- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
There are few people who have never had a stomachache. In most cases, this unpleasant symptom is associated with malnutrition or diseases of the digestive system, such as gastritis, ulcers or cholecystitis. If the pain in the abdomen is acute, plus the patient has nausea and vomiting, appendicitis is often diagnosed. And the cause of all these he alth troubles can be Payr's syndrome. What kind of disease it is and how it manifests itself, not even every doctor knows, which is why the wrong treatment is prescribed. In this case, the patient not only does not improve, but the problem is aggravated. As a result, it has to be solved only surgically. In fairness, it must be said that clinically diagnosing Payr's syndrome, based only on the history and palpation of the abdomen and without the results of special tests, is really difficult. But this disease has some features that distinguish it from other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. About how to recognize this dangerous syndrome and whether it can be curedailment without surgery - our article.
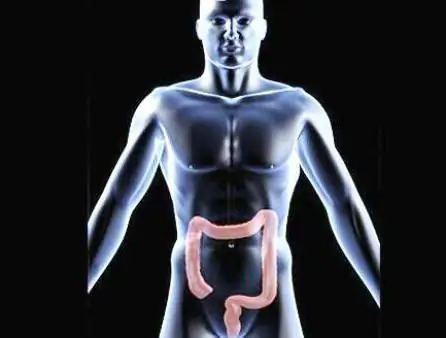
Payr syndrome - what is it?
Recall the school anatomy. All the food that we have eaten begins to be digested in the stomach, and then moves to the small intestine, where the digestion process ends. There, from the food mass, everything valuable enters the bloodstream, and everything that is useless for the body passes into the large intestine. Here, water is absorbed from this mass, leaving a thicker consistency waste, which we call feces. The large intestine has several sections, the longest of which is the colon. Simplified, it can be represented as a hollow tube with a diameter of about 7 cm, like a rim, bordering the small intestines. The colon is divided into three segments. The ascending segment is located on the right side of the abdomen. It rises to the liver, where it bends at an angle close to 90° and passes into the transverse segment. This part of the colon reaches the region of the spleen (an organ lying in the left hypochondrium), bends again, passes into the descending segment, then into the sigmoid colon and into the rectum. Fecal masses, starting to form at the exit from the small intestine, go all this long way, gradually thickening. As a result, at the exit, we have a formed feces that is quite dense in density. Payr's syndrome, or Payr's disease, is observed when the second bend of the colon (in the area of the spleen) is much larger than physiologically necessary. In this place, the diameter of the intestinal cavity is greatly narrowed, which in medicine is called stenosis. Through a narrow opening, already thickened fecesthe masses do not move fast enough to make room for those who follow. As a result, a kind of congestion is formed from what the body is trying to bring out. Often, gases are added to the feces, which are formed during the digestion of food.

What is the danger of Payr's syndrome
In the small intestine, useful trace elements, vitamins and other substances pass from food into the blood, and all unnecessary and even harmful remain, forming fecal masses. Normally, we must remove them from the body every day, that is, perform an act of defecation. If the feces are delayed, which is observed with constipation, the harmful substances present in them begin to enter the blood, and gradual poisoning of the body (intoxication) begins. This is the main danger that Payr's syndrome causes. Intoxication has many adverse effects, one of which can be called immunosuppression. This, in turn, leads to a decrease in resistance to various diseases. In addition, hard feces irritate the intestinal walls, leading to their ulceration, and attempts by a person with constipation can cause hemorrhoids. Another serious problem caused by Payr's syndrome is colonoptosis, which means the prolapse of the colon. This leads to intestinal obstruction and sometimes volvulus.
Etiology
Payr's syndrome was described by the German surgeon Irwin Payr back in 1905. For more than 100 years, the prevalence of this pathology has increased and reached approximately 40% amongthe adult population of the planet. The inflection of the colon is observed with a congenital pathological structure of the intestine, for example, with an elongated transverse segment of the colon. Since these anomalies are congenital, the causes of their occurrence lie in any failures in the formation of the intestine at the stage of the embryo. Among them are unfavorable ecology, mother's illnesses during pregnancy, medication, bad habits, nervous stress, alcohol consumption by a pregnant woman and other factors affecting the development of the fetus. Medical statistics have established that children whose father and mother suffer from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are born with Payr's syndrome more often than children of absolutely he althy parents.

Pathogenesis
Payr's syndrome has symptoms that are standard for many other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and therefore a misdiagnosis is often made. Patients may experience:
- constipation;
- nausea;
- loss of appetite;
- pain in the peritoneum;
- vomiting;
- bloated stomach (due to the fact that gases cannot leave the colon);
- headache;
- irritability.
In addition, the following manifestations of Payr's syndrome may indicate:
- paroxysmal pain of unclear localization (due to the accumulation of gas and feces in the place of inflection of the intestine);
- severe pain in the area of the heart (sometimes they give under the shoