- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
In the article we will consider what is the innervation of the teeth.
Innervation is a biological process of supplying different organs and tissues of a person with nerves. Thanks to this, a connection arises between them and the main share of the nervous system, which is central. This supply is efferent, otherwise it is also called motor, as well as afferent. Any information about the organs, their general condition and various processes occurring in them is perceived by receptors, and then sent directly to the central nervous system via a sensitive fiber. Almost immediately, the system sends response signals through the nerve endings, which control the work of internal organs. We will discuss the innervation of the teeth in more detail below.
Concept
Innervation (from the Latin "in", which means "in" or"inside", and "nervus", which, in turn, translates as "nerves"). So, under this term in medicine, as well as in the field of dentistry, it is customary to understand the supply of tissues and organs with nerves, due to which their connection with the central nervous system is ensured.
Thus, the innervation of the teeth, as well as other organs, is required to achieve regulation of their CNS activity. This is a very important process in the framework of human life, affecting the work of tissues according to emerging needs. In more detail about the innervation, and in addition, the dental blood supply will be discussed later.
Lower jaw
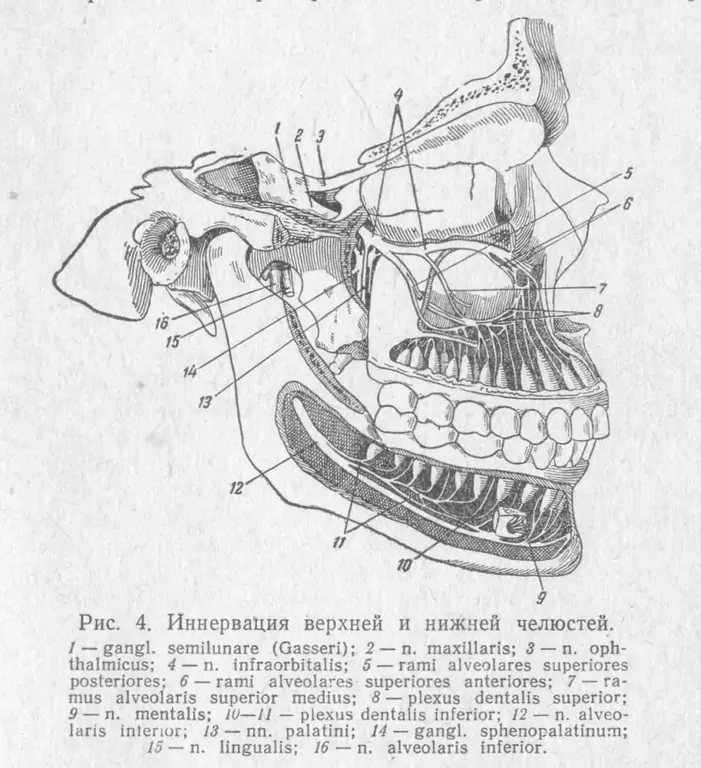
There are several main nerves that branch out from the mandibular sensory ending. I must say that in accordance with them, the innervation of the lower teeth occurs. Thus, we are talking about the buccal, lingual and alveolar element. All of them perform certain functions, and they are located in different parts of the human body. Next, consider each of them separately.
Innervation of the mandibular incisors and buccal nerve
This element is considered one of the most powerful in its group. Among other things, he is the only sensitive one. It usually runs from the head of the pterygoid lateral muscle to the mucous membrane and skin of the cheeks of a person. Then it follows along the buccal muscle. This nerve supplies (innervates) the skin around the corner of the mouth. It also connects to the front elements at the fork.

