- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-06-01 06:18.
Hepatitis C is a disease of the liver. It occurs because of a virus that can only live in the human body. The disease is also called the "gentle killer", because it has the ability to disguise itself as other ailments and at the same time poses a danger to life. All people should learn about the clinic, diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C, because no one is immune from infection.
Discovery of hepatitis C and study of the pathogen
Experts began to think about the existence of "neither A nor B" hepatitis back in the 70s of the last century. However, it was not possible to confirm the conjectures. Virological methods at that time did not allow to identify the pathogen, although the search for the etiological agent was carried out. Only a few years later, the attempts were crowned with success. A step forward in the study of hepatitis C has been made thanks to new molecular biological methods.
The study of the causative agent of the disease is associated with the names of such people as M. Houghton and Q. Choo. The first researcher inA group of scientists in 1988 sequenced the genome of HCV, a small RNA-containing virus. A year later, the second scientist, together with his colleagues, successfully completed the cloning of HCV RNA. Were obtained immunoreactive oligopeptides. They became the basis of diagnostic preparations designed to detect antibodies to the virus.
Further study of the pathogen and causes of hepatitis C allowed specialists to identify 6 genetically different groups (genotypes) of the virus: 1a, 1b, 2a, 2b, 3a and 4. More than 100 subtypes of the pathogen were also found. Regarding genotypes, it is worth noting that researchers have identified some features in the geographical distribution. For example, genotype 1b is most often registered in European countries, 1a in North America, and 1b in Russia.

World He alth Organization on Hepatitis
The World He alth Organization reports that the Hepatitis C clinic is known worldwide. This disease is registered everywhere. According to statistics, on a global scale, approximately 130-150 million people are infected with the hepatitis C virus. The most affected regions of our planet are West and North Africa, East and Central Asia. The highest prevalence of the disease in these places is due to the use of unsafe methods for various medical procedures, injections. It is also worth noting that the number of people with the hepatitis C virus is actually on the rise, even though effective treatments are available.
According to WHO, hepatitis C, as well as other viralHepatitis is a very serious public he alth threat on an international scale. Previously, these diseases were not given due attention. Today, it is necessary to take any measures to reduce the number of infected people and save human lives.
In 2016, the World He alth Organization released a global he alth sector strategy on viral hepatitis. This document presents the targets to be achieved by 2030:
- reduce 90% incidence (number of new hepatitis C virus infections);
- reduce mortality by 65%;
- achieve blood safety (verify 100% of donated blood using quality assured tests);
- improve the diagnosis of viral hepatitis;
- improve the quality of care.
Etiology and epidemiology
The hepatitis C clinic is the result of the existence of HCV in the human body. It is a small spherical virus. Its dimensions in diameter are 50 nm. The genus of the pathogen is Hepacivirus, and the family is Flaviviridae. The structure of a viral particle includes a single-stranded linear RNA, a nucleocapsid, and a protein-lipid shell. A characteristic feature of the pathogen genome is its mutational variability associated with the replacement of individual nucleotides. The constant renewal of the antigenic structure leads to the simultaneous existence of multiple variants of the virus. This explains the fact of the long, and sometimes even lifelong survival of HCV. The human immune system simply does not have time to respond to antigenic variants.exciter.
Sources of the hepatitis C virus are people who have an acute or chronic stage of the disease. How is hepatitis C transmitted from a person? The least important are the natural ways of spreading the pathogen. The probability of infection through sexual contact, at home, at the birth of a child from an infected woman is extremely low.
Answering the question of how hepatitis C is transmitted from a person, it is worth noting that the parietal mechanism of transmission plays the greatest role. Infection often occurs at the time of medical and non-medical manipulations. The first group includes invasive medical and diagnostic procedures, surgical interventions, transfusions of blood and its components. Among the non-medical manipulations that have a risk of infection with the hepatitis C virus, include piercing, tattooing, injection drug addiction. By the way, today drug addicts are one of the most epidemiologically significant and numerous risk groups for HCV infection. According to the World He alth Organization, about 67% of people who inject drugs have hepatitis C.

