- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
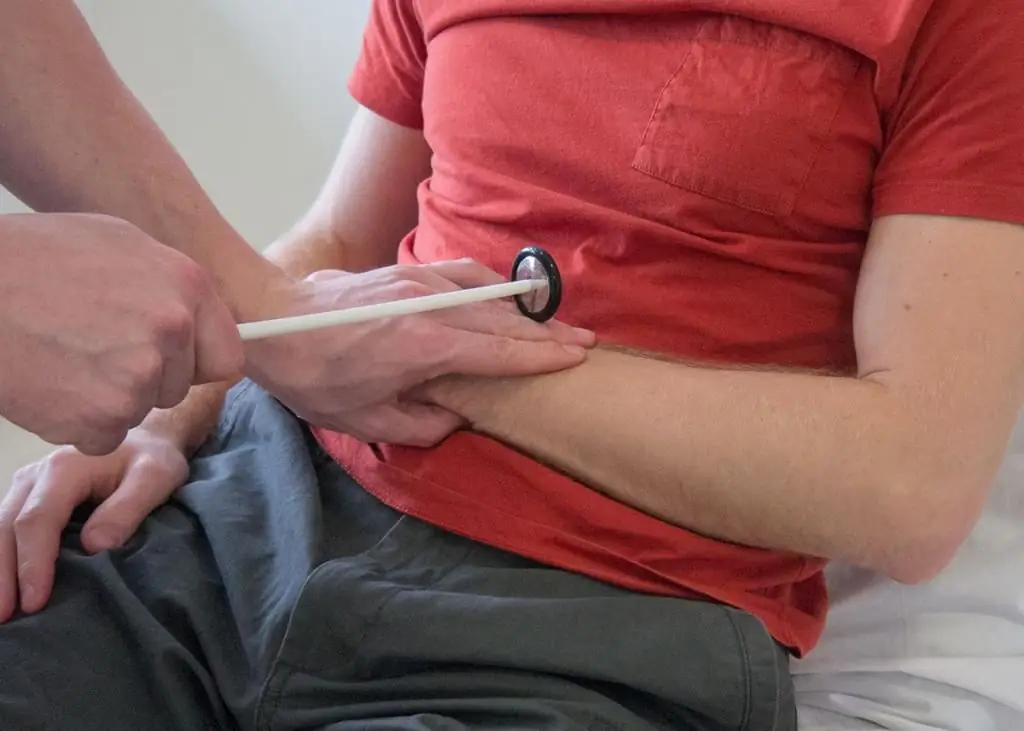
Perhaps, one of the most famous reflexes for all people is the metacarpopular-radial reflex, also called carporadial. It can be summoned by hitting the ray sprout with a special hammer. And the carporadial reflex manifests itself in flexion of the elbow joint, as well as pronation (turning inwards) of the fingers.
General information
Start with a definition. The carporadial reflex is deep. What does it mean? Deep reflexes are called involuntary muscle contractions, acting as a response to a stimulus.
How does this process happen? Muscles involuntarily contract, tendons stretch at this moment. Often, this type of reaction is determined by a short, jerky strike at the point where the tendons attach to the muscles.
It is very important that the patient is relaxed. You need to get rid of stiffness, tension. Muscle tissue should be completely relaxed. Otherwise, it will be simply impossible to determine the degree and presence of any reflex (carporadial, all the more so). Why?Because at the moment of tension, the muscles are stretched. Because of this, reflexes either disappear or become inaccurate.
How is a reflex determined?
To do this, you need a special device - a neurological hammer. With its help, an initial examination is carried out for the presence of disorders and reflexes.
A hammer designed for percussion (percussion) is indispensable for a neurologist. Of course, it differs radically from the usual. This is a special device for the primary detection of neurological disorders. Hammers are made exclusively of metal, equipped with rubber pads, and also with a brush and a needle to test the sensitivity of certain parts of the body.
After the test, this device determines the depth of the carporadial reflex. The following grades exist:
- 0 points. The reflex is completely absent.
- 1 point. The reaction is very low.
- 2 points. There is a reaction, and it is normal.
- 3 points. There is a very lively reaction, with normal severity.
- 4 points. The reaction is maximally increased.
Of course, the degree of expression may vary. Interestingly, tendon reflexes are much more pronounced (and easier to elicit) in the lower extremities than in the case of the hands.
The manifestation of the reflex
Now we should discuss this topic. The carporadial reflex is induced by striking the styloid process of the radius. The correct response to thisaction - flexion of the limb in the elbow joint, as well as pronation and flexion of the fingers.
