- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Arthritis is an inflammation of a single joint, and if we are talking about the defeat of several, then there is such a disease as polyarthritis. Its symptoms are different and depend on the severity of the course of the disease, so each of the patients notes different manifestations of polyarthritis.
General information
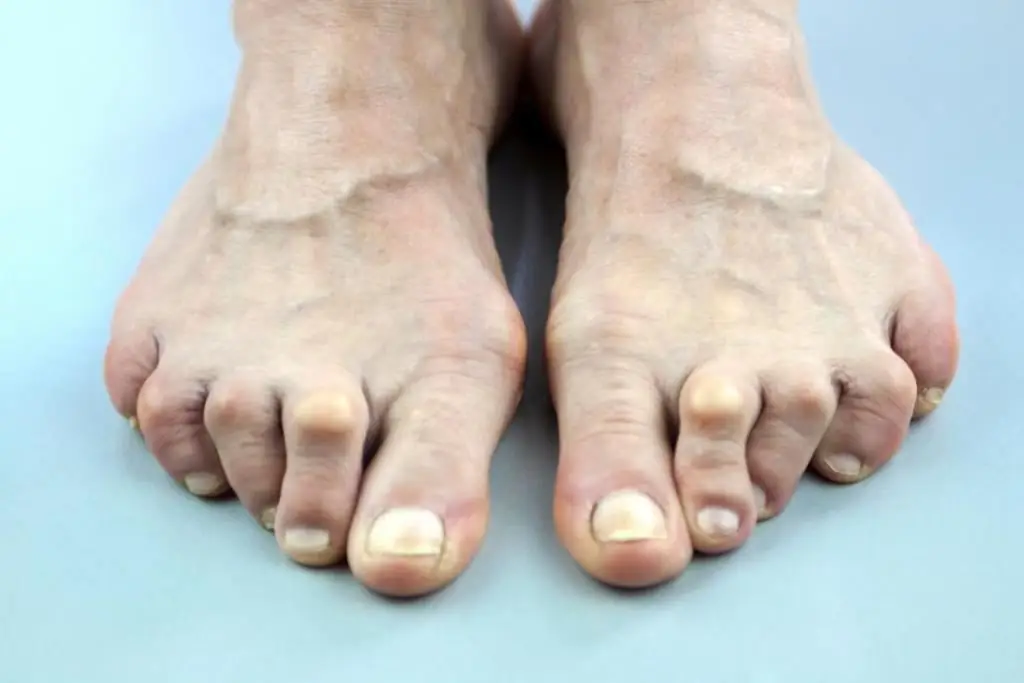
Many reasons can provoke an illness, starting with metabolic disorders in the body, allergic reactions, injuries, ending with the consequences of infectious diseases. It should be noted that the membranes and tissues surrounding the joint itself have a huge number of nerve endings and blood vessels. Due to this, they instantly respond in the form of inflammation to the impact of adverse external or internal factors.
Views
Depending on the factors that cause the symptoms of polyarthritis, the course of the pathological process is different. Depending on the type of disease, therapy is prescribed.
By the type of course, two forms of the disease are distinguished:
- acute manifestation - howusually begins unexpectedly, accompanied by classic symptoms, which are just characteristic of the disease;
- chronic course - develops gradually and slowly. For some time, the disease proceeds in a latent form, with virtually no symptoms. Periodic exacerbations are replaced by remissions. During exacerbations, patients develop painful symptoms characteristic of an acute process.
Depending on the provoking factors, the following types of polyarthritis can be distinguished:
- Gouty - occurs due to the deposition of urates (s alts of uric acid) in the joints. The disease proceeds with periodic exacerbations - pain and intense inflammation of the joints. During periods of remission, the symptoms of polyarthritis of the fingers or other limbs disappear.
- Psoriatic - appears with psoriasis and is characterized by skin manifestations. Sometimes joint problems precede skin changes.
