- Author Curtis Blomfield [email protected].
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
With total pneumonia, the pathological process extends to the entire lung (unlike subtotal lesion, in which only part of the organ is affected). In this case, inflammation can be present both on one and on two lobes of the organ. The results of treatment and the prognosis for recovery will depend on the degree and severity of lung damage, which is due to the volume of tissue damage. Timely diagnosis and treatment is important. The principle of treatment of total and subtotal pneumonia is largely similar.
Pathology information
Total pneumonia is a disease that is well studied by specialists. The condition is an inflammation, more often of an infectious plan, in which the alveoli of the lungs are filled with purulent formations or fluid. As a result, the natural process of gas exchange between oxygen and carbon dioxide is disrupted. Either one lobe is affectedlung, or both. The disease is also called pneumonia. Viruses, fungi or bacteria act as provocateurs for the development of the disease.
Classification of pathology
Pneumonia can be divided into several types:
- Community-acquired - develops outside the hospital under the influence of fungi, bacteria or viruses.
- Hospital - can develop in a hospital if a person stays there for more than 72 hours.
- Aspiration - develops if food, water or other objects enter the respiratory tract.
- Atypical - occurs under the influence of unfavorable microflora.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease
Provoking factors can be internal and external. External causes include:
- variety of pathogen;
- human conditions;
- timely diagnosis;
- quality of treatment activities.
Many patients with the onset of a cough do not try to seek medical help, preferring self-medication, resulting in a complication in the form of pneumonia.
Despite the fact that many drugs can have a therapeutic and even complex effect, but if they are used incorrectly, the condition worsens. In addition, many viruses and bacteria are able to mutate and adapt to the effects of a particular drug.
Internal factors:
- compromised immunity;
- age of patient;
- comorbidities;
- bad habits.
Specialreduced immunity is dangerous, since the body in this case is not able to resist even a mild cold, which, under favorable conditions, can turn into pneumonia.
Etiology of pneumonia
There are many causes of pneumonia. It can be divided into infectious or non-infectious, it can develop as a complication of the underlying disease or proceed as an independent disease. In most cases, the lung tissue is affected as a result of the development of a bacterial infection. In second place is a viral or mixed (bacterial-viral) infection.
Main pathogens:
- Gram-positive microbes are staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci.
- Gram-negative enterobacteria - Pseudomonas aeruginosa, intestinal bacterium, Klepsiella, etc.
- Mtcoplasma.
- Viruses - adenoviruses, influenza and herpes viruses, picornaviruses.
- Fungal infections - candida, dimorphic yeasts, etc.
If pneumonia is non-infectious, then the following reasons can cause the disease:
- Inhalation of poisonous and asphyxiating gases - chlorophos, gasoline vapors, kerosene, oil.
- Injury to the chest area - a severe bruise, compression type compression or blow.
- Presence of allergens - plant pollen, industrial dust, animal dander or exposure to certain drugs.
- Burns in the airways.
- Radiation therapy for cancer.
Acute total pneumonia oftendevelops against the background of exposure to the main pathogen in the presence of diseases such as measles, anthrax, scarlet fever, leptospirosis, etc.
Symptomatic manifestations

The most dangerous condition is the period when the signs of the disease do not appear. The person does not cough, his temperature remains normal. Under such circumstances, diagnosis is carried out late, which aggravates the situation of the patient.
If symptoms of total pneumonia are present, they manifest as follows:
- Body temperature can rise to 39 degrees and even higher.
- Shortness of breath begins.
- When coughing, sputum is separated, in which, in a severe course of the disease, blood formations may be present.
- The patient is shivering.
- Pain is felt in the area of the affected lung, especially when inhaling.
- Most often the pain is felt during pleural pneumonia.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Bluish patches of skin.
- Headache.
If a baby is ill, then many of the listed signs may be absent, you can recognize something is wrong by the child's lethargy, weakness, poor appetite and fever. The most dangerous manifestation of the disease is lack of air, this condition can even lead to death. Therefore, total pneumonia in children is treated only in a hospital.

