- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Not all people have come across such a concept as a “skin analyzer”. Most are accustomed to calling it a shortened, more familiar term. That is skin. But, in fact, both concepts denote a complex organ, which is our outer cover. One of the few in our body, which can be easily touched at any time. The skin area of an adult is approximately 1.5 - 2.3 square meters. And the mass, together with the hypodermis (the integumentary layer, which is deeper than the surface), is 16-17% of the body weight. However, all this should be told in more detail.
Epidermis
First of all, when talking about the skin analyzer, you need to pay attention to the epidermis. It is our outer layer. But this is in simple terms. In fact, the epidermis is a multilayer derivative of the epithelium. In thick skin, which is not covered with hair, it includes as many as 5 layers. Each of them is located above the dermis. And they all perform a barrier function.
An important nuance: the epidermis is characterized by constant renewal. And this is connectedspecificity with migration and transformation of the so-called keratinocytes. These are epithelial cells. Their filaments are represented by the protein keratin. In addition, it is also important to know that the epidermis contains certain components of the immune system.
The structure of the epidermis
Skin anatomy is very complex. Only the epidermis (one of its components) includes five different layers. The first one is basic. Or, as it is also called, sprout. What is really important to know about the basal layer is that it contains the so-called melanosomes. These are melanin granules that protect us from the effects of UV rays.
The second layer is called prickly. It also includes a mass of cells, but the tonofibrillary apparatus can be considered the most important "brick". It protects the cell nucleus from mechanical damage.
There is also a grainy layer. Consisting of 1-2 rows of elongated cells. It is in this layer that filaggrin and keratolinin (structural proteins) are synthesized. And they contribute to the keratinization of the epithelium. This, by the way, is the most complicated process, thanks to which the horny skin layer acquires its inherent elasticity and strength.
The fourth layer is known as cyclic (or brilliant). There are no organelles or nuclei in its cells. And it looks like a shiny pinkish stripe. This layer is well developed on the soles and palms.
And the last one is horny. This is the skin that performs a protective function. There are no living cells in it. Which is not surprising, because it is formed by dead keratinocytes. Or, as they are also called, hornyscales. How thick this layer is depends on the loads exerted on this skin.

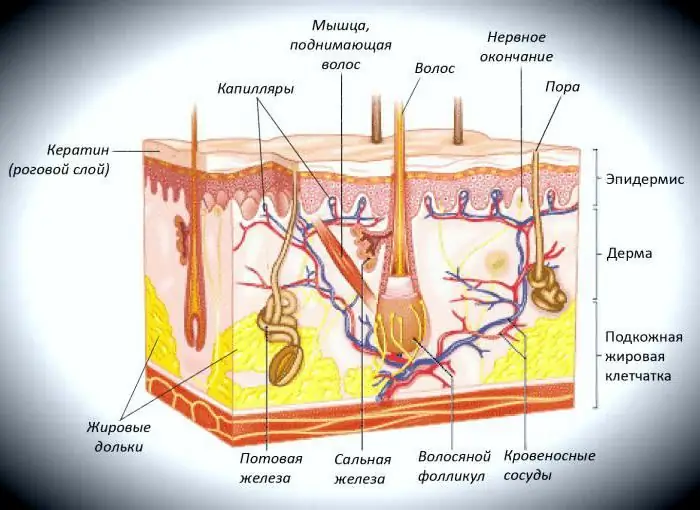
Derma
This is the next thing to pay attention to when talking about the skin analyzer. Because the dermis is actually the skin. And to put it in scientific language - its connective tissue part.
The dermis is under the epidermis. But not directly, they are separated by a basement membrane. It is distinguished by an abundance of capillaries and fibers, due to which the dermis is assigned supporting and trophic functions. It, like the epidermis, consists of several layers. True, there are only three of them out of a smaller number.
Components of the dermis
The anatomy of the skin is very complex, but it can be understood. There are only three layers, and the first, which deserves attention, is papillary. Why is it called that? Because this is the first layer, represented by "papillae" that penetrate the epidermis. It consists of dozens of "components". These are tissue basophils, macrophages and many other cells that contribute to the implementation of the protective function of our immune system.
The second layer is called mesh. It is made up of dense fibrous connective tissue. In fact, this is the main part of the dermis. It is in the mesh layer that contains the most powerful collagen fibers that contribute to the support function.
The last layer is called the hypodermis. It is also called subcutaneous adipose tissue. It is located directly under the dermis. And, as you can understand, based on the name, it is formed by adipose tissue. It is due to her under the skinaccumulates water and nutrients. In addition, the hypodermis contributes to thermoregulation.
Functions: protection and cleansing
So, what is a skin analyzer, clearly. Now you can list the functions it performs.
The first is protective. As already mentioned, the epidermis protects nerves, tissues and blood vessels from the direct influence of the external environment. The skin contains sebaceous glands. There are about 300,000 of them. And during the month they secrete an average of 500-800 grams of fat. It lubricates the surface of the skin, thus protecting it from various influences.
The second function is cleansing. The skin tends to produce sweat. So it frees the body from substances that are unfavorable for the body, which got inside along with medicines or food. Interestingly, there are about 2 million sweat glands in the skin.
Regulation, nutrition and breathing
These are also skin analyzer functions that traditionally belong to the main ones.
So, regulation. The skin cools the blood if the external temperature is lower than that of the body. It has the opposite effect in the opposite case. If the ambient temperature is very high, then the skin muscles become relaxed, as a result of which the vessels expand, and the body's heat transfer increases. Blood flow is also accelerated. As a result - copious sweat.
Performance of the function of nutrition is also determined by the departments of the skin analyzer. It is through our cover that animals penetrate into the body, andas well as vegetable fats. Solutions and creams are absorbed due to their special structure. No wonder these cosmetic substances are often called "nutrient".
Respiratory function, in principle, is characterized by the same specifics. Due to the porous structure of the upper layer, 2% of carbon dioxide is released through the skin. Surely not everyone knows that in 24 hours our cover removes about 800 grams of water vapor!