Hepatitis C Clinic
After the virus enters the body, the incubation period begins. In duration, it can be from 2 to 26 weeks (average - from 6 to 8 weeks). The course of hepatitis C includes 2 stages - acute (AHC) and chronic (CHC). The acute stage in a large number of patients proceeds without any suspicious symptoms. Only in 10-20% of cases does the hepatitis C clinic appear.have the following features:
- After the incubation period comes the prodromal period. The first signs of hepatitis C in women and men are malaise, weakness. Dyspeptic syndrome is observed, which is characterized by such signs as nausea, loss of appetite.
- The prodromal period is replaced by the peak period. Some people develop moderate jaundice (this symptom of hepatitis C in a woman is clearly visible in the photo), but most often this change is not observed. The anicteric variant of the course remains unrecognized due to the absence of complaints in sick people. Sometimes it occurs under the guise of other diseases of the digestive system. At the same time, the characteristic difference between the anicteric variant of hepatitis C and other ailments is the painful itching on the trunk and legs without the appearance of rashes on the skin.
In 20-25% of people, the clinic of acute hepatitis C disappears, and the disease ends with recovery. In 75-80% of cases, the disease becomes chronic. It includes 2 phases - latent and reactivation. The latent phase begins first. No signs of hepatitis C are observed at this time. The duration of the latent phase can be from 10 to 20 years. During this period, infected people feel he althy. Some of them only complain of a slight heaviness, localized in the region of the right hypochondrium. However, no one attaches special importance to this symptom, since it usually occurs during physical exertion and a violation of the diet.
The reactivation phase of CHC is characterized by an increase in replicativevirus activity. During this period, there is a clinic of chronic hepatitis C - certain symptoms of the disease. These include asthenovegetative syndrome. It combines a number of suspicious signs. Here is a list of them:
- fatigue;
- weakness;
- disability;
- excessive sweating;
- headache;
- sleep disorder;
- emotional instability.
Clinic of chronic hepatitis C in the reactivation phase still includes dyspeptic syndrome. Sick people complain of worsening appetite, a bitter taste in the mouth, nausea, heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium and epigastric region. In the later stages of the disease, pruritus is observed. Some infected people develop extrahepatic symptoms of chronic viral hepatitis: gastritis, pancreatitis, skeletal muscle damage, kidney damage, etc.

HCV natural history and consequences
In 2001, T. Poynard et al. isolated in the natural course of chronic hepatitis C 4 periods:
- The first 10 years from the moment the pathogen enters the human body. The rate of progression of the disease at this time is minimal. The exception is people who become infected over the age of 50.
- Next 15 years (estimated). This period is characterized by a slow and constant progression of the disease.
- The next 10 years. The rate of development of the disease is increasing.
- Last5 year period. It is characterized by high activity of the pathological process. This period leads to the terminal stage of the disease.
In 25-50% of cases, the end of chronic hepatitis C is cirrhosis of the liver. This is a severe disease in which parenchymal tissue is irreversibly replaced by fibrous tissue. HCV cirrhosis can be continuously progressive or slowly progressive with periods of prolonged remission.
In the initial stage of a compensated disease, people may notice a feeling of heaviness and pain in the upper abdomen, flatulence, weight loss, decreased performance, asthenia (fatigue). In about 20% of patients, the initial stage of liver cirrhosis is latent. The disease is usually discovered by specialists by chance during an examination for some other diagnosis or during a preventive examination.
With the progression of the pathological process in the clinic of viral hepatitis C complicated by cirrhosis, asthenic and dyspeptic syndromes become more pronounced. There are nosebleeds, bleeding gums. The following signs are characteristic of the advanced decompensated stage of liver cirrhosis:
- big belly with thin legs and arms ("spider figurine");
- portal hypertension (increased pressure in the portal vein system caused by impaired blood flow in the inferior vena cava, hepatic veins, portal vessels);
- jaundice;
- pronounced manifestations of hemorrhagic syndrome, etc.
Intensifies when entering the terminal stagehepatocellular insufficiency, portal hypertension, hepatic encephalopathy. Patients develop hepatorenal and hemorrhagic syndromes, ascites, bacterial infection joins.
About 5-7% of people with chronic viral hepatitis C develop hepatocarcinoma, a malignant disease of the liver. The main risk factors for cancer development are cirrhosis of the liver, concomitant HBV infection, alcohol abuse, male sex, age over 55 years. The most common clinical signs of this disease include hepatomegaly (an increase in the size of the liver), a palpable tumor, and pain in the upper abdomen. Later, jaundice, dilatation of the superficial abdominal veins, and ascites are added to the clinical picture.
Diagnosis of disease
Hepatitis C is diagnosed using:
- Molecular biological laboratory methods. With the help of them, specialists detect viral RNA, measure the viral load, determine the genetic characteristics of the patient and the virus.
- Immunochemical laboratory methods. They are designed to detect hepatitis C markers - antigens of the virus and antibodies to them.
A rather significant role in the diagnosis of viral hepatitis is played by ultrasound of the abdominal organs. This method allows you to detect changes that cannot be detected by physical examination. Ultrasound provides doctors with information:
- about the increase (decrease) of the liver;
- state of the edge of the body;
- change in parenchyma echogenicity;
- dilation of the splenic and portal veins andetc.
The most important method for diagnosing chronic viral hepatitis is a morphological study of liver biopsy specimens. Based on the results, one can learn about histological changes that occurred even before the onset of clinical symptoms and violations of functional indicators (the degree of activity of the pathological process, the severity of fibrosis are determined, other causes of liver damage are excluded). Specialists obtain material for research by percutaneous puncture biopsy. It is important to carry it out correctly in compliance with standard techniques. The optimal length of the biopsy specimen is 2.5 cm. With a decrease in its length from 3 to 1 cm and a diameter from 1.4 to 1 mm, the risk of obtaining a false conclusion about the degree of histological activity increases to 70%.
Liver biopsy may not be performed in all cases, because this study has contraindications. For this reason, non-invasive methods for assessing liver fibrosis are currently being introduced into the diagnosis. For example, the usefulness of elastometry has been proven. This study is carried out on the apparatus "FibroScan". It allows you to judge the change in the elastic properties of the liver by reflected vibrational impulses, which are subjected to computer analysis. Non-invasiveness is not the only advantage of elastometry. The positive aspects of this method also include:
- convenience and speed of use (it takes about 5 minutes to examine a patient);
- larger estimated volume of liver tissue compared to biopsy (about 100-200 times more);
- Children can be tested.

