- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
The term "stomatitis" refers to a number of clinical manifestations indicating the progression of the infectious process in the body. The disease is accompanied by the formation of ulcers and wounds in the oral cavity. In most cases, they are localized on the lips and cheeks. In such situations, the wounds are easy to notice, due to which the treatment is prescribed in a timely manner and recovery is faster. If the child has stomatitis in the throat (a photo of the swollen tissue is presented below), it is more difficult to detect. In addition, the treatment of pathology is associated with some difficulties associated with the localization of wounds. The disease requires an integrated approach, it is possible to achieve recovery in a short time only with strict adherence to all the doctor's recommendations.

Pathogenesis
Behind the external manifestations of the disease, very deep and significant problems are hidden. In a child, stomatitis in the throat can develop under the influence of even the mostminor precipitating factor. This is due to the fact that the mucous membrane lining the oral cavity is a favorable environment for the vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms, especially if it is damaged.
Transmission of the causative agent of stomatitis is carried out by alimentary or drip-aerogenous way. If at this time the child's defenses are weakened and the oral mucosa has a low degree of resistance to infectious agents, the active life of the pathogen starts. In addition, under these conditions, the pathogenic properties of microbes are often manifested, which are normally part of the microflora.
Etiology
The most common cause of stomatitis in the throat of a child is ignoring or insufficient compliance with the rules of oral hygiene. The following factors can act as provoking factors:
- Violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane resulting from burns. As a rule, lesions occur due to eating too hot food.
- Mechanical damage to the mucosa.
- Penetration of chemical compounds into the oral cavity.
- Lack of vitamins and minerals in the body.
- Cold diseases.
- Measles
- Scarlet fever.
- Eating foods that are allergens for the baby.
- Taking antibiotics.
- Unbalanced diet.
- Violation of the functioning of the digestive system.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Presence in the bodyfungi and herpes virus.
- Failure of the immune system.
In addition, sometimes stomatitis in the throat of a child may occur after using toothpaste, which contains sodium lauryl sulfate. This compound effectively removes plaque from the enamel, but at the same time has a negative effect on the condition of the mucosa.
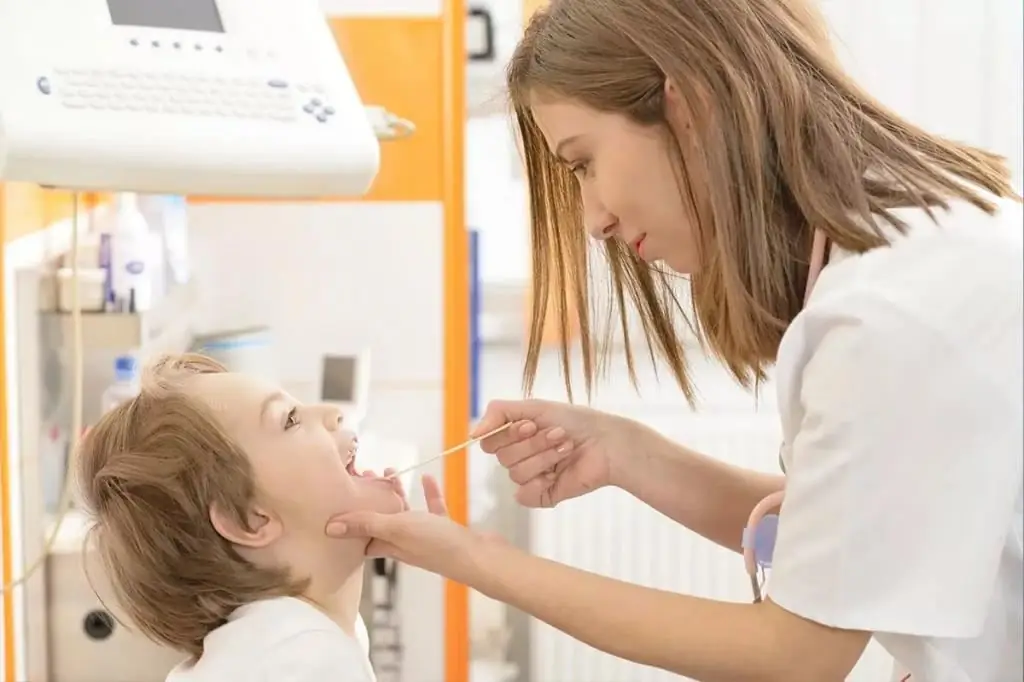
Clinical manifestations
The main symptom of throat stomatitis in children are sores. They differ in shade from the he althy mucosa and cause severe pain.