What else suggestsinnervation of teeth?
Lingual nerve
This is a more sensitive end in nature, which connects to the mandibular element in the region of the foramen ovale. The lingual nerve runs between the pterygoid muscle fibers, next to the pterygoid medial tissue, or rather in its upper part. The so-called drum string is attached to the lingual structure, which is a thin branch, which in Latin sounds like “chorda tympani”.
The drum string is a parasympathetic root, consisting of a thin fiber. This element, which is a continuation of the intermediate nerves, is intended to transmit taste irritation from the tongue receptors. This, in turn, provokes salivation from several glands at once (sublingual and submandibular). The drum string usually consists of two types of fibers.
Alveolar nerve
This element passes into the mandibular foramen located in the inner surface of the branch, or rather, directly in its middle part. This alveolar element is included in the lower jaw. This is a very important component of the nervous system, since it is designed to innervate the dentition located throughout the lower jaw. The nerve itself lies below the dental roots.
Innervation of the upper jaw
In the process of innervation of the teeth of the upper jaw, the alveolar and palatine branches of the maxillary nerve located here play an important role. It is worth noting that they are the source of sensitivity. Below are the main branches in the bones of the upper jaw that form the dental plexus. Consider now the main structures of the innervation of the upper teeth:
- Greater palatal element. He is directly involved in the innervation of the gums from the palate (in this regard, this branch is called so). Innervation lies in the region of such incisors as premolars, molars and canines.
- Nasal fabric. Translated from the Latin "nasopalatinus" means the nerve that connects the corresponding area. It is located closer to the region of the respiratory organ and is directly involved in the processes of innervation from the palate. True, in this case, directly in the region of the incisors and canines. The innervation of the teeth of the upper jaw is of interest to many patients.
- Superior posterior alveolar. It is formed from the dental plexus, in the formation of which nerve receptor fibers take part. This nerve can simultaneously innervate the vestibular surface of the gum tissue in the region of the molars and the teeth themselves.
- Upper middle alveolar element. This branch is located above the molar in the upper region of the human jaw. She, as a rule, takes part in the process of innervation of the premolars and the first molar, and in addition, the vestibular side of the gums in the area of the above incisors.
- Upper anterior alveolar element. It is located in the anterior region of the upper jaw. At the same time, he takes part in the innervation of the incisors and canines. Among other things, this branch innervates the gum tissue in the area of these teeth.
It is worth noting thatthe alveolar upper nerves, or rather the anterior and middle ones, branch off approximately in the region of the bottom of the orbit, they also detach from the maxillary elements. Their path runs through the maxillary sinus to the incisors, which these branches innervate.

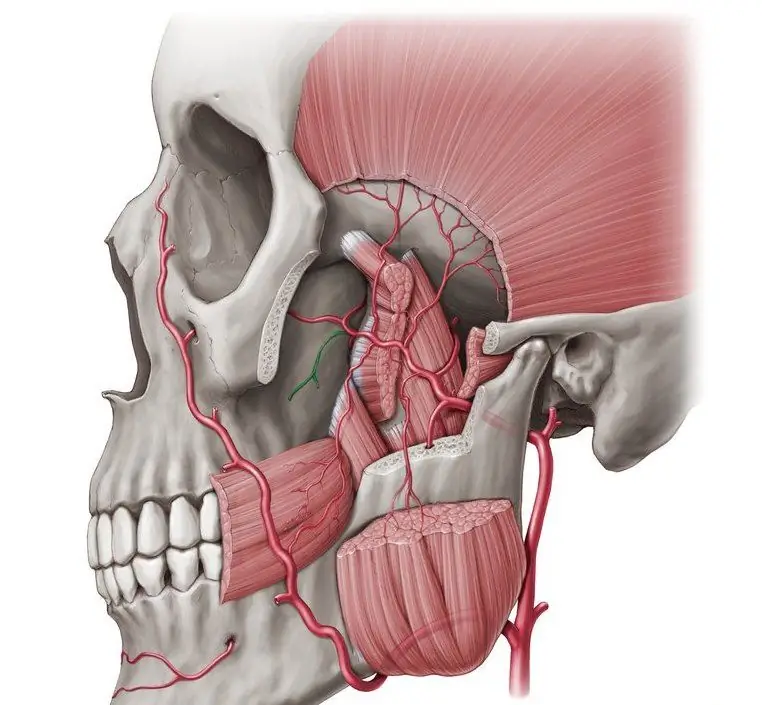
Blood supply and innervation of teeth
In addition to innervation, the incisors require a full supply of blood, along with it they receive all the substances they need. This process, as a rule, is carried out by the branches of the maxillary artery. The corresponding canals approach the posterior elements, and, of course, their anterior alveolar counterparts approach the anterior elements. All this has to do with the teeth in the upper jaw. In certain areas, the alveolar arteries can branch into several of the following types of branches:
- Interalveolar (that is, to the incisor alveolus and gums).
- Gingival (respectively, to gum tissues).
- And the teeth - directly to the incisors.
The veins accompanying the blood arteries are involved in the blood outflow from the teeth. It is worth emphasizing that the pterygoid venous plexus is exactly the place where the nutrient composition flows.
why is the innervation of the teeth of the upper and lower jaws minimized?
Features of the anesthesia procedure
Anesthesia is one of the ways to minimize nerve sensitivity, which is based on blocking the patient's consciousness due to deep inhibition of nerve transmission and synapse of the cerebral cortex using variousdrugs.