Complications and possible consequences of pneumonia
Complications can be pulmonary or extrapulmonary. The second are:
- hepatitis;
- meningoencephalitis or simply encephalitis or meningitis;
- endocarditis;
- various otitis media;
- myocarditis;
- anemic condition;
- mastoiditis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- septic lesion;
- psychosis.
Complications of the pulmonary plan:
- bronchitis;
- appearance of pneumosclerosis;
- pulmonary atelectasis;
- exudative pleurisy;
- lung tissue abscess;
- obstructive condition;
- pleurisy.
With extensive damage to lung tissues under the influence of released toxins, severe complications develop:
- acute respiratory, cardiac or hepatic failure;
- violation of acid-base balance with severe manifestations;
- toxic shock;
- thrombotic hemorrhagic syndrome;
- kidney failure.
Bilateral total pneumonia is considered the most dangerous.
Diagnostic measures
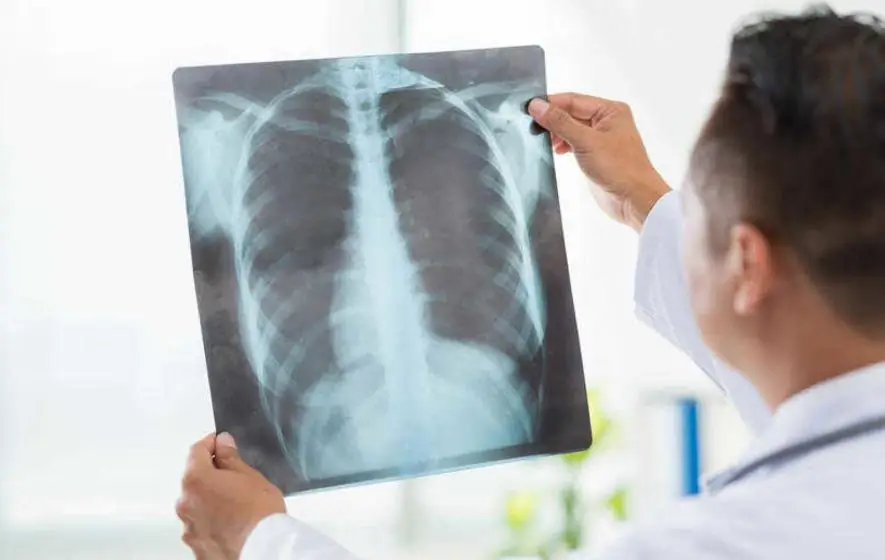
The basis of diagnostic measures for total pneumonia is as follows:
- Fiscal examination, this includes history taking, percussion and lung auscultation.
- Determining the clinical picture.
- Results of laboratory and instrumental studies.
Mandatory diagnostic actions include a blood test and determinationtotal pneumonia on x-ray.
How to treat the disease?

Treatment activities are carried out in a hospital. Depending on the patient's condition and lung damage (total right-sided pneumonia, left-sided lesion or bilateral), it is determined:
- To the pulmonology department where supplemental oxygen is available.
- To the intensive care unit with a ventilator.
- With extensive bilateral total pneumonia, chemotherapy is indicated using several drugs at once, depending on the direction of the infection.
The use of antibiotics, even with a wide range of effects, does not always lead to positive results. Since with viral inflammation it will be necessary to supplement the treatment with drugs based on Tamiflu.
Anti-inflammatory and symptomatic treatment

If there is total bilateral pneumonia, then be sure to prescribe heart medication to reduce the load on this organ, which is forced to work at full capacity.
The following antibiotics are mandatory prescribed:
- Cephalosporins - the most popular drugs from this group are Ceftriaxone and Cephilim.
- Macrolides - Clarithromycin, Azithromycin, Erythromycin.
- Fluoroquinolones - Levofloxacin,Moxifloxan.
- Carbapenems - this antibiotic is less common, the main drug is Meronem.
For total pneumonia, Moxifloxacin is most commonly prescribed.
It is important to take antifungal medicines such as Nystatin or Fluconazole while taking antibacterials.
Of the mucolytics most often prescribed:
- "Ambroxol";
- "Mukolvan";
- "Acetylcysteine".
The duration of their intake is determined by the doctor, most often it is 10 days or more. As an adjunct to treatment, it is important to take bronchodilators such as Eufillin and Ephidrine.
Prevention of pneumonia
In order not to face such a dangerous disease as pneumonia, it is necessary to develop for ourselves a number of preventive actions that will strengthen the body's defense mechanisms:
- Start tempering.
- Try to strengthen the immune system.
- Timely eliminate chronic foci of infections.
- Timely treat carious teeth.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Eliminate bad habits in the form of alcohol and smoking, they contribute to the development of a number of diseases.
- Combat indoor dust.
- When working in hazardous production, use all means of protection, but it is better to change such work activity to a safer one.
- If you have allergies, minimize contact withprovocateurs.
Will help prevent the development of pneumonia and the flu vaccine during sickness season. Human nutrition also plays an important role, it should be not only complete, but also balanced.