Treatment of acute hepatitis C
In acute viral hepatitis C, treatment is not prescribed immediately. Therapy is postponed for 8-12 weeks after the onset of the disease. This delay is done for the reason that the human immune system can cope with the virus on its own. If this period passes, and HCV RNA continues to be detected in the blood, then antiviral treatment is started (no later than 12 weeks).
If there is a clinic of acute hepatitis C, standard interferon preparations are used. Monotherapy is quite effective (80-90%). For those who do not know what interferon is, it is an immunostimulatory protein produced in the body in response to a viral infection. The doctor, prescribing treatment to the patient, may give preference to PegIFN. This is a special kind of long-acting interferon. The advantage of PegIFN is that for effective treatment, a smaller frequency of administration is required (compared to standard interferons).
Optimal duration of therapy for acute hepatitis C is 24 weeks. Standard interferons can be used for 24 weeks at 3 million IU every other day or for the first 4 weeks at 5 million IU daily, and for the remaining 20 weeks at 5 million IU every other day. For the use of long-acting interferons, the doses established are as follows:
- for PegIFGα2a - 180 mcg once a week;
- for PegIFGα2b - 1.5 mcg/kg once a week;
- for CePEG-IFNα2b - 1.5 mcg/kg once a week.
WoDuring interferon therapy, the clinic of viral hepatitis C can be supplemented by side effects from the use of drugs. Flu-like syndrome often occurs. In patients, body temperature rises, malaise, sweating, headache occur, appetite worsens, aching joints and muscles begin to be felt. Usually, all these symptoms are observed only at the very beginning of treatment. More rarely, during the period of immunotherapy, mental disorders, dyspeptic syndrome, dermatological reactions are recorded.
To combat side effects, doctors prescribe additional drugs. For example, with influenza-like syndrome, the use of paracetamol or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is indicated. In 10-15% of cases, the doctor considers the issue of reducing the dose of interferon, and in some cases, drug withdrawal may be required.