Thanks to new developments in the field of anesthesiology, modern dental clinics have stopped the use of anesthesia associated with the inhalation of a specialized gas. From now on, a new licensed technique called "sedation" is used. This technology involves the introduction into the human body of drugs that introduce the patient into a controlled short-term medical sleep. The cost of a new sedative technique aimed at loss of sensitivity within twenty minutes is three thousand seven hundred rubles. From the way medicinal substances are currently introduced into the body, several of the following types of sedation are distinguished: inhalation, oral and intravenous.
In the field of dentistry, intravenous superficial technology is often used. Since with a shallow form of minimizing nervous sensitivity, all functions of the body carry out normal activity, but the person is in a light sleep.
Indications in outpatient dentistry
The use of modern pain relief technologies in the field of dental treatment is advisable in the following cases:
- Having an allergy to local anesthetic medications.
- The patient has a strong fear of any pain, and dental manipulation in particular.
Given the innovations in the field of practical dentistry, it is also worth adding the great desire of many patients to undergo therapy under general anesthesia.
Withinmaking an informed decision on the use of such technologies for the innervation of the teeth of the lower jaw or upper jaw in modern clinics, each patient is necessarily informed about all possible complications and dangers of any type of anesthesia. But you should not be afraid, because in good dental clinics, operations for therapy, prosthetics, removal and implantation of teeth using general anesthesia are carried out by licensed doctors, anesthesiologists and resuscitators with more than ten years of experience.

Contraindications for temporary minimization of tooth and jaw innervation in patients
All contraindications to the use of local anesthetic can be combined into the following three points:
- Hypersensitivity of the immune system to local anesthetics. At the same time, the doctor selects the pain medication that is most suitable for the planned intervention (taking into account the depth, duration and nature).
- Failure of the patient's metabolic system (purification and withdrawal). Here, the characteristics of the organism of patients, their general somatic condition, along with the presence of contraindications are taken into account.
- Age limit. In this case, the dosing of painkillers is taken into account, the criteria for choosing local drugs are taken into account.
Reviews
Thus, the innervation of the teeth of the upper and lower jaws suggests their strong sensitivity. Therefore, when there is a need for serious and deep treatment affectingnerve tissue, pain relief is indispensable.
In the comments and various discussions on the forums, people share with each other the modern possibilities of dental therapy. It is noted that certain methods used to achieve a temporary loss of sensitivity in the region of the upper and lower jaw are very effective and safe.

In fact, in dentistry, pain has long been a major problem in dental office visits around the world. It is precisely because of the fear of pain that many people prefer to avoid visiting the dentist, mistakenly believing that the therapy will be extremely unpleasant and painful.
But as experienced patients assure, modern techniques help to minimize these fears. According to the stories of people who regularly undergo dental treatment, the most popular technologies today are injection and application anesthesia, as well as general anesthesia.
We looked at the blood supply and innervation of the teeth.






