- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
One of the most beautiful times in a woman's life is pregnancy. It is good if the embryo develops according to the terms in the place established by physiology. But it also happens that the attachment of the fetal egg does not occur where it is provided. Then there is a suspicion that the patient had an ectopic pregnancy (tubal, ovarian, abdominal, cervical). This article will tell you about one of these species. You will learn what a tubal pregnancy is. Causes and symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment will be described below.

Mechanism of occurrence and classification of ectopic pregnancy
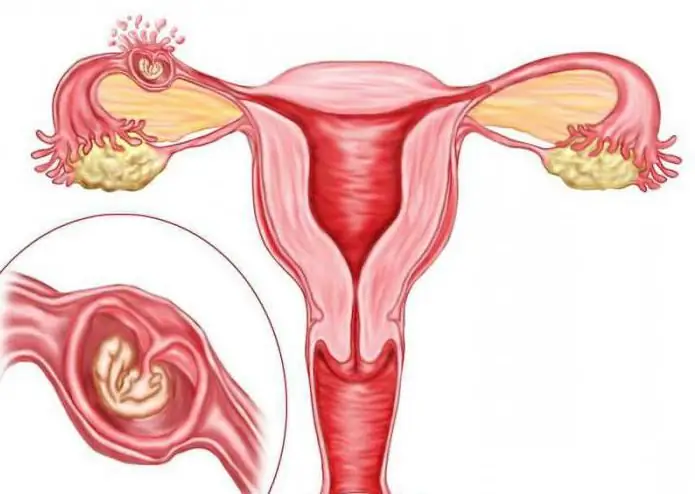
After the fusion of the male and female gametes (sperm and egg), the active division of the resulting mass begins. Slowly but surely, the zygote moves into the uterine cavity. This is where the fertilized egg should be fixed, according to the rules of physiology. But this is not always the case.
For certain reasons, the fertilized egg does not enter the uterus, but remains in the fallopian canal. In this case, pregnancy developspipe. If the zygote is pushed back, then the embryo can attach in the ovary or abdominal cavity. It rarely happens that the fetal egg bypasses the reproductive organ and is fixed in the cervical canal (cervical pregnancy).
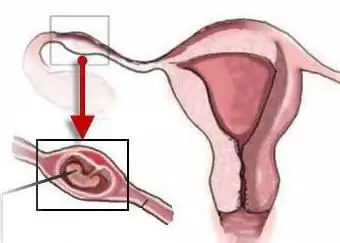
Tubal pregnancy: causes
In general, ectopic attachment of the ovum occurs in two percent of all cases. At the same time, tubal pregnancy occurs in 97% of them. In half of the situations, the reasons for this outcome remain unknown. But gynecologists identify risk factors that can lead to the described pathology. Consider them.
- Operations performed on the abdominal organs. If a woman has previously had surgical interventions, then this can cause the formation of adhesions. These films, in turn, prevent the normal progression of the fertilized cell.
- Wrong choice of contraception. If you use oral hormonal agents in an inappropriate dose, then conception can take place, but the embryo will not develop correctly. Also, tubal pregnancy occurs when using intrauterine devices.
- Infectious diseases and pelvic inflammation. These pathologies (even in history) lead to deformation of the reproductive organs, hormonal failure and the formation of adhesions. The fallopian tubes become thinner, the inner villi stop functioning properly.
- Neoplasms. If there are fibroids, polyps or ovarian cysts in the uterus, then the entire process of conception is disrupted. Therefore, there is a high probabilityattachment of the fetal egg outside the cavity of the genital organ.
- Anomalies of the genital organs. Often, an ectopic (tubal) pregnancy occurs with congenital or acquired pathologies of the pelvic organs (the presence of a septum, adhesions, a bicornuate uterus, and so on).

Signs of pathology
What are the symptoms of tubal pregnancy? This question interests many women. Clinical manifestations are divided into primary and secondary. At first, the symptoms are no different from those that appear during a normal pregnancy. But later signs join, signaling a pathological process.
