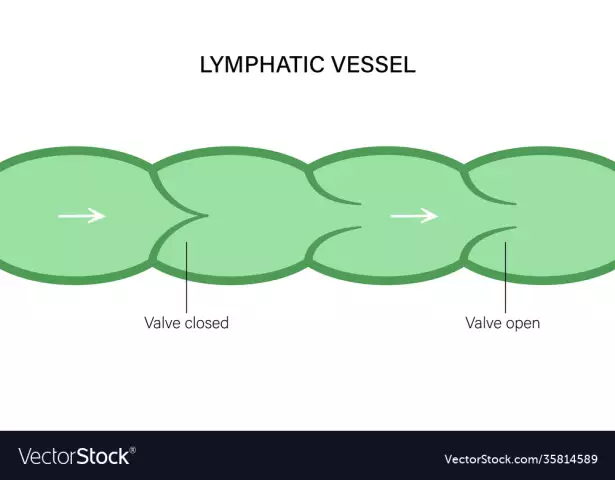
It plays a rather important role in the functioning of a person: thanks to the lymphatic system, useful substances are transported, excess interstitial fluid is removed. Another important ability is to provide immunity. The fluid that performs these tasks is called lymph. It has a transparent color, the composition is dominated by lymphocytes. The smallest structural unit of the system are capillaries. They pass into the vessels, which are both intraorganic and extraorganic. Their structure also includes valves that prevent the reverse flow of fluid. The largest lymphatic vessels are called collectors. It is in themfluid accumulates from the internal organs and other large parts of the body. Another component that the lymphatic system has (the photo is located below) is the nodes. These are round formations that have different diameters (from half a millimeter to 5 centimeters). They are located in groups along the path of the vessels. The main function is lymph filtration. It is here that it is cleansed of harmful microorganisms.

Lymphatic organs
The following organs are also part of the human lymphatic system: tonsils, thymus gland (thymus), spleen, bone marrow. The lymphocytes that form in the thymus are called T cells. Their feature is continuous circulation between lymph and blood. The particles that form in the bone marrow are called B cells. Both types after maturation are spread throughout the body. B cells remain in the lymphoid organs. This stops their migration. Another large organ, which is an integral part of the lymphatic system, is located in the abdominal cavity - this is the spleen. It consists of two parts, one of them (white pulp) generates antibodies.

Lymphoproliferative disease. What is it
This group of diseases basically has an overgrowth of lymphocytes. If changes occur in the bone marrow, then the term "leukemia" is used. Tumors of the lymphatic system that occur in tissue outside the bone marrow are called lymphomas. According to statistics, most often such diseasesoccur in older patients. In men, this diagnosis occurs to a greater extent than in women. This disease is characterized by a focus of cells, which eventually begins to grow. Allocate low, medium and high degree, which characterizes the malignancy of the process.
Possible causes
Among the causes that can cause lymphoproliferative diseases, there is a certain group of viruses. The factor of heredity also plays an important role. Skin diseases that last a long time (eg, psoriasis) can trigger the growth of malignant neoplasms. And, of course, radiation significantly affects this process. Radiation, some allergens, toxic substances activate the process of cell growth.
Lymphomas. Diagnosis
One of the types of malignant neoplasms of the lymphatic system is lymphoma. Symptoms in the early stages may not be severe.

Swollen lymph nodes that are not painful. Another striking sign is fatigue, and to a fairly large extent. The patient may complain of excessive sweating at night, a significant and sudden loss of body weight. Itching, red spots are also possible. Body temperature sometimes rises, especially in the evenings. These symptoms should be alerted if they do not disappear after a few weeks. For effective treatment, it is very important to determine the type of lymphoma. When diagnosing, take into account the placelocation, appearance of the tumor, the type of protein that is on its surface. The specialist prescribes a complete medical examination, a blood test for cancer cells, and a diagnosis of internal organs. For more information, a biopsy is needed. Under the microscope, affected cells have a specific appearance.
Lymphoma treatment
Methods of treatment of this disease are as follows. To destroy the neoplasm, chemotherapy or radiotherapy (using x-rays) is used. A combination of drugs is used, they are distributed in the body and can also destroy those cells that could not be diagnosed. After chemotherapy, the bone marrow is also affected, so it may need to be transplanted. It is carried out both from the donor material and directly from the patient's own bone marrow (it is previously removed before the start of the procedures). Lymphoproliferative diseases are also amenable to biological therapy, but it is predominantly experimental. It is based on the use of substances that are synthesized from the patient's cells. To achieve a good result, you must carefully follow the instructions of the attending physician, take medications on time, and pay due attention to nutrition.

Leukemia. Clinical picture
The disease is characterized by a change in hematopoietic cells, in which the he althy elements of the bone marrow are replaced by the affected ones. The level of lymphocytes in the blood increases significantly. Depending on which cells weredegenerate, secrete the disease lymphocytic leukemia (changes in lymphocytes), myeloid leukemia (myelocytes are affected). You can determine the type of disease under a microscope and by analyzing the protein. Lymphoproliferative disease (what it is, was described above) in this case has two forms of course: chronic and acute. The last one is pretty hard. In this case, immediate treatment is necessary, since the cells are immature and unable to perform their functions. The chronic form can last for many years.

Chronic lymphoproliferative diseases
In older people, chronic lymphocytic leukemia is often diagnosed. The disease proceeds rather slowly, and only in the later stages are disturbances in the process of blood formation observed. Symptoms include swollen lymph nodes and spleen, frequent infections, weight loss, and sweating. Often, these lymphoproliferative disorders are discovered incidentally.

There are three stages of the disease: A, B, C. The first affects 1-2 lymph nodes, the second - 3 or more, but there is no anemia and thrombocytopenia. At the third, these states are observed. In the early stages, experts do not recommend therapy, as a person retains his usual lifestyle. At the same time, it is important to observe the daily regimen, the doctor can give advice on nutrition. Restorative therapy is being carried out. Treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia should begin when signs of progression are detected. Itincludes chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplantation. With the rapid growth of the organ, the removal of the spleen may be necessary.