In addition, the following conditions are clinical manifestations of stomatitis:
- Tissue swelling.
- Increased body temperature.
- Frequent headache episodes.
- Inflamed cervical lymph nodes.
- Lack of appetite. This is due to painful sensations that make it difficult for the child to swallow.
- In some cases, vomiting occurs after eating food.
- Tongue coated with a light coating.
- Increased salivation.
- General weakness.
- Fast onset of fatigue.
- If you try to press on the sores, a cloudy liquid will come out of them.
- Irregularities in the digestive system. This condition occurs against the background of failures in the process of digestion of products.
- Bad breath.
If a child has a red throat and stomatitis (this can be understood by the presence of several of the above symptoms at once), you need to see a doctor. treatmentpathology is handled by a pediatric dentist.

Types of stomatitis
There are several forms of the disease. Each of them differs in clinical manifestations and their intensity, as well as the causes of development.
Types of stomatitis:
- Catarrhal. The mildest form of the disease. It is characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane, while there are no painful ulcers. The main reason for the development is non-observance of hygiene rules.
- Aphthous. Most often localized in the larynx. In children, aphthous stomatitis (a photo of the throat with this form does not cause positive emotions, a schematic image is presented below) is accompanied by the formation of specific bubbles. Over time, they burst, and in their place are white ulcers with a red halo.
- Candidiasis. Most often diagnosed in children. The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Candida. During the examination of the throat, a white coating can be found, resembling cottage cheese in consistency. It is easily removed, there are red wounds under it.
- Herpetic. The clinical manifestations of the pathology are as similar as possible to the symptoms of colds. However, during examination of the throat, ulcers characteristic of stomatitis can be found.
Only a doctor can determine the form of the disease and draw up the most effective treatment regimen.
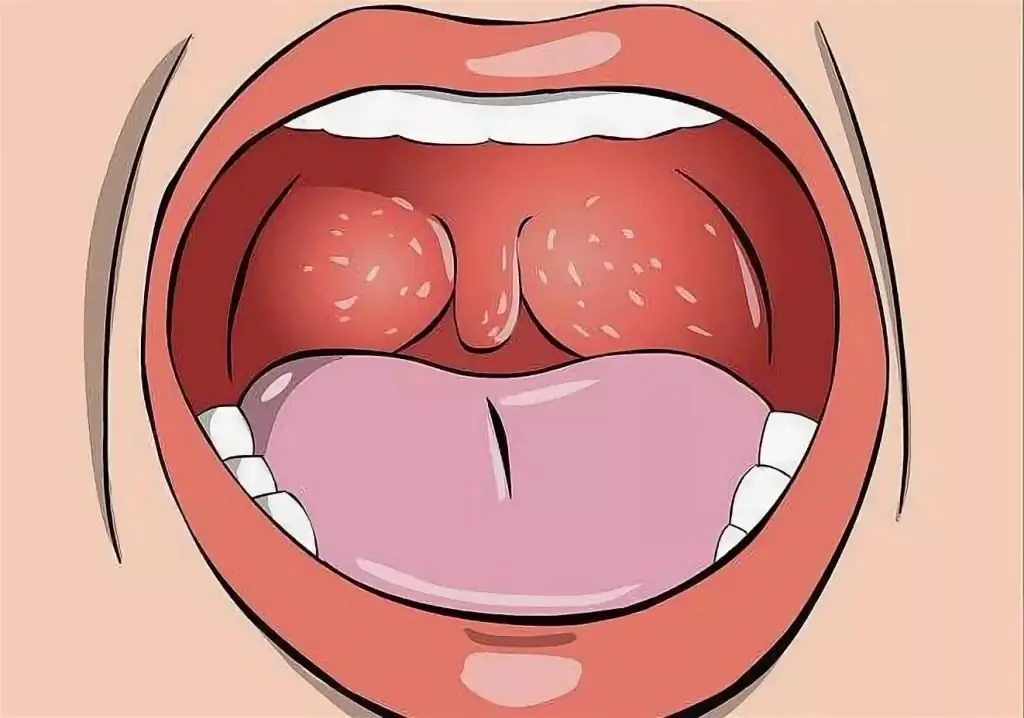
Diagnosis
For an experienced dentist, one quick examination is enough to differentiate stomatitis from a cold. To identify the cause of pathologythe specialist needs to conduct a thorough history taking.