Chronic hepatitis C treatment
The goal of medical treatment for chronic hepatitis C is to improve the quality of life and increase life expectancy for people with the disease. Therapy is prescribed when virus RNA is detected in the blood serum and histological signs of liver damage. Before starting antiviral treatment, patients must be referred by doctors for a series of examinations. This is necessary in order to exclude concomitant diseases and ensure maximum safety and effectiveness of further therapy.
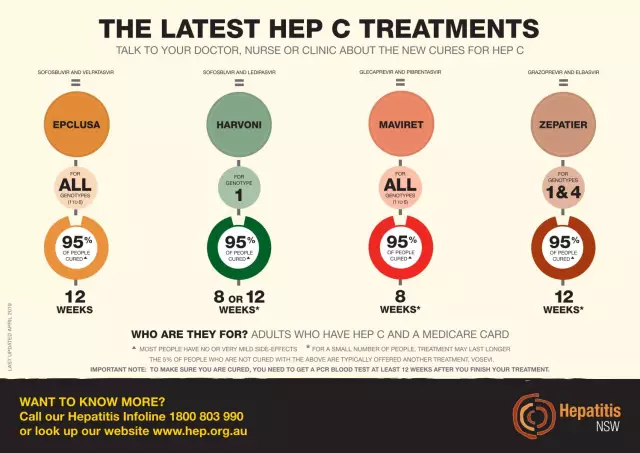
There are several treatment regimens available for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. They can be found below intable.
| Schemes | Drug combination | Comments |
| interferon based | Standard IFNα and ribavirin |
Ribavirin is an antiviral substance. It inhibits the replication of various DNA and RNA viruses. This combination is recommended when no other treatment options are available and there are favorable response predictors. |
| PegIFNα and ribavirin | This regimen is recommended for genotypes other than 1. For genotype 1, it may be used when other regimens are not available and there are favorable predictors of response. | |
| PegIFNα, sofosbuvir and ribavirin |
Sofusbuvir is a nucleotide analogue used in combination with other medicines in the treatment of hepatitis C. Hepatitis C treatment regimen with sofosbuvir and other drugs is suitable for all genotypes. |
|
| PegIFNα, simeprevir and ribavirin |
Simeprevir is an antiviral agent. Drug regimen suitable for genotypes 1, 4. |
|
| PegIFNα, narlaprevir and ribavirin |
Narlaprevir is an antiviral agent, a strong oral inhibitor of the NS3 serine protease of the hepatitis C virus. The scheme is suitable for genotype 1. |
|
| PegIFNα, asunaprevir, daclatasvir, ribavirin |
Asunaprevir - enzyme inhibitorNS3 serine protease of hepatitis C virus. Daclatasvir is an inhibitor of non-structural protein 5A (NS5A), a multifunctional protein that plays an important role in the process of hepatitis C virus replication. The scheme is suitable for genotype 1. |
|
| interferon-free |
For genotype 1:
For genotype 1b: daclatasvir, asunaprevirFor all genotypes: daclatasvir, sofosbuvir (+/- ribavirin) |
|
Additional nuances
All those people who have manifest forms of viral hepatitis are subject to hospitalization. Patients are treated in infectious diseases hospitals. In chronic viral hepatitis (CVH), the indication for hospitalization in the infectious or hepatological department is a clinical and biochemical exacerbation or decompensation at the stage of liver cirrhosis. In the presence of a latent form of the disease, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis.

Therapy for hepatitis C involves more than just drugs. The patient is advised to consider several recommendations:
- It is important to observe the protective mode - more rest, avoid overload. In severe cases of the disease (acute form, exacerbation of chronic hepatitis, decompensated cirrhosis of the liver), bed rest is needed. In a horizontal position, blood supply to the liver improves, reparative processes in thethis body.
- An important element of treatment is stool control, fluid balance. Constipation is unacceptable, because they provoke intestinal autointoxication. In getting rid of this delicate problem, laxatives of plant origin, food sorbitol, lactulose help. Regarding the control of fluid balance, it is worth noting that drinking should be plentiful (2-3 liters per day).
- During treatment, it is important to eat right, make up your diet from such products that do not adversely affect the digestive system, do not disrupt metabolism, do not damage hepatocytes.
- You need to protect the liver from additional stress. Experts advise not to take medications without prescriptions and indications. Patients are also strongly advised to avoid drinking alcoholic beverages in any dose. Ethanol depresses the immune system, affects the liver. With alcohol abuse, fibrosis develops faster, and the risk of cirrhosis increases significantly.
Preventive measures
Hepatitis C cannot be prevented by vaccination because there is no vaccine that can protect against HCV. However, preventive measures have been developed. They are recommended to be observed by medical workers, because sometimes he althy people are infected due to their negligence. Professionals should:
- pay attention to hand hygiene (wash hands thoroughly, debride hands, use gloves);
- properly carry out medical injections, operations, diagnostic invasive procedures, strictly adhere to the universal measuressecurity;
- test donated blood for hepatitis B, C, syphilis, HIV.
The World He alth Organization says action needs to be taken to reduce harm for injecting drug users. Access to sterile injecting equipment and effective addiction treatment needs to be ensured.
Preventive measures include using condoms during sex. The chance of transmitting the hepatitis C virus in this way is extremely small, but still not worth the risk. And it is important to remember that condoms protect against a huge list of sexually transmitted infections.
All of the above measures are primary prevention of hepatitis C. There is also secondary prevention, which is provided for people infected with HVC. For them, the World He alth Organization recommends:
- seek advice from specialists in treatment and care;
- get immunized with vaccines that protect against the development of other viral hepatitis (A and B);
- get regular check-ups for early detection of chronic liver disease.

The clinic, diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C can be called a hot topic. This disease is a very serious problem. It did not cover any particular country, but the whole world. Every year on July 28, World Hepatitis Day is celebrated. On this day, activities are being implemented in all corners of the planet to deepen the understanding of this problem. Informing people is being intensively carried out. By the way, it is very important. Knowledge helps people prevent the onset of a disease or properly deal with an ailment that has arisen.