- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
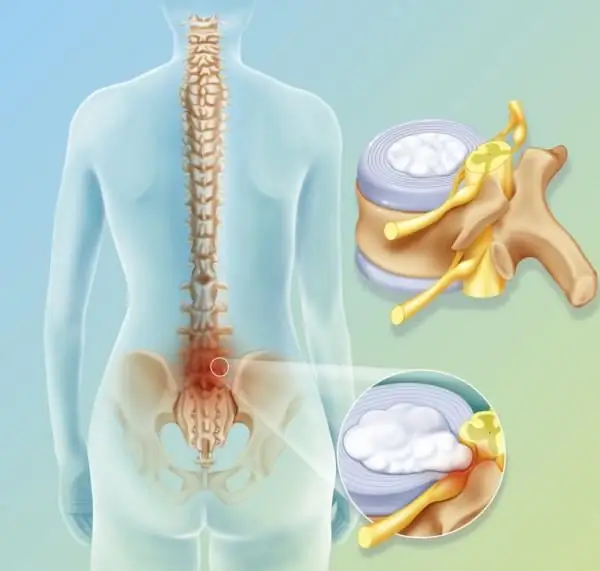
Intervertebral hernia in the lumbar indicates wear or overload of the lower segment of the spinal column. This pathology is one of the most common and dangerous. It is characterized by a protrusion of the intervertebral disc, the task of which is to distribute pressure on the vertebrae at the slightest load.
Features of the disease
Hernia in the lower back most often occurs between the fourth and fifth vertebrae, or between the first sacral and extreme lumbar. Pain in the intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine, which radiate to the leg and prevent full-fledged motor activity, is a characteristic feature of the disease. Against the background of a lumbar hernia, protrusion of the intervertebral discs in other parts of the spine often occurs, which contributes to the blurring of the clinical picture and the appearance of atypical symptoms.
What can cause a hernia in the lower back
In the sacral and lumbar region, the disease is more commondevelops as a result of the progression of osteochondrosis - a complex dystrophic change in articular cartilage. The risk group is predominantly people over 60 years of age, but despite this, the disease can also occur in people at a young age. Among the factors predisposing to the development of a herniated lumbar disc, it is worth noting:
- traffic injuries, falls from heights;
- excessive exercise (work-related);
- constantly carrying heavy weights;
- metabolic problems;
- sedentary work and a sedentary lifestyle;
- deformation (curvature) of the spinal column;
- overweight;
- congenital anomalies;
- benign and malignant tumors.
Recent infectious and inflammatory diseases, alcohol abuse, and smoking can play a negative role in the occurrence of a hernia.
How pathology manifests
Symptoms of a lumbar disc herniation at an early stage can be hidden. As the formation and duration of the disease increase, the severity of its manifestations increases. In this case, the main symptom of a hernia is pain of various kinds. Symptoms also include tingling and heaviness in the limbs, numbness of the toes after sitting for a long time.
At first, the symptoms of a lumbar disc herniation do not cause significant discomfort to the patient. Unpleasantsensations, localized in the lumbosacral region, are unstable, occur periodically. Most often, the pain intensifies during movement, with bending over, sharp turns of the torso and lifting weights. At the same time, pain is clearly felt in the lower back, that is, exclusively in the affected segment of the spine.
When the protrusion of the disc becomes larger, the nature of the pain syndrome changes:
- sudden shootings in the lower back;
- pain radiates to the pelvis, thigh, lower leg and even foot, as a result of which the patient begins to limp, and every movement is difficult;
- when coughing or sneezing, the lower back starts to hurt even more;
- possibly visually noticeable curvature of the spine;
- swelling in the sacro-lumbar segment;
- development of hypertonicity of the muscles of the back and abdomen;
- limited mobility.
It is not difficult to recognize a herniated lumbar disc by clinical manifestations. However, to make a diagnosis, as well as determine the exact location and size of the protrusion, a comprehensive diagnosis (MRI, CT, radiography) will be required.
