- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
The eyes are quite an important organ for the normal functioning of the body and a full life. The main function is the perception of light stimuli, due to which the picture appears.

Building features
This peripheral organ of vision is located in a special cavity of the skull, which is called the eye socket. From the sides of the eye is surrounded by muscles, with the help of which it is held and moved. The eye consists of several parts:
- Directly the eyeball, which has the shape of a ball about 24 mm in size. It consists of the vitreous body, the lens and aqueous humor. All this is surrounded by three shells: protein, vascular and mesh, arranged in reverse order. The elements that make up the picture are located on the retina. These elements are receptors that are sensitive to light;
- Protective apparatus, which consists of the upper and lower eyelids, eye sockets;
- Adnexal apparatus. The main components are the lacrimal gland and its ducts;
- The oculomotor apparatus, which is responsible for the movements of the eyeball and consists of muscles;
- Optic nerve.
Main Functions
The main function of vision is to distinguish between various physical characteristics of objects, such as brightness, color, shape, size. In combination with the action of other analyzers (hearing, smell, and others), it allows you to adjust the position of the body in space, as well as determine the distance to the object. That is why the prevention of eye diseases should be carried out with enviable regularity.
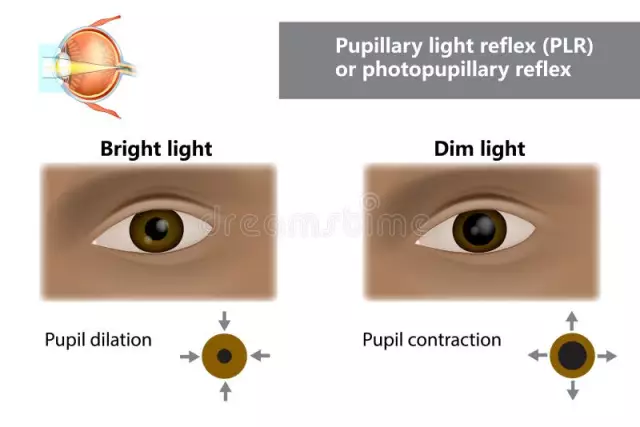
Presence of pupillary reflex
With the normal functioning of the organs of vision, with certain external reactions, the so-called pupillary reflexes occur, in which the pupil narrows or expands. The pupillary reflex, the reflex arc of which is the anatomical substrate of the pupil's reaction to light, indicates the he alth of the eyes and the whole organism as a whole. That is why, in some diseases, the doctor first checks for the presence of this reflex.

What is a reaction?
Pupillary reaction or the so-called pupillary reflex (other names - iris reflex, irritant reflex) is some change in the linear dimensions of the pupil of the eye. Constriction is usually caused by contraction of the muscles of the iris, and the reverse process - relaxation - leads to the expansion of the pupil.
Possible causes
This reflex is caused by a combination of certain stimuli, the main of which is considered to be a change in the level of illumination of the surrounding space. In addition, changes in pupil size canhappen for the following reasons:
- action of a number of medicines. That is why they are used as a way to diagnose the state of drug overdose or excessive depth of anesthesia;
- changing the focus of a person's view;
- emotional outbursts, both negative and positive equally.
If there is no reaction
Lack of pupil reaction to light may indicate various human conditions that pose a threat to life and require immediate intervention by specialists.

Pupillary reflex pattern
The muscles that control the work of the pupil can easily influence its size if they received a certain stimulus from the outside. This allows you to control the amount of light that enters the eye directly. If the eye is covered from the incoming sunlight, and then opened, then the pupil, which previously expanded in the dark, immediately decreases in size when the light appears. The pupillary reflex, the reflex arc of which begins on the retina, indicates the normal functioning of the organ.
The iris has two kinds of muscles. One group is circular muscle fibers. They are innervated by parasympathetic fibers of the optic nerve. If these muscles contract, this process causes pupil constriction. The other group is responsible for pupil dilation. It includes radial muscle fibers that are innervated by sympathetic nerves.

Pupillary reflex, the scheme of which is quite typical, occurs in the following order. Light that passes through the layers of the eye and is refracted in them hits the retina directly. The photoreceptors that are located here, in this case, are the beginning of the reflex. In other words, this is where the path of the pupillary reflex begins. The innervation of the parasympathetic nerves affects the work of the sphincter of the eye, and the arc of the pupillary reflex contains it in its composition. The process itself is called the efferent shoulder. The so-called center of the pupillary reflex is also located here, after which various nerves change their direction: some of them go through the legs of the brain and enter the orbit through the upper fissure, others - to the sphincter of the pupil. This is where the path ends. That is, the pupillary reflex closes. The absence of such a reaction may indicate any disturbances in the human body, which is why it is given such great importance.
Pupillary reflex and signs of its defeat
When examining this reflex, several characteristics of the reaction itself are taken into account:
- pupil constriction;
- shape;
- uniformity of reaction;
- pupil mobility.
There are several of the most popular pathologies that indicate that the pupillary and accommodative reflexes are impaired, which indicates malfunctions in the body:
- Amaurotic immobility of the pupils. This phenomenon is a loss of direct reaction when illuminating a blind eye and a friendly reaction,if there are no problems with vision. The most common causes are various diseases of the retina itself and the visual pathway. If the immobility is unilateral, is a consequence of amaurosis (retinal damage) and is combined with pupil dilation, albeit slight, then there is a possibility of developing anisocoria (pupils become different sizes). With such a violation, other pupillary reactions are not affected in any way. If amaurosis develops on both sides (that is, both eyes are affected at the same time), then the pupils do not react in any way and even when exposed to sunlight remain dilated, that is, the pupillary reflex is completely absent.
- Another type of amaurotic pupillary immobility is hemianopic pupillary immobility. Perhaps there is a lesion of the visual tract itself, which is accompanied by hemianopia, that is, blindness of half of the visual field, which is expressed by the absence of a pupillary reflex in both eyes.

Reflex immobility or Robertson's syndrome. It consists in the complete absence of both direct and friendly reaction of the pupils. However, unlike the previous type of lesion, the reaction to convergence (narrowing of the pupils if the gaze is focused on a certain point) and accommodation (changes in the external conditions in which the person is located) is not impaired. This symptom is due to the fact that changes occur in the parasympathetic innervation of the eye in the case when there is damage to the parasympathetic nucleus, its fibers. This syndrome canindicate the presence of a severe stage of syphilis of the nervous system, less often the syndrome reports encephalitis, a brain tumor (namely in the legs), as well as a traumatic brain injury

- Absolute, or complete immobility of the pupil (that is, it does not narrow, and does not expand at all). When the pupil is exposed to a beam of light rays, the absence of both direct and friendly reactions to the stimulus is diagnosed. Such a reaction does not develop instantly, but gradually. As a rule, it begins with a violation of physiological pupillary reactions - mydriasis (pupil dilation), lack of pupil mobility.

The causes may be inflammatory processes in the nucleus, root or trunk of the nerve responsible for eye movements, a focus in the ciliary body, tumors, abscesses of the posterior ciliary nerves.