- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
This is a condition in which there is a curvature of the ridge to the side, with the defect occurring from birth in 1 in 10,000 newborns, and much less frequently than the acquired form of the disease. Congenital scoliosis in the ICD-10 is listed under the code M41.

Reasons
There is no hereditary predisposition, and the causes of congenital scoliosis in infants are violations in the formation of the spinal column at the fetal stage. In total, there are three main types of anomalies that begin to develop even in the womb:
- Mild form, in which there is a slight deformation of the structure of one vertebra or a small group (2-3). It most often occurs in the chest area.
- The average form of congenital scoliosis of the thoracic spine. In this case, some of the vertebrae lose their mobility, as a result of which large immovable sections are formed from several bone formations. In this case, inactive areas begin to shift sideways.
- In severe form, the vertebrae and discs begin togrow together. This is the most dangerous type, as it can lead to displacement and deformation of internal organs. Defects of all three types develop in the first weeks of pregnancy.
The main reasons are factors such as taking contraindicated drugs during pregnancy, drinking alcohol, smoking and other forms of intoxication, as well as radiation exposure. In addition to external harmful influence, a lack of vitamin D also plays a role. It is impossible to completely cure congenital scoliosis in children.

Symptoms
For congenital scoliosis of the spine is not characterized by pronounced pain. Symptoms of it at an early age can be detected by parents and pediatricians with careful examinations. The main signs of congenital scoliosis visible on examination include the following pathological changes:
- shoulders are uneven (not at the same level);
- with an external assessment of the position of the body, certain curvatures can be detected;
- there is asymmetry in the location of the hips, moreover, there may be a bulge in the thigh area on one side;
- a visual distortion is noted on the waistline.
Other signs
In the event that nerve endings are affected during scoliosis, partial numbness in the limbs, impaired coordination of movement can be diagnosed. As medical practice shows, birth injuries can lead to right-sided congenital scoliosis. This type of spinal deformity is characterized by the followingsymptoms:
- the asymmetry described above in the position of the shoulder blades, shoulders;
- respiratory dysfunction (deformation of the chest with right-sided scoliosis affects the respiratory system);
- fixation of intense pain in the lumbar region.
Physical diagnosis
The common way to detect scoliosis is the forward bend test. At the same time, the doctor examines the spinal column and finds a difference in the shape of the ribs on each side. The deformation of the spine is more noticeable in this pose.
Next, the doctor checks the level of the hips, shoulders and the position of the head in relation to each other. The movements of the ridge in all directions are also checked.
To determine pathologies with the spinal cord and nerve roots, the doctor checks muscle strength and tendon reflexes. Used for congenital or acquired scoliosis.

Instrumental diagnostics
Directly, the forward bend test makes it possible to detect curvature, but does not allow to establish congenital deformities of the vertebrae. For this reason, radial diagnostic methods are carried out.
X-ray
The easiest and most acceptable way to diagnose. He is able to demonstrate the existence of vertebral destruction, as well as to assess the level of curvature of the ridge. Radiography is performed in two projections: anteroposterior and lateral.
If the doctor diagnosed "congenital scoliosis", he refers to an orthopedist for follow-updiagnostics.
Computed tomography
It makes it possible to notice not only the bone tissue of the vertebrae, but also soft tissues - the spinal cord and nerve roots. The advantage of CT is that it provides a layer-by-layer accurate image of the ridge. In addition, the doctor may prescribe a multidimensional computed tomography for the most detailed assessment of the patient's condition.
Ultrasound
Carried out to uncover possible concomitant abnormalities, for example, kidneys or bladder.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
MRI is considered to provide a more accurate assessment of the condition of soft tissues, for this reason it is used to assess abnormalities in the spinal cord. This method is not associated with X-rays, its principle is based on a strong magnetic field, for this reason it is contraindicated in patients with implanted devices (pacemakers, cochlear implants, artificial joints, etc.).
Treatment
Treatment for congenital scoliosis depends on its stage. If the disease is not pronounced, the problem can be solved with the help of conservative treatment, in other cases, surgical intervention is indispensable.
First stage
At the first stage, when the deviation does not exceed 10 degrees, in order to achieve positive dynamics, specialists prescribe treatment, the complex of which includes:
- therapeutic gymnastics;
- physiotherapy treatments;
- sports;
- massage.