- Infectious - is formed due to the ingestion of infections of any kind. Usually, the disease affects the joints on the background of a chronic genitourinary or intestinal infection.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. The symptoms of this disease are very colorful, as it is an autoimmune disease, due to which the deformation of the joints begins. The disease symmetrically affects the joints of the feet and hands.
- Bekhterev's syndrome is a polyarthritis that affects the joints in the spine. Without adequate treatment, this disease leads to immobilization of the back.
Symptoms of polyarthritis of the joints
Despite the fact that there are several varieties of polyarthritis, there arecommon signs that accompany all kinds of ailments:
- fluctuations in body temperature;
- joint pain;
- deformity in affected joints;
- limitation of mobility and activity;
- redness of the skin in areas of inflammation.
There are also specific symptoms of polyarthritis, which are characteristic of a certain type of pathology. They are caused by factors that provoke the onset of the disease.
Exchange polyarthritis appears due to a violation of the flow of metabolic processes in the body. This form of malaise is manifested by a rather pronounced inflammatory process, which is concentrated at the site of joint damage. This type of disease is characterized by acute pain in the affected joint, which disappears after a few days. There is also hyperemia and swelling. The disease has a chronic course with 1-3 exacerbations during one month.
Polyarthritis deformans develops due to a weakened immune system or autoimmune disorders. This disease is characterized by a chronic course. During exacerbations, patients complain of the classic symptoms of polyarthritis. A photo of the diagnostic process is shown below.
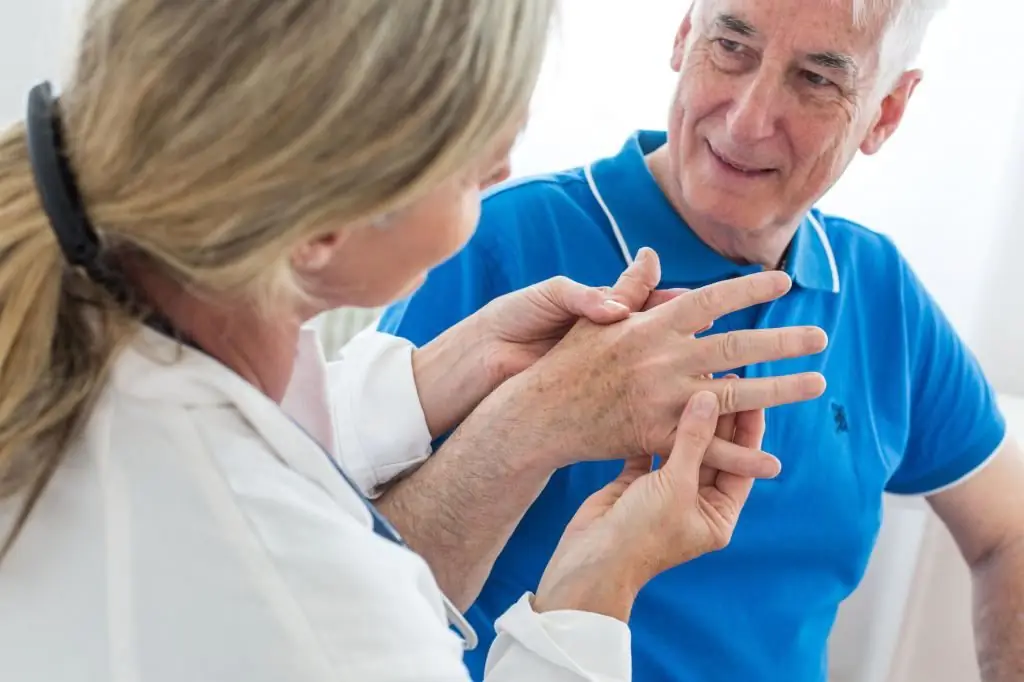
So, the main symptoms:
- joint pain;
- muscular atrophy;
- general weakness, fatigue, decreased performance;
- impaired joint mobility (this is especially pronounced in the morning);
- swelling, fever;
- joint deformity;
- redness of the skin in the affected area;
- significant enlargement of the diseased joint.
