- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
According to traumatology statistics, the hand is damaged most often. The most common sprain is the wrist joint. It occurs at the moment of landing when falling on an outstretched arm with excessive flexion or overextension of the hand.
Very often this phenomenon occurs in contact, power or extreme sports - hockey, football, handball, wrestling, lifting the barbell, gymnastics, etc. Sprain of the right wrist joint occurs more often than the left, and is explained by the fact that that 85% of people are right-handed.
The essence of trauma
A sprain is a damage to the bundle of tissue fibers that provide articulation of the bones of the joint. It occurs when the load is excessive, when the strong tension of the ligament exceeds its physical strength. According to ICD-10, wrist sprain has code S63.
Tissues of the ligaments in most cases remain intact, but for a certain time they cannot perform their functions. get damagedcan she or several bundles at the same time.
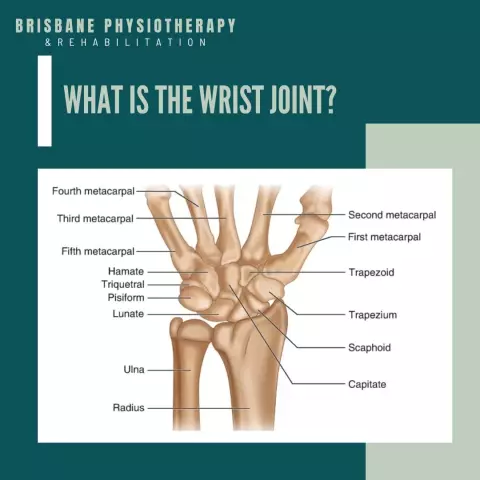
A bit of anatomy and physiology

Tissues of ligaments contain collagen and elastin fibers that are arranged in parallel. Collagen is responsible for their strength, and elastin for elasticity. The wider the ligament in diameter, the stronger it is, and the ability to resist deformation is determined by its length. It turns out that the narrow and short ligaments of the hand are just the most vulnerable.
Left wrist sprain occurs more frequently in left-handers, who make up 15% of the population. The anatomy of the wrist is different from other joints:
- The joint is complex because it has more than 2 articular surfaces.
- There is an additional cartilaginous triangular disc inside the joint capsule for joint congruence.
- The shape of the joint is elliptical (one surface is concave, the other is convex). This provides him with 2 axes - horizontal and vertical, as well as the ability to rotate.
More than a quarter of the bones of the hand (8 out of 27) are concentrated in the wrist and connected by ligaments. The ligaments of the wrist are strong and elastic, but this does not determine their ability to withstand continuous loads. There are 6 ligaments, lateral (collateral) ligaments are injured more than others - radial and ulnar.
Such a complex structure provides subtle movements, but the same circumstance gives a high level of injury.
Causes of damage
Wrist sprain according to ICD-10 belongs to the classS3-S63.6 - ruptures and sprains of ligaments of different parts of the hand. This includes all traumatic injuries of the wrist.
The most common causes of wrist sprains:
- landing on the arm when falling or hitting hard;
- wrist fall;
- dislocations;
- fractures;
- sharp movements;
- lifting weights with a snatch;
- lifting weights with outstretched arms;
- holding body weight with hands without support.
No one is immune from such factors: neither athletes nor ordinary people.
According to the ICD, a wrist sprain has been assigned code S63.5. This paragraph includes the following injuries - sprain and overstrain of the capsular-ligamentous apparatus at the level of the carpal, wrist joint and ligaments.
There are also risk factors for some segments of the population:
- hypodynamia and hypokinesia;
- old age, when ligament tissues are broken;
- tendon anomalies from birth;
- arthritis and arthrosis;
- poor muscle development and lack of training due to poor physical fitness.
This exacerbates the stretching of the ligaments, because in such conditions they become inelastic and thinner.
Wrist sprain (ICD-10 code - S63) includes the above sprains, overstrain of the ligamentous apparatus, dislocations of the hand and wrist.
Also, ligaments can stretch when:
- diseases of the joints;
- gravity injury;
- when bone fragments are displaced infractures;
- hanging on the horizontal bar without foot support.
Symptomatic manifestations

Wrist sprain symptoms and treatment are interrelated. With severe sprains, the tendons are torn, and a loud crack is heard. The joint in such cases is not restrained by anything and becomes dangling. There is a sharp sharp pain, redness of the skin, a bruise (hematoma) quickly occurs at the site of injury, swelling increases. Complete immobility of the hand sets in.
According to ICD-10, wrist sprains also include code S63.3:
- traumatic rupture of the ligament of the wrist and metacarpus;
- lateral ligament of the joint;
- palmar ligament.
A joint injury goes through 3 stages, but pain is present in each.
- First stage, easy. Most often there are no symptoms, the patient leads a normal life. A wrist sprain in stages 1 and 2 may or may not have symptoms. The pain is minor. Damage area is minimal.
- Second degree, moderate. Rupture of fibers is partial. The pain is severe, there is inflammatory edema. The mobility of the joint is reduced, the person goes to the doctor.
- Third degree, severe. Symptoms of sprain of the wrist joint are pronounced sharply, brightly. Here there is a rupture of the entire ligament with a characteristic crunch. The pain is unbearable, bruising and swelling immediately appear. If help is not provided, the blood flows into the joint bag and a hygroma of the joint is formed. Occurs after 1-2 hoursfever, which indicates the start of an inflammatory reaction. Torn ligaments do not hold the joint, and it becomes excessively mobile.
Wrist sprain is quite easy to distinguish from more serious injuries: it is not typical for it to protrude and deform articular and bone fragments as in a dislocation or fracture. And one more feature: unlike fractures of the hand, when stretched, mobility is found at the site of the lesion, with an increased amplitude.
First Aid