Up to 5-7 weeks, a woman may feel nausea, sometimes she is accompanied by vomiting. There is increased fatigue, drowsiness. There is a delay in menstruation, and a pregnancy test shows a positive result.
With the onset of 4-8 weeks, additional symptoms join. It is they who should alert the woman and become the reason for contacting the doctor. These manifestations include:
- pain (pulling sensations in the lower part, radiating to the back or leg; girdle shootings);
- bleeding from the genital tract (more often the discharge is spotting, they are associated with a decrease in progesterone levels).

Missed tubal pregnancy
Violation of the viability of the embryo can be considered an abortion. In this case, it can take two forms:
- interrupted pipetubal abortion type pregnancy;
- termination of embryonic development by the type of fallopian tube rupture.
Both conditions are manifested by increased bleeding, pain in the lower abdomen. It is worth noting that the rupture of the fallopian tube is characterized by acute pain in the abdominal cavity, a decrease in pressure and pulse, pallor of the skin, respiratory failure and fainting. Such a picture is life-threatening, and therefore requires immediate medical attention.
Methods for diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy
How is an ectopic pregnancy, tubal abortion defined by doctors? Specialists conduct a series of studies to make a correct diagnosis. Among them are the following:
- Gynecological examination. When a patient contacts with the described gutters, the doctor first of all performs palpation on the chair. At the same time, the size of the reproductive organ is noted, the ovaries are probed. In some cases, the doctor can determine the presence of a neoplasm (fetal egg) between the uterus and ovaries. After such an examination, only a preliminary diagnosis is made, since it is not yet possible to say for sure whether this is a tubal pregnancy or another pathology.
- The next step in the diagnosis will be an ultrasound. After that, the picture becomes clearer. During the procedure, the specialist measures the uterus and ovaries, compares the data obtained with the set day of the cycle. With an ectopic pregnancy, the reproductive organ does not correspond to the gestational age. Also, a fetal egg is not determined in the uterus. For a period of 7-10 weeks, the doctor can quite clearly see the placeembryo location.
Diagnosis of tubal abortion is more complicated, it requires a thorough history taking, examination of the patient (objective and vaginal examination, bimanual examination, determination of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood serum, ultrasound, laparoscopy). Often a differential diagnosis is required.
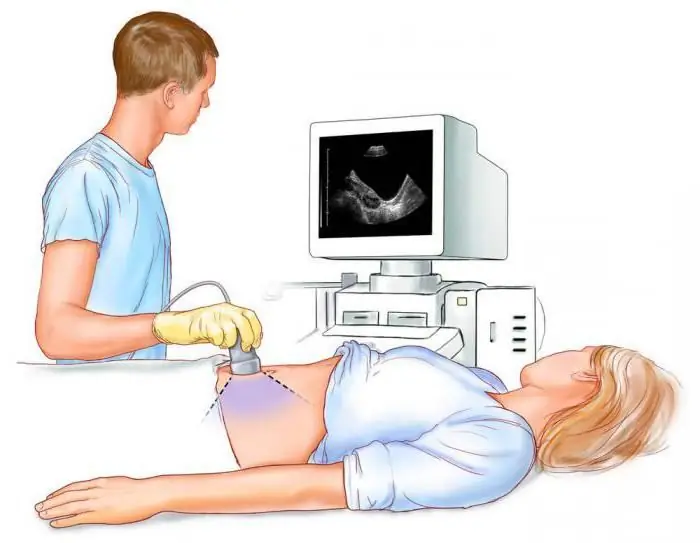
Laboratory studies
Tubal pregnancy can also be confirmed with the help of laboratory diagnostics. To do this, the patient needs to donate blood to determine the level of two substances: progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin. During a normal pregnancy, these values constantly increase, corresponding to the period. If you get values that are lower, there is a possibility that the embryo has attached outside the uterine cavity.
To make a reliable diagnosis, you need to retake the test in a few days. Positive dynamics or lack of it will allow you to correctly interpret the situation.
Treatment: is medical correction possible?