Reactive polyarthritis develops due to past inflammatory or infectious diseases. The first clinical signs are not specific. There is increased fatigue, the temperature rises slightly, the lymph nodes increase. As the disease progresses, the following symptoms of polyarthritis of the hands and feet appear:
- skin lesion;
- muscle and joint pain in limbs;
- change in the skin;
- fever syndrome.
Reasons
There are a lot of factors that provoke the disease. Among them are the most common hypothermia, metabolic disorders, a banal genetic predisposition.
For infectious polyarthritis, underlying factors may be previous infectious diseases (gonorrhea, viral hepatitis, dysentery).
Another kind of polyarthritis appears as a result of a violation of the body's metabolic processes.
Post-traumatic arthritis is formed due to local trauma or severe allergic reactions.
As for the causes of the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, there is currently no consensus among specialists about them.
Danger of disease
Polyarthritis in a neglected form can lead to very dangerous consequences for the body, as the disease disrupts the patient's motor activity, deforms the joints and affects almost the entireorganism. Polyarthritis is especially dangerous in the absence of adequate and timely treatment. According to experts, this pathology can cause the development of the following ailments:
- heart disease;
- vasculitis;
- change in visual function;
- anemia;
- pericarditis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- bleeding disorder;
- fibrotic processes;
- neuritis.
Treatment of symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and its other manifestations is required to begin at the earliest stages of the pathological process. In this case, when there is adequate therapy and strict adherence to all medical advice, a stable remission can be achieved, and as a result, the formation of the above complications can be avoided.
Diagnosis

All examinations for this disease begin after studying the clinical picture. In addition, in order to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the type of disease, the patient must undergo the following types of examinations:
- take rheumatoid tests;
- laboratory blood and urine tests;
- x-ray;
- arthrography;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging;
- histological diagnosis.
Only based on the results of complex measures, the doctor prescribes the appropriate therapy for the patient.
Photo
Treatment of symptoms of polyarthritis and a comprehensive examination of the patient is in the first place among doctors. This disease bringsmany unpleasant consequences, which will be described in detail later in the article.
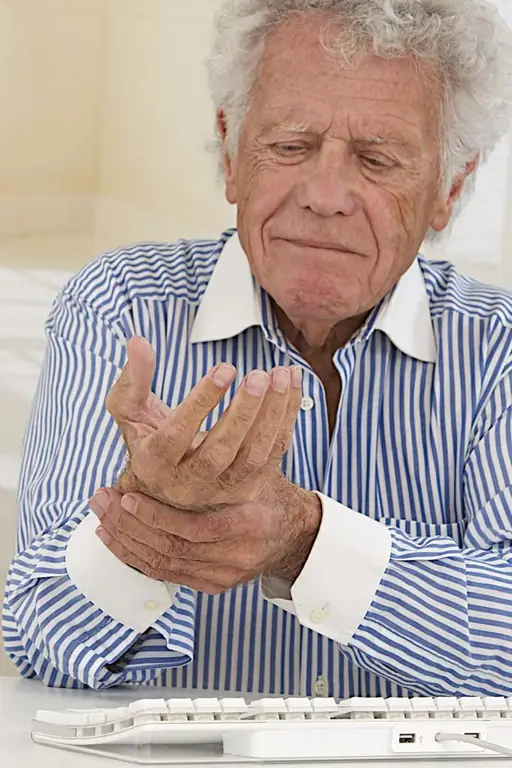

From the photo and the symptoms described above, it is clear that patients affected by this disease cannot get all the benefits of life that are available to people with he althy joints. Polyarthritis does not go away on its own, you need to seek medical help.
Who should I contact?
An unequivocal answer to the question: "When treating the symptoms of polyarthritis, which doctor should I contact to get qualified help?" no, since there are a lot of varieties of the disease and signs of their appearance, and each doctor is responsible only for his narrow specialization.