Algorithm of actions:
- remove jewelry from the brush, if any, and unbutton the sleeve of the shirt;
- ensure complete rest of the limb;
- exclude any load;
- immobilize hand;
- apply a cold compress;
- in case of dislocation and rupture of ligaments, apply a splint;
- give an analgesic;
- transport to emergency room.
Ice wrapped in rags can become a cold compress, its application time is 30 minutes, after a half-hour break you can repeat. Ice will constrict blood vessels, relieve pain and reduce swelling. Of the analgesics, Paracetamol, Analgin, Ibuprofen can be used.
A tight bandage is applied with an elastic or regular bandage. Immobilization of the hand will be better carried out not on weight, but on a flat surface.
Also, to relieve swelling and stagnation of blood at the site of injury, it is better to keep a fixed arm above the level of the body. It is betterto do this on special beds in the trauma department. Moreover, outpatient treatment is possible only with 1 degree. When ligaments are torn, therapy is carried out in a hospital.
Diagnostic measures

X-ray, ultrasound and MRI are used for diagnosis. With MRI, images of tissues are taken layer by layer, from different angles. This method is especially valuable in children.
An experienced traumatologist can make a diagnosis immediately, through examination, questioning and palpation. And only if a fracture is suspected, an instrumental study may be required. Ultrasound is especially often used to assess the condition of the ligaments before and after treatment.
X-ray remains the most famous and accessible. The doctor from the picture can confidently and without a long wait determine the type of injury - a fracture or sprain.

Signs of injury on x-ray:
- When bruised or sprained, there are no changes on the x-ray.
- In dislocations, the articular surfaces are not matched.
- In case of fractures, the fracture line is visible, there may be displacement of bone fragments.
Possible complications of sprains
Sprain can be complicated by the following pathologies:
- long non-healing due to incorrect or no treatment;
- transition to arthritis or arthrosis;
- joint instability and weakness;
- stiffness;
- predisposition to repeated sprains;
- reduced athletic ability in the area where the hand is involved.
Principles of treatment
Treatment for a wrist sprain can be conservative, surgical, non-traditional.
Conservative method:
- medication;
- topical treatment;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- exercise.
A recovery period is required for any treatment.
Drug therapy

Medical treatment is necessary at any stage of the injury. First of all, NSAIDs (anti-inflammatory non-steroids) and analgesics are prescribed: Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Voltaren, Ketonal, Nise, Ortofen, etc. They are used in tablets and injections.
Anti-inflammatory ointments are also prescribed: "Fastum gel", "Voltaren gel", "Nise gel", etc. Ointments relieve swelling and pain at the site of injury, help the fastest resorption of hematomas.
To strengthen the joint, it is good to take calcium supplements and multivitamin complexes. The first 5 days after the injury, you need to take antithrombotic drugs.
In case of dislocations, a splint is applied and worn for at least two weeks. With a moderate degree of injury, after 2 weeks, the process of rehabilitation in the diseased limb begins. These days, they move on to performing special exercises. This speeds up the recovery process in the wrist joint. It is important that the affected ligamentsdo not strain.
Physiotherapy
The following procedures are most often prescribed:
- phono and electrophoresis;
- paraffin and ozokerite treatment;
- UHF treatment;
- laser and magnetotherapy;
- balneotherapy.
Physiotherapy eliminates the symptoms of stretching, restores the motor functions of the hand. At the same time, blood flow normalizes faster, spasms of the muscles of the wrist joint go away, tissues are better saturated with oxygen, and metabolism is restored.
Rehabilitation exercises

Exercise will restore the mobility of the fingers. Among them:
- piano finger movements;
- circular rotation with a brush;
- hand movements to the sides;
- to improve fine motor skills, picking up small objects from the surface (matches, beads, buttons) is shown;
- rolling the ball on the table with your palm.
The load increases gradually. It is better to exercise under the supervision of a specialist.
You can combine exercise therapy with massage. It is even better to rub a healing ointment during the massage to enhance the therapeutic effect.
Massage will contribute to the fastest rehabilitation. With the right approach, joint mobility is fully restored.
Surgical treatment
It is performed with a complete rupture of the ligaments. During the operation, the damaged tissue is sutured, and its functionality is fully restored. Then a seam is applied, and the arm is fixed with plaster. After removing it alsoprescribe local treatment with ointments and physiotherapy.
If there is a threat of secondary infection, antibiotic therapy is prescribed for up to 10 days.
What are the forecasts
With timely first aid, adequate treatment and compliance with medical prescriptions, the healing period is significantly reduced, and the functioning of the hand can be fully restored. There will be no complications in this case.
When can I give my arm a full load?
Loads can be given only when the hand is completely healed. Otherwise, the situation will only get worse.
So, loading is possible if:
- if there is no pain in the arm at rest and with a slight load;
- feelings of strength in an injured hand are no different from those in a he althy one;
- there is permission from the attending physician to actively use the brush.
Prevention
Of course, no one is immune from periodic falls, and it is impossible to prevent arm strain. 85% of sprains happen in everyday life. But it is still possible to take some precautions. These include careful and careful handling of the injured hand for the next 6 months after the injury, the use of braces, bandages, taping to protect the wrist during sports training, and the constant strengthening of the muscles of the wrist with exercises.
Before any physical activity, the ligaments and muscles of the hand must be kneaded and warmed up with a warm-up. You should also avoid gaining weight and eat right.