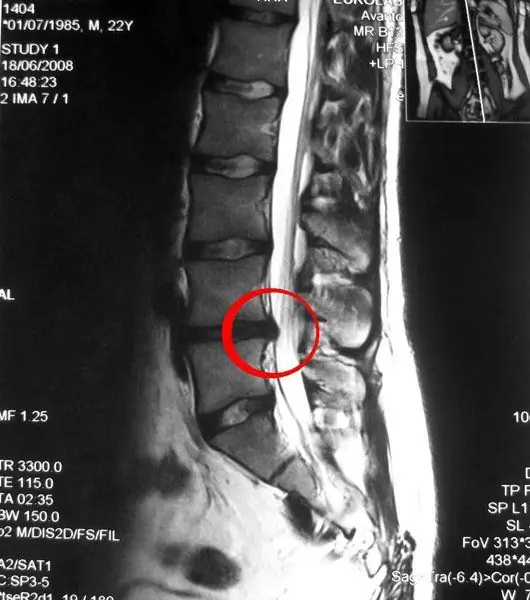
What pathology can lead to
Without proper treatment, a hernia can lead to disability. The fact that the disease is developing may be indicated by the symptoms of sciatica. It is characterized by inflammation of the nerve fibers, which cause severe shooting pain.
An even more dangerous consequence of a herniated disclumbar region is considered paralysis of the legs. Immobility of the lower body is possible due to the neglect of the pathology or its belated diagnosis. The result of a progressive disease is disability and the inability of the patient to live a full life. A bulging intervertebral disc can cause pelvic dysfunction, loss of the ability to control urination and defecation. Due to the compression of the nerve processes, the sensitivity of the genital organs is lost, which leads to a number of problems in the reproductive system.
Basic treatments
With intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine, the patient can be helped conservatively or surgically. As a rule, treatment begins with the use of non-radical methods. It is important to understand that it is possible to achieve a complete cure for the disease only with the help of surgical intervention. In some cases, conservative therapy helps to stop the development of the disease and improve the quality of life of the patient. The average course of treatment is 3-4 months. During this period, it is possible to stop the pain syndrome in case of an acute manifestation of a hernia and prevent its increase in size.

An individual program is created for each patient, including the following components:
- physiotherapy and massage;
- drug pain relief.
If conservative therapy does not allow to observe positive dynamics or the patient's condition is rapidly deteriorating, in some casesthe intervention of surgeons becomes appropriate, despite the risks inherent in the radical treatment of the intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine. Without surgery, it is impossible to get rid of the cauda equina syndrome, cure a pinched nerve and restore partially lost musculoskeletal functions. Thanks to surgery, pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots is removed, which allows the patient to feel much better.
Therapeutic gymnastics
Exercises for intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine is an integral part of both conservative treatment and the postoperative rehabilitation period. Physical education demonstrates the maximum therapeutic effect when combined with taking medications. All exercises that are performed to treat a hernia are based on the principle of stretching the spinal column, extension and flexion of the back. The gymnastic complex is selected individually for each patient after MRI diagnostics.
Training begins with several warm-up exercises (turns, tilts of the head, torso), after which they proceed to the main ones:
- Sit on the floor, put your feet to the buttocks. Press your palms to the floor and try to reach out with your hands as far as possible without unclenching your hips. The patient should feel a stretch in the lower back. You need to repeat the exercise 10-12 times.
- Lie on your back, bend your knees. With outstretched arms, you need to slightly rise and stay in this position for 5-7 seconds, then return to the starting position and repeat the exercise 10 times.
- Roll over on your stomach, rest your chin on the floor, stretch your arms at the seams, palms up. The task of the patient in this exercise with an intervertebral hernia of the lumbar is to maximize the torso and arch back. It is important that the hands are raised up. In this position, you need to freeze for a couple of seconds and return to the starting position.
- Take a knee-elbow position, alternately stretch the arm and opposite leg forward, fixing the position for 10 seconds. For example, extend the right arm and left leg, freeze in this position for a while, return to the starting position and put forward the left arm and right leg.
If the patient's he alth improves, he may be allowed to include twisting and bending exercises in the therapeutic-gymnastic complex. You can train at home, since such activities do not require the use of sports equipment, special devices, equipment.
