- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Anatomically, the femoral head is held by the annular glenoid fossa. The femur is considered the largest in the body, and therefore, it has a complex structure and performs a large number of motor functions. It is not easy for a person who is far from medicine to understand this, but it is necessary to understand the causes and course of diseases of the femur.
Anatomy of the femur

The femur plays an important role in the human body, as it is the largest tubular bone tissue in the skeleton. She, like other bones of the tubular type, has two ends and a body. It connects to the pelvis with the help of the head, which ends the upper proximal section.
The transition of the neck into the bone body ends with tubercles - skewers. The bone body ends precisely with a large trochanter. On its medial surface there is a small depression. On the back of the lower edge of the neck is a small trochanter. The large one is connected to it by an intertrochanteric ridge that runs along the back side.bones.
Hip functions
The entire lower limb is very important for a person, as it takes part in all movements of the body. In addition, the structure of the femur helps a person to be in an upright position, while enduring all static loads. Thanks to the femur, a person has the ability to walk, run, jump, play sports and perform more difficult activities.
Main lesions of the femur
The main and most common injuries and lesions of the femur are: fracture of the greater trochanter of the femur, fracture of the lesser trochanter, bursitis, trochanteritis, tendinosis.
Types of trochanteric fractures
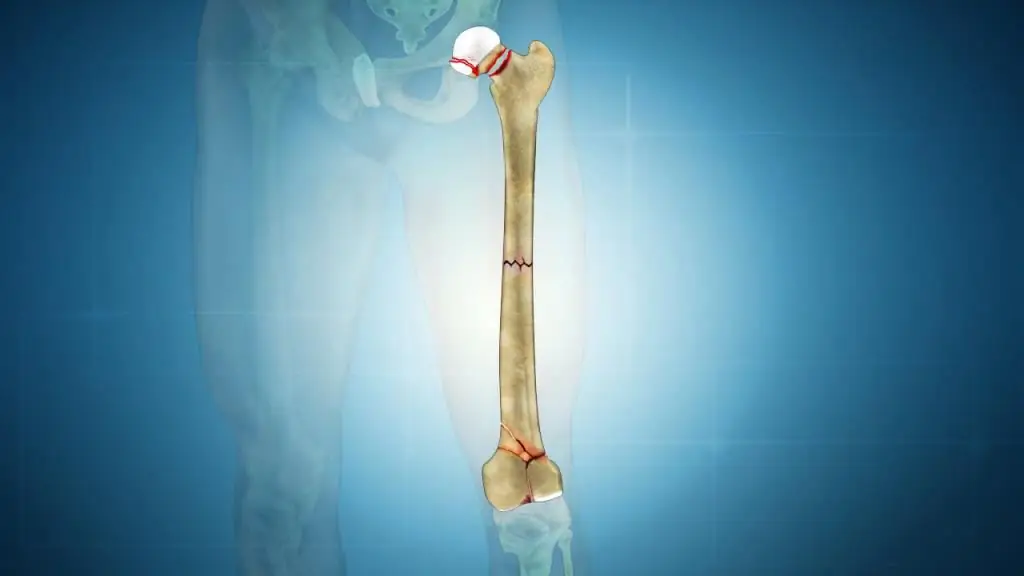
Trotatic fractures are typical for elderly people diagnosed with such a common disease as osteoporosis. The most common trochanteric fractures are:
- Chervertelny simple and comminuted. With such a fracture, the direction of the fracture line of the bone coincides with the one that connects the large and small trochanters.
- Intertrochanteric. Such a fracture is characterized by the fact that the line of damage crosses the line that connects the large and small trochanters.
Such injuries are impacted and non-impacted, here is the clinical picture.
Due to muscle traction in simple fractures, the fragments converge. This facilitates the fusion of the bones and their reposition. Fractures with many fragments heal less well and require a strongercommit.
Intertrochanteric fractures are characterized by the fact that the work of the muscles around does not contribute to fusion, but vice versa. This explains the importance of a hard fix.
Fracture of the greater trochanter