The causes of the disease can be many - various infections, pathological changes and injuries. Depending on the symptoms, the patient is referred to an orthopedist, rheumatologist or traumatologist. In large clinics with a large staff, you can get advice from an arthrologist.
An approach is also considered effective when each specialist takes part in therapy at a certain stage. For example:
- surgeon - examines the condition of tissues;
- rheumatologist - most often it is he who prescribes the main treatment and monitors the course of the disease;
- traumatologist - will provide advice and prescribe treatment if the cause of the symptoms of polyarthritis of the hands and feet is an old injury.
Many specialists can be involved in the treatment. Therefore, initially you need to go to the therapist, and he will tell you which of the doctors to contact if there issymptoms of polyarthritis and prescribe all the necessary tests.
Therapeutic interventions
Any treatment should aim to achieve the following positive results:
- prevent further joint deformity;
- stopping inflammation;
- stopping the process of destruction of cartilage and articular tissues;
- restoration of blood circulation in affected tissues;
- activation of tissue regeneration and renewal.
To achieve all these goals, modern specialists use physiotherapy, diet and medication.
Sometimes, in particularly difficult situations, there is a need for surgical intervention to improve the patient's condition.
Treatment with drugs
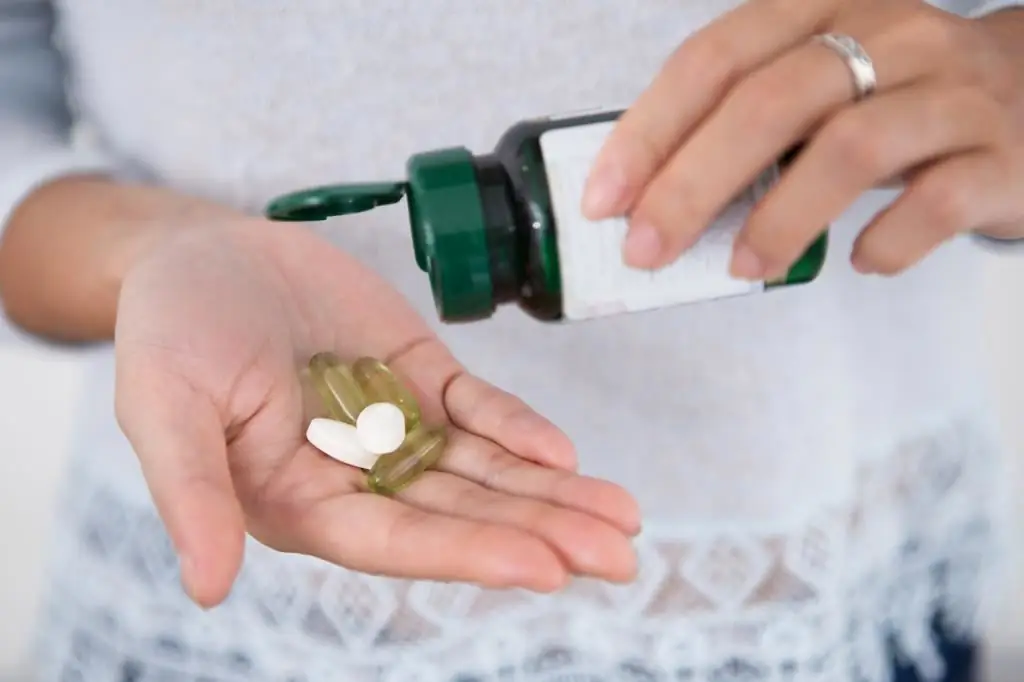

For the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and its other forms, various medicines are used. Here are some of them:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - their action is aimed at reducing inflammation and blocking the activity of prostaglandins, because they play a major role in inflammatory processes. NSAIDs relieve mild to moderate pain. These drugs act very quickly, but have a huge number of side effects. These drugs include Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Indomethacin and Ketoprofen.