The most important thing in examining the reflex is to bend the limb at a slight obtuse angle. Also, the patient should hold the hand on weight with his free hand. Middle position - between supination and pronation.
Reflex arc
This is the name given in medicine to the path that nerve impulses take during the implementation of a reflex. In this case, it looks like this:
- Pronators (mm. pronatores).
- Superficial flexor (flexor digitorum).
- The brachio-radialis and biceps.
- Media nerve (nn. Medianus).
- Radial nerve (radialis).
- Musculocutaneous nerve (musculo-cutaneus).
- Cervical segments of the spinal cord. V, VI, VII and VIII are involved.
This is the path of the nerve impulse at the moment of manifestation of the carporadial reflex.
Role of the spinal cord
He is directly involved in the implementation of the tendon reflex. In the reflex arc, the cervical segments of the spinal cord are the end point of nerve impulse transmission.
It is interesting that almost all of them have collaterals - branches. They are sensitive and directly contact with peripheral motor neurons. Those, in turn, are located in the anterior horns.
Collaterals not only reach motor neurons, they also penetrate into its neighboring segments. As a result, spinal-spinal intersegmentalconnections that provide irradiation of excitation. It, as you might guess, enters the spinal cord after the receptors of superficial and deep sensitivity located on the periphery are irritated.
This is what explains the widespread motor-reflex reaction, which is a response to local irritation.

Features of the reaction
The carporadial reflex is carried out by hitting with a hammer on a very specific part of the arm - on the process of the beam. There is another similar type, and this is the flexion-elbow reaction. You can call it by hitting the area of \u200b\u200bthe phalanx of the thumb. It must be placed on the elbow and pressed on the area where the tendon of the 2-head muscle is localized.
At this moment, the patient's arm should be bent, and the forearm should be relaxed, always lying on the surface of the thigh. Visually, reflex tests may seem similar, but in this case, the reaction is only flexion of the arm at the elbow joint.
Hyperreflexia
Within the framework of the topic under discussion, it would be appropriate to study violations. And you can start with a story about an increased tendon reflex.
This is also called hyperreflexia. What is the reason for this violation? In fact, it lies in the increased reflex activity of the segmental apparatus. It, as mentioned earlier, includes the brain stem and spinal cord.
Usually this pathology indicates that a person hasany disease. The most common causes of hyperreflexia include the following conditions:
- Viral transverse myelitis.
- Spinal cord lesions.
- Autonomic disorders.
- Machado-Joseph Diseases.
- Saint Louis encephalitis virus.
- Spinal infarction.
- Hepatic encephalopathy.
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
- Eclampsia.
- Preeclampsia.
- Insomnia.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- AIDS-dementia syndrome.
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Also, hyperreflexia can develop as a result of a bite from a Latrodectus ("Black Widow") spider, due to psychostimulant poisoning, or as a result of the influence of tetanotoxin.

Hyporeflexia
This phenomenon also needs to be addressed. Above we talked about an increased tendon reflex, now it’s worth discussing cases when a person’s reactions are slowed down.
What are the reasons? A decrease in tendon reflexes occurs due to damage to peripheral neurons. But not always. Hyporeflexia is observed in such cases:
- As a variant of the norm. Some he althy people have weakened deep reflexes, but this does not affect their he alth in any way.
- Relaxation delay. Quite a rare case. Pathology is characteristic of hypothyroidism. If it is observed in a patient, it is possible that he has impaired thyroid function.
- Spinal shock. Quite a common cause of areflexia. Observedin the early stages of spinal cord injury. The cause is usually a vascular lesion, trauma, or tumor.
- Stroke in the acute stage. In this case, hyporeflexia after a while is replaced by hyperreflexia.
- Myopathies.
Some patients also have asymptomatic areflexia. Pathology is combined with the expansion of the pupil and the lack of its reaction to light. Also, medicine knows cases of isolated unilateral loss of one of the reflexes.
Areflexia
This phenomenon deserves special attention. It consists in the absence of tendon reflexes. The reason is a violation of the integrity of the reflex arc. Also, areflexia can occur due to the inhibitory effect exerted by the higher parts of the nervous system. This, in turn, usually provokes either a serious illness or injury.
Absence of reflexes is a valuable diagnostic feature that allows the neurologist to assess how severely the nervous system is affected.
An example should be given. If a person has no reflexes of the lower extremities, but the upper ones are not disturbed in any way, then most likely, his spinal cord is affected in the thoracic or lumbar region.
However, in some cases there is a total absence of reflexes. Then we can talk about the oppression of the central nervous system. For example, during anesthesia and coma, most of the reflex arcs do not react to anything. And the deeper one of these states, the more pronounced the depression of the central nervous system.