This type of lesion of the femur occurs directly with the direct action of force on the area of the greater trochanter. In children, this is usually apophyseolysis with displacement of the diaphysis. In this case, 2 or 3 fragments of the greater spit may be completely crushed.
The most common hip fractures in the elderly are trochanteric and femoral neck fractures. With a fracture of the greater trochanter, the displacement of the bone can be directed upwards backwards or forwards. This is due to the fact that over the years, bone strength decreases, and normal loads on the musculoskeletal system can already be traumatic.
With a trochanteric fracture, the patient feels a sharp pain in the affected area; palpation can detect a slight joint mobility. In addition, a small crackling sound is characteristic of a fresh fracture. The functional part of the thigh is broken during a fracture, especially with regard to its retraction. If the greater trochanteric bone is fractured, the affected leg may be loaded, but lameness will be felt.
A patient with such a fracture can freely bend and straighten the leg at the knee joint, however, attempts to turn the leg cause the patient severe pain. If he can raise his outstretched leg up, then this means that there is no fracture of the femoral neck. It is worth noting thatit is impossible to take the leg to the side with a fracture of the femur due to sharp pain in the affected area.
Tendinosis of greater trochanters
This disease is a fairly common pathology. It is typical for people who overload the hip joint. This category mainly includes athletes.
With tendinosis in the greater trochanter, the inflammatory process begins in the ligaments and tendons, subsequently spreading to the tissues. The process originates at the point where the bone connects to the ligament. If a person does not pay attention to this, continuing to load the joint, inflammation becomes chronic.
Provoking factors include the following:
- Joint injury.
- Failures in metabolic processes.
- Congenital joint dysplasia, which affects not only the articular surfaces, but the entire ligamentous apparatus.
- Disturbances in the endocrine system.
- Aging of the body, in which the structure of bones and ligaments changes.
- Systematic loads associated with the monotony of work.
- Spread of infection to surrounding tissues.
- Inflammatory processes in the joints.
Clinical picture:
- Pain on palpation and movement of the limb.
- During movement, the bones begin to crackle.
- The skin at the site of the lesion changes color and becomes red.
- Local temperature increase at the site of injury.
- The joint cannot perform its direct functions.
Inflammation

Terchanical bursitis is an inflammation between the fascia lata and the greater trochanter. It is located on the outer side of the femur in its upper part. At the same time, fluid collects in the bag, its walls expand, and pain appears. This disease is very dangerous due to its complications, including complete immobilization of the joint.
Pain that occurs at the protrusion of the femur of the greater trochanter is the most basic sign of the onset of the development of pathology. During walking and with any impact on the joint, the pain intensifies. At a later stage, the inflammatory process caused by bursitis begins to spread to the lower part of the thigh, thereby causing lameness in the patient. Even if the load on the affected limb does not decrease, then after a while pain may begin to appear even at rest.
Diagnosis

To diagnose a fracture of the greater trochanter of the femur, an x-ray is performed, if necessary, the doctor decides to send the patient for computed tomography. Tendinosis is diagnosed by palpation, radiography, magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound of the affected area.
Methods for treating fractures
In case of a fracture of the greater trochanter of the femur, the patient is usually put on a plaster circular bandage in the abduction position for 3 weeks. After the expiration of the prescribed period, the plaster is removed, and the patient is prescribed a course of massage foraffected area. During this period, the patient can move with the help of crutches, since such a load does not cause him any discomfort or pain.
But in some cases, doctors have to resort to open reposition using bone holders specially designed for such procedures, that is, bone fragments are compared with each other, which provides them with better fusion. This procedure is carried out if, when the leg is abducted, it is not possible to set the bone fragments.
Tendinosis therapy

Treatment of this pathology is carried out by complex measures. Depending on the location of the lesion and on what stage the disease is at, the doctor prescribes optimal therapy. To relieve pain, the patient is prescribed painkillers and ice compresses to be applied to the affected area.
With the help of elastic bandages or bandages, the affected joint is limited in movement. In addition, physiotherapy procedures are used to treat tendinosis. A good effect, for example, is exerted by magnetic therapy, laser, ultrasound, applications from therapeutic mud and baths with mineral s alts also help. As the recovery progresses, the patient should begin to perform a course of exercise therapy. Classes help improve joint mobility, elasticity and muscle strength.
Surgical intervention for tendinosis is an extreme measure for the treatment of this disease and it is used in very rare cases. Doctorstrying to get by with conservative therapies.
What to do with bursitis?
Treatment of bursitis should start with simple procedures. Very rarely, such a disease requires surgical intervention. Patients under the age of thirty are advised to reduce the load on the affected joint and undergo a course of rehabilitation therapy, which includes exercises to stretch the muscles of the thighs and buttocks.
Therapy for inflammation of the greater trochanter involves the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. With the help of such drugs, swelling of the affected joint and pain are effectively removed. The use of cold, ultrasound, heating and UHF helps to get rid of pain and relieve swelling.
One of the most convenient home remedies is the use of heat or cold. At the same time, it is important to remember that cold is applied immediately after an injury, and heat is used for inflammatory processes that occur in a chronic form. An experienced physiotherapist will be able to give useful recommendations, using which you can fully restore all the motor functions of the joint. If fluid accumulates in the trochanteric bag, then the patient is recommended to make a puncture in order to pump out all the water and send it to the laboratory for analysis.
During this procedure, a small dose of steroid hormones, such as cortisone, is injected into the trochanteric pouch, but this can only be done if the patient does not have any infectious diseases. Hormonal drug quickly relieves inflammation. The effect of the procedurecan last for 6-8 months.
Timely visit to the doctor will help cure all existing disorders in the femur in a short time. If any of the pathologies in this part of the human body becomes chronic, then the pain syndrome stops only for a while.