Second stage
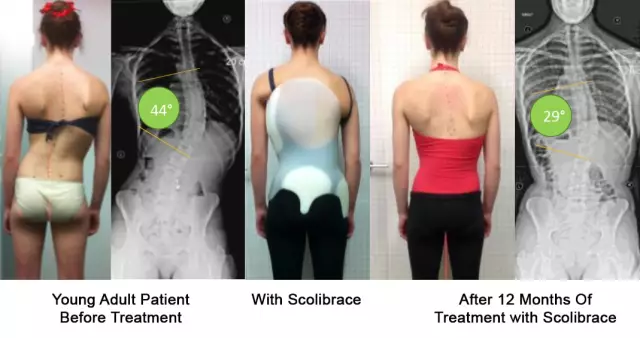
At this stage of development of scoliosis, the radius of curvature does not exceed 25 degrees. With the help of medical procedures and exercises, it is no longer possible to correct the situation. A special supporting corset is used as the main method of treatment.

Third stage
Treatable even more difficult, as the deviation can reach 50 degrees. In this case, in addition to the usual supporting corset, a special corrective device with a stretching effect can be additionally used. In addition, the doctor prescribes physiotherapy procedures. Therapeutic exercises should be carried out only under the supervision of a specialist, all exercises are performed carefully, without sudden movements.
Fourth stage
At the fourth stage of the disease, when the curvature exceeds 50 degrees, all the above methods of treatment will not give a positive result. The only way to correct the situation is through surgery.
Recently, most experts agree that the first stage of congenital scoliosis is the norm and you should not panic. You just need to monitor the development of the disease and prevent its progression.
Surgical treatment is prescribed if conservative methods have failed, the corset and plaster have not been able to correct the situation, or the patient's he alth is in real danger.

Surgical treatment can be carried outin the following ways:
- Hemiapiphysiodesis.
- Removal of hemivertebrae.
- Growing designs.
- Merge.
In the first case, the operation is performed on one side of the deformity, and its essence is to remove areas of growth. The deformation is usually concave on one side and convex on the other. With the help of special implants, the latter is corrected by the surgeon, and the concave part can continue to grow, which will lead to self-correction.
To remedy the situation, you can remove the hemivertebrae. The surgeon eliminates the anomaly, after which the patient will need some time for the lower and higher located vertebrae to grow together.
The postoperative period involves wearing a special corset. Only a specialist sets the duration of recovery. Although the operation is effective, the likelihood of complications such as bleeding and neuralgic disorders is quite high.
Often during surgery, the method of establishing special growing structures is used. Their main advantage is that they gradually lengthen, and this does not prevent the child from growing and developing.
All manipulations are carried out from the rear access. During the operation, rods are used, which are attached to the spine with the help of special screws. Approximately once every 6-8 months, the structure is lengthened. Most often, in addition, the child must wear a corset. Modern technology has significantly improved treatment. Now you do not need to frequently carry out operations by inserting a new rod. Designlengthens itself as the patient grows.
Fusion surgery aims to stop the growth of the spine in a certain area. For the operation to be successful, the surgeon must remove only the back of the vertebra, installing a bone graft in its place, which eventually fuses with the "relatives", forming a single structure.
As the child matures and grows, the spine will no longer change shape, which means that the deformity will no longer progress. It should be borne in mind that the operation is also associated with certain risks. After surgery, the bone block can behave unpredictably. This process leads to a curvature of the spine in another department.

Surgical intervention most often has a positive effect on the further condition of the patient. If no complications have arisen, the patient can get out of bed already 2-3 weeks after the operation. In the normal course of the postoperative period, the patient is in the hospital for a week, after which he can continue to recover at home.
Typically, physical activity restriction is 1 year. During this period, you need to move carefully, do not lift weights. The lower the load on the spine, the faster the recovery will be. At first, the patient wears a corset. For 1-2 years, you need to be constantly monitored by a doctor, undergo an X-ray examination.