- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:18.
Today, the Goryaev camera is one of the most used devices in laboratory diagnostics. With its help, you can calculate the number of certain blood cells. As you know, a blood test is extremely important for the process of diagnosing and treating almost every disease.
What is Goryaev's Chamber?

Such a well-known and useful device was developed and proposed by the Russian doctor N. K. Goryaev. Goryaev's camera, in fact, is a specific glass slide with a microscopic grid applied to it.
What is this camera used for? First of all, it is used to determine the number of blood cells, in particular leukocytes and erythrocytes. By the way, with its help you can determine the magnification of the microscope used. The formula for this is as follows:
Kg=(m2 - m1)/ aN
In this case:
- Kg is the magnification of the microscope;
- m2 - position of the right border of the Goryaev camera cell;
- m1 - left border position;
- a - the size of onecells which is standard and is 0.05mm;
- N is the number of cells between measured camera borders.
Chamber structure

Goryaev's camera is nothing more than a glass slide (but much thicker than usual), divided into three parts by transverse grooves. The middle part of the glass contains a special grid for counting. The extreme parts of the chamber serve to grind the coverslip - thus, a closed chamber is created in the center with capillary spaces on the sides, through which it is filled with liquid.
As for the grid, Goryaev's cell is divided into 225 large squares of equal size - they are arranged in fifteen rows. 25 large squares are additionally divided into smaller ones, 16 each. The length of each side of this small square is 0.05mm.
Preparing for counting uniforms
Of course, in this case, the technique of laboratory research is of great importance. Of course, all surfaces of the Goryaev chamber must be clean and dry. After that, the coverslip is rubbed so that the characteristic iridescent rings can be seen. It is extremely important that there are no air bubbles in the chamber, as this may distort the results of the analysis.
Naturally, in order to count the number of formed elements, different reagents are used for each type of blood cell. For example, 0.9% sodium chloride solution is used to count red blood cells. In vitroyou need to mix 8 ml of s alt solution and 0.02 ml of blood. So, the laboratory assistant dilutes the blood 400 times. Sometimes the breeding can be large.
In order to count the number of leukocytes, you need to mix 0.4 ml of acetic acid (take a 3% or 5% solution) and 0.02 ml of blood.
After the components are mixed in the test tube, use a special pipette to collect a small amount of the mixture and carefully fill the counting chamber (usually one or two drops will be enough).
How to calculate the number of blood cells?

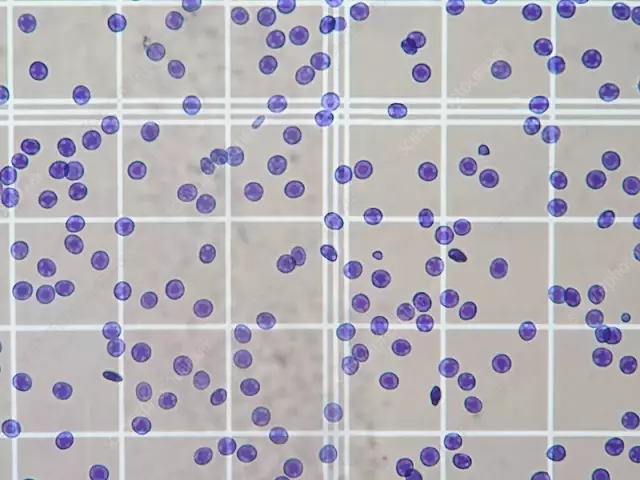
Erythrocyte counting in Goryaev's chamber is carried out in five large squares, which is equal to eighty small ones. Diagonal squares are chosen to avoid error due to uneven distribution of blood samples. Special attention is paid to the cells located along the edges - here they count the erythrocytes on the left and upper walls, but do not take into account those located on the lower and right lines.
In order to determine the number of red blood cells in a milliliter of blood, the number of cells in five large squares is multiplied by 20,000 (when diluted 400 times).
Leukocytes in Goryaev's chamber count differently. Here you need to calculate the number of elements in at least a hundred large squares. The resulting amount is divided by 1600, after which it is multiplied by 4000, and then by 20 (the degree of dilution).