If a tubal pregnancy is confirmed, treatment should begin immediately. It should be said right away that it is impossible to eliminate the pathology with pills and drugs. Even means for medical or pill abortion will not help here. Interruption and elimination of a pathologically located fetal egg is possible only by surgery. Correction is always carried out under anesthesia. Currently, doctors use two methods of treating tubal pregnancy: laparotomy and laparoscopy.
Laparotomy surgery
Such an intervention is rather difficult for patients. The recovery period lasts from two weeks to several months. During the manipulation, the abdominal cavity is cut in layers. After that, the ectopic pregnancy is corrected.
Tubectomy is more common during laparotomy. In other words, the affected fallopian tube is completely excised along with the embryo. After that, the toilet of the peritoneum is carried out, and the wound is sutured in the reverse order.
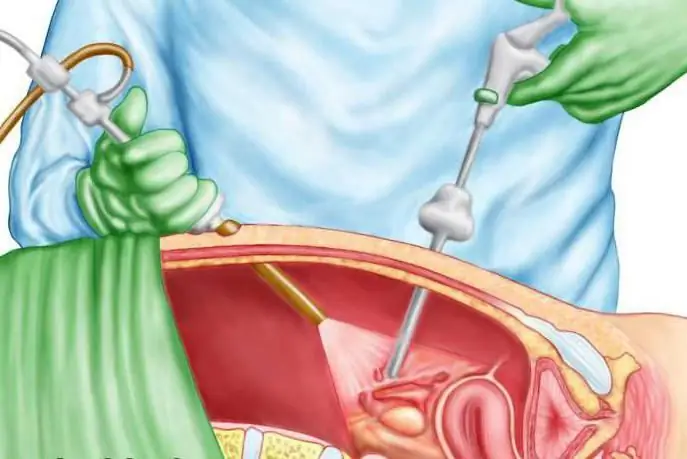
Sparing method: laparoscopy
Laparoscopic surgery has been the most popular in recent years. It involves two to four punctures in the abdominal cavity. Laparoscopy allows not to completely remove the fallopian tube, but only to excise its damaged area. This operation is called tubotomy.
This method is chosen taking into account the age, condition and desires of the patient. Preservation of the fallopian tube allows you to further preserve the childbearing function. However, with a recurrence of an ectopic pregnancy, complete removal of the fallopian canal is indicated.
Heterotopic pregnancy and its features
Rarely enough, but still there are cases when tubal pregnancy is combined with normal. In this case, one fetal egg is located as indicated above, and the second is in the uterus.
The possibilities of modern medicine and the high qualification of surgeons make it possible to eliminate a pathologically attached embryo while preservingviability of a normal embryo. Note that the sooner a problem is detected, the greater the chance of a positive outcome.
Consequences of pregnancy developing in the fallopian tube
If a tubal pregnancy is removed, then it is necessary to carry out drug therapy. It provides for physiotherapy, acupuncture, selection of the correct contraceptives. Also, a woman needs antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and restorative therapy.
The consequences of the pathology can be different: it all depends on the term and method of completing the tubal pregnancy. The probability of normal conception and subsequent birth is 50%. In 30% of cases, infertility occurs (usually with a recurrence of the pathology and complete removal of the fallopian tubes). The recurrence rate of ectopic pregnancy is defined as 20%.
The consequences of the pathology include adhesions in the pelvis, pain, menstrual irregularities, hormonal failure, psychological abnormalities. With a second conception, a woman should be under the close attention of specialists from the very first days of the delay. This will help to detect and correct or refute a relapse in time.
Summarize
If you suspect you have a tubal pregnancy, you should contact your gynecologist as soon as possible. The doctor will be able to dispel or confirm your doubts and, if necessary, prescribe treatment. Remember that during the period of bearing a baby, it is unacceptable to be nervous. So it's better one more timeconsult a gynecologist.
If both fallopian tubes were removed during treatment (operation), do not lose hope. Modern medicine allows you to conceive a child even in this case. To find out more information about this, you need to visit a gynecologist. All the best to you!