Based on the initial information received, the doctor directs the patient for a deeper examination. This is necessary to identify the causative agent of the disease.
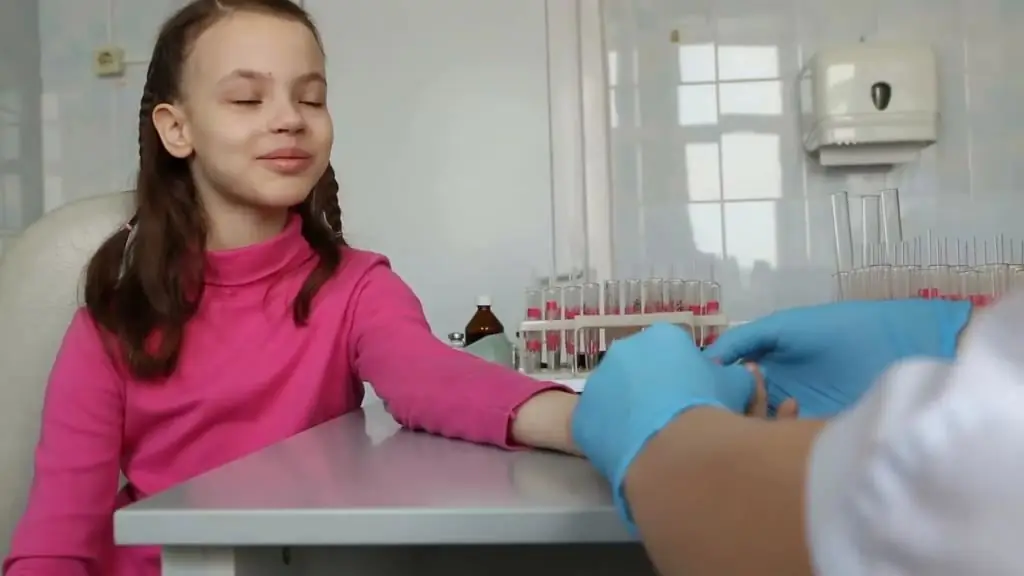
Laboratory diagnosis of stomatitis includes the following tests:
- Complete blood count.
- Studying the smear.
- Saliva study.
With a protracted nature of the disease, a biochemical blood test and immunoenzymogram are indicated.
Based on the results of the diagnosis, the doctor determines the tactics of treating stomatitis in the child's throat.
Antiviral and antibiotic therapy
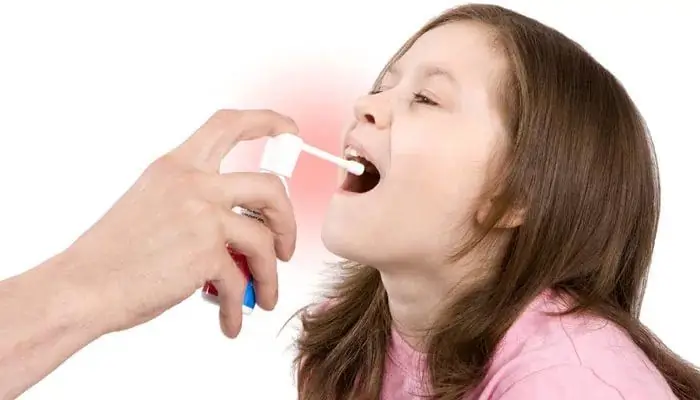
Initially, it is necessary to stop the infectious process. This task is well handled by topical preparations. Information about how to gargle children with stomatitis should be provided by a doctor. Most experts recommend using Miramistin for patients. This is a universal antiseptic, which is available in the form of a solution. It has no taste, and therefore children do not refuse to gargle with it.
The pharmaceutical market sells drugs that are intended for the preparation of solutions. The most effective are "Ingafitol" and "Evkar". Rinse your mouth immediately after preparing the solution.