Nerve connections
A lot has been said above about what human skin is. Its structure and functions are of particular interest. And it is impossible not to touch upon the topic of nerves, with which our "shell" is abundantly supplied.
To put it in an accessible language, the skin is a large field strewn with receptors. They constantly, every second, perceive irritations of a different nature coming from the internal and external environment.
Nerve fibers and endings (both encapsulated and free) - that's what else includes human skin. Their structure and functions are specific. The nervous apparatus is located in the epidermis and dermis. In the hypodermis, they are practically absent. Only the nerve trunks penetrate into it, forming a plexus there, from which the fibers extend into the dermis. From there - to the hair follicles, muscles, blood vessels and sweat glands.
Nerve endings have their own names. For example, thanks to Krause flasks, the skin feels cold. And Meissner's bodies contribute to the perception of touch. Due to Ruffini's bodies, we feel warm. The list can be long. But the mostThe interesting thing is that there are about 200 pain, 2 heat, 12 cold and 20 tactile receptors per square centimeter of skin.
Blood
Naturally, the structure of the skin analyzer has a special specificity, due to which blood circulation is carried out.
So, in the hypodermis, in addition to nerve fibers and endings, there are large vessels. There are even arteries. They originate from the so-called arterial network, located directly above the fascia. They were mentioned at the very beginning.
From there, the arterial network spreads further - into the deep parts of the reticular layer. And from there - straight to the papillary.
It is important to know that in the skin layers there are not only capillaries and venules, but also arterioles. Which are directly involved in the regulation of OPSS (total peripheral vascular resistance). The tone of the arterioles is extremely important. After all, peripheral resistance, which determines blood pressure, depends on it. This is the characteristic of the skin analyzer. However, she is not surprised. After all, we are talking about a single, holistic organism in which absolutely everything is interconnected.

Sensitivity
This topic is also worth noting. There is such a thing as musculoskeletal sensitivity. Its origin is clear. After all, often the muscles are affected by touching the skin first. Take, for example, the same massage.
But skin sensitivity is special. It consists of various analyzers. Touch, for example, is a complex sense that arises from touching objects. Tactile sensations play an important role here. Analyzers that perceive pressure and touch give us information about the density of an object, its shape, temperature, condition, size, and much more. Especially many receptors are concentrated on the fingertips. It is from them that the “path” of information signals transmitted to the brain begins.
Regeneration
It comes in two varieties. The first is called physiological. Quite a normal, natural process that involves cell renewal. Its course depends on the nutrition, physical he alth and immunity of a person. This, in turn, affects the appearance and youthfulness of the skin.
And reparative regeneration involves the restoration of the cover after mechanical damage. After surgery, for example. The process is very interesting. First, the inflammation phase proceeds - bleeding stops, swelling occurs, pressing on the nerve endings and causing pain. Then proliferation begins. The wound is filled with capillaries and connective tissue - thus collagen. The last phase involves the formation of a scar. This process ends with the filling of the lesion site with epithelial tissue.
Some scars may take up to a year to form. And even though the skin is characterized by regeneration, the damage does not disappear without a trace. Therefore, you need to treat yourself with care.

Interesting facts
They should finish the story about what constitutes a skin-muscle sensitivity (we also considered the structure of the analyzer and its functions). Indeed, there are several interesting facts, and here are some of them that deserve attention:
- It's hard to imagine, there are about five million hairs on the entire surface of our skin!
- Adult human skin is 60% moisture. In children - by 90% (but this is the maximum).
- There are 100 pores for every square centimeter of skin.
- On average, the cover reaches 1-2 millimeters in thickness.
- The roughest leather on the soles. The most thin and transparent - on the eyelids.
- Throughout a lifetime, about 18 kilograms of dead skin is replaced by new skin.
Well, there are many more interesting things to tell about our cover, its structure and specific features. But the main points of anatomy were listed above, and it is useful for everyone to remember them, since this topic concerns all of us directly.