In addition to standard physical education, yoga, swimming, Pilates are very effective for lumbar hernia. At the same time, you need to understand that improper exercise can bring harm instead of the expected improvement. At the beginning of the treatment of intervertebral hernia of the lumbar without surgery, it is advisable to exercise under the supervision of a physiotherapist. After the patient has mastered the sequence and technique of performing the exercises, you can move on to home workouts.

Drugs for lumbar hernia to relieve inflammation
Medicinalmeans can reduce the intensity of manifestations, relieve inflammation and swelling. In the treatment of a bulging intervertebral disc, use:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that help with mild to moderate pain. In diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such drugs are not prescribed. These include Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Nimesil, Aspirin, Celebrex, Diclofenac. With respect to the circulatory system, they have practically no side effects, can be used before or after surgery.
- Hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs. Unlike the previous ones, they are applied for a limited period (5-7 days). For intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine, Methylprednisolone, Decadron are used, which relieve swelling and inflammation.
- Muscle relaxants. Indicated for patients with spasms of paravertebral muscles (Valium, Mydocalm, Sirdalud).
Analgesic (systemic and local) drugs
To block pain receptors, not only painkillers such as Analgin, Paracetamol, Tylenol, but also antidepressants are used. The latter stimulate the production of natural painkillers in the body - endorphins. At an advanced stage of the disease, when the patient suffers from severe pain, opiates can be prescribed - analgesics based on narcotic components (Morphine, Codeine, Tramadol), which, if used uncontrollably, are addictive and cause serious side effects.

Many remedies for pain relief and inflammation in case of intervertebral hernia of the lumbosacral region are made on the basis of bee or snake venom (Apizartron, Viprosal, Virapin). As a local external anesthesia for this disease, you can use Diclofenac, Movalis, Ketoprofen, Phenylbutazone or combined ointments and gel-chondroprotectors (Dolobene, Teraflex, Deep Relief).
Surgery
Radical treatment of intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine is justified and expedient only in severe advanced cases. Regardless of the method of access to the affected disc, the essence of the intervention is as follows: an incision is made through which the surgeon removes the annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus partially or completely (in this case, the subsequent installation of an intervertebral disc implant is supposed).
Laser removal
This method of lumbar disc herniation is one of the most effective and expensive. During the operation, anesthesia is not required, since the specialist does not perform a tissue incision. This minimally invasive procedure can be performed using one of the following methods:
- Reconstruction - means weak radiation, provoking heating of the intervertebral cartilage. Usually multiple treatments are required.
- Vaporization - evaporation of a portion of the intervertebral disc. The laser beam destroys the protruding mass.
Electric impulses
In addition to operations to remove the intervertebral hernia of the lumbar,surgical treatment involves the use of other, more modern and innovative techniques. One of them, which has proven itself positively, is spinal cord stimulation. The principle of such intervention is as follows. Stimulating electrodes are implanted in the sacro-lumbar region of the patient, and an electric pulse generator is inserted into the buttocks or abdomen.
The device is controlled by special devices and connecting wires. The product stimulates the work of the spinal cord, peripheral nerve endings and cerebral hemispheres, thereby eliminating pain. Thus, chronic malaise, characteristic of the intervertebral hernia of the lumbar region, is relieved by the pulsating action of electrical signals.
Rehabilitation after surgery
After surgery, be it laser removal or total discectomy, it is important to strictly follow all the instructions of the attending physician, which is guaranteed to minimize the risk of complications and recurrence of the disease.
After removal of the intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine, patients are prescribed to wear a special supporting corset. In addition, it is strictly prohibited:
- weight lifting;
- physical activity;
- hypothermia and overheating.
For a speedy recovery, it is important to choose a comfortable orthopedic mattress and lie only in those positionswhich are recommended by the doctor. For example, you can’t sleep half-sitting. Caution should be taken when climbing stairs - you need to walk along them slowly and unhurriedly, without sudden movements. Also, in no case should you wear tight clothing and remove a bandage or supportive corset without the permission of a doctor.