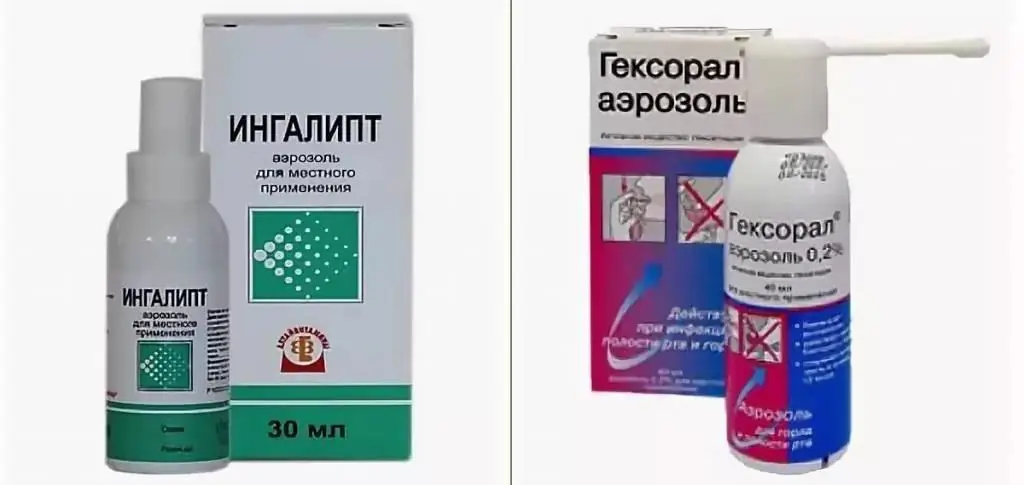
Effective in the treatment of stomatitis of the throat in children (the photo of the funds is presented below) sprays are recognized: "Ingalipt", "Gexoral", "Lugol's solution". Against the background of their use in a short timepain is also relieved.
Along with medicines, doctors recommend sucking on eucalyptus lozenges.
Tissue regeneration
Treatment of stomatitis in children on the throat is not complete without the use of drugs that accelerate the healing of the mucosa. The expediency of using this or that medication is evaluated by the doctor based on the individual characteristics of the child's he alth.
Most frequently, dentists prescribe the following remedies:
- "Lugol's solution".
- Carotolin.
- Solkoseril.
- "Vinilin".
- "Sea buckthorn oil".
All of the above means significantly accelerate the process of mucosal regeneration.
Symptomatic therapy
Severe pain is a constant companion of stomatitis. Topical preparations weaken their intensity, but in advanced cases, doctors recommend additional treatment of the throat with products containing lidocaine.
During the treatment of stomatitis, it is necessary to take drugs that help strengthen the immune system. As a rule, children are prescribed oral multivitamin complexes. In some cases, and immunomodulators.
Often in children, the course of pathology is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. In these cases, reception or rectal administration of antipyretics is indicated. These include: Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Cefecon.
Folk methods
To reduce the severity of unpleasant symptomsnon-traditional means are allowed.
Most Effective Recipes:
- Take dried calendula leaves, grind them. The resulting raw material in the amount of 1 tbsp. l. pour 200 ml of boiling water. Let it brew for 1 hour. Gargle with the resulting remedy as often as possible. A similar infusion can be prepared from chamomile leaves and flowers.
- Chop Kalanchoe, squeeze juice. Soak cotton wool or gauze in the liquid. Lubricate the child's throat immediately after rinsing.
- You can treat sores with propolis tincture in the form of an aqueous solution. (You can not use a bee product prepared with alcohol for babies). If the child is small, drop the product on the tongue. Older children can treat the throat with a cotton or gauze swab. However, it will be better to let the baby chew on a small pea of propolis. The frequency of taking the bee product in this case can be no more than 7 times a day, if there is no allergy to it.
It is important to understand that the use of traditional methods does not exclude the need to seek qualified medical help.
Doctors advice
Dentists recommend following the principles of a sparing diet during the treatment of stomatitis. In the presence of ulcers, you should not eat too hot dishes. The use of cold foods also delivers a number of unpleasant sensations. In addition, it is not recommended to eat solid foods that can disrupt the integrity of the mucosa, as well as foods that irritate tissues (s alty, fatty, fried, smoked). It is advisable to grind food before eating.
To prevent the disease again, doctors recommend:
- Both in the morning and in the evening thoroughly clean your teeth and tongue. The final step should be rinsing the mouth with special means.
- Treat all dental diseases in a timely manner.
- Do not eat foods that are allergenic.
- Keep yourself out of stressful situations.
- Reduce as much as possible the likelihood of contact with infected people.
Parents need to supervise their children and teach them to brush their teeth twice a day from childhood.

In conclusion
Stomatitis is an infectious disease. The course of the pathology is accompanied by the formation of ulcers on the oral mucosa, which cause pain. In babies, they are often localized in the larynx. Awareness of how to treat stomatitis in the throat in children does not mean that you need to do it yourself. Self-medication will never bring good results. If there are warning signs, then you need to show the baby to the dentist.