- Corticosteroids reduce inflammation and work to suppress the action of the immune system. They help relieve pain, and cope with the symptoms of polyarthritis faster than other remedies. These include: "Dexamethasone", "Prednisolone",Triamcinolone and Methioprednisolone.
- Essential antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Their use is aimed at eliminating the causes of polyarthritis. Very often the drug "Methotrexate" is prescribed, but it can harm the liver, so blood tests are constantly required during the course of taking the drug. Means of this group are also "Hydroxychloroquine" and "Sulfasalazine".
- Anti-TNF drugs contain substances that block tumor necrosis factors. The most commonly prescribed are Infliximab, Etanercept, or Adalimumab, given intravenously or intramuscularly.
Treatment of the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis should be carried out regularly, since it is impossible to completely remove the signs of the disease. Through therapy, the patient can return to excellent he alth and normal activity levels.
Physiological treatments
These methods allow you to stop the pain syndrome, as well as stop the subsequent development of the pathological process and increase the indices of articular mobility. The following procedures are excellent for this purpose:
- exercise therapy;
- massage;
- ultrasound therapy;
- cryotherapy;
- paraffin applications;
- magnetotherapy;
- barotherapy;
- phonophoresis;
- ozocerite applications.
For the treatment of symptoms of polyarthritis of the legs and hands, it is often recommended to visit dispensaries and sanatoriums.
Diet
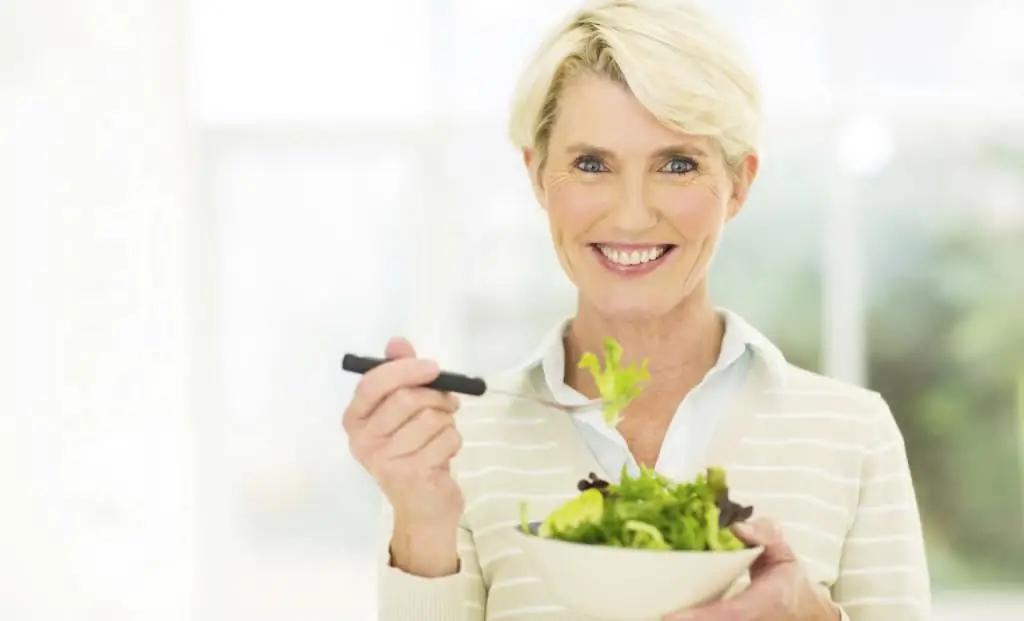

In the fight against the disease, a hugeA proper and balanced diet is essential. It is important that all the necessary vitamins and microelements enter the patient's body with food. This is necessary for the normalization of metabolic processes.
It is recommended that patients eat small meals, but eat often to prevent obesity, which negatively affects the general condition of the joint tissue.
To prevent the symptoms of shoulder arthritis and polyarthritis of other parts of the body, add the following foods to your diet:
- jelly;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- fermented milk products;
- fish and lean meats;
- jelly;
- sorrel;
- rice;
- blueberries;
- fruit drinks from various berries.
And here is a list of foods and dishes that are better to refrain from:
- tea;
- sweets;
- tomatoes;
- potato;
- baked goods;
- s alty, spicy and spicy foods;
- alcohol;
- legumes;
- drinks containing caffeine;
- meat broths.
Surgery
Surgical interventions in the treatment of symptoms of rheumatic polyarthritis and its other varieties are resorted to only in the most severe and neglected situations, at the later stages of the pathological process, as well as when other types of therapy are ineffective. In the case of a sufficiently severe destruction of the joints, the operation is the only option to normalize the patient's condition and return all the colors to himlife.
Surgical intervention, regardless of the type, is aimed at the complete elimination of pain and the normalization of the functioning of the joints. Depending on the characteristics of the course of the pathological process and on individual indications, the following surgical methods are used to combat the symptoms of polyarthritis of the shoulder joint or other parts of the patient:
- Prosthetics of a destroyed joint element or its partial replacement.
- Artificial immobilization of the articulation of the joint to activate the processes of bone tissue fusion.
- Surgical removal of damaged parts of the joint and synovial membranes. This therapy is used to prevent the spread of inflammation to the area of nearby bone tissue structures.
The optimal type of surgical intervention is selected by the surgeon after making the correct diagnosis, determining the degree of joint damage. The presence of contraindications to surgery and the general he alth of a particular patient are taken into account.
Folk ways
Treatment of symptoms of polyarthritis by folk methods is used in cases where the disease was detected at an early stage. Polyarthritis is treated with various herbs. But before using this method, it is imperative to consult with your doctor so as not to harm the body.
Recipes:
- You need to take an equal number of inflorescences of blackthorn flowers, black elderberry, nettle and warty birch leaves to make tea from this collection. For this, 2 tbsp. l.collection is poured with 500 ml of hot water. The mixture is brewed for 10 minutes. Consume 2 cups per day.
- St. John's wort, calamus root, sage and bearberry are taken in equal parts. Two tablespoons of the mixture should be poured with 1 cup of boiling water and brewed for 15 minutes. Drink this decoction 500 ml per day.
- The decoction is prepared according to the previous recipe, only for it you will need herbs such as hernia, buckthorn bark, juniper berries and horsetail.
- It is also recommended to prepare a collection of field steelwort, soapwort and willow bark. 1.5 tbsp collection is poured with a glass of boiling water and infused for 10 minutes. After you need to boil the broth for 10 minutes. The decoction should be drunk in 3 doses throughout the day.
Prevention
Since many reasons can provoke the development of polyarthritis, as a preventive measure, you should try to prevent their influence on his body. Namely, you need:
- eat a balanced and wholesome diet;
- lead a he althy and active lifestyle;
- start the treatment of infections, injuries and other ailments in a timely manner and prevent them from becoming chronic;
- avoid joint damage;
- do not exhaust the joints with excessive loads;
- do not get cold.
People with a hereditary predisposition to the formation of the disease are required after 45 years of age every six months as a preventive measure to visit a doctor and take all the necessary tests.
Conclusions

Polyarthritis issevere inflammatory articular pathology. This disease affects several joints at once. The reasons for this problem are quite diverse and numerous. Since the disease is fraught with the formation of a huge number of complications and, in the absence of treatment, leads to disability, it is recommended to start fighting it at the earliest stages of the course of the disease.
Physiotherapy, medicines and proper nutrition have proven themselves as therapeutic measures. Only when applying such an integrated approach is there a high probability of achieving positive and lasting results. With advanced forms of the disease, such methods will no longer help; only surgical intervention is used as a treatment.
To prevent such serious he alth problems, we advise you to carry out the prevention of the disease, so that later you do not have to look for ways to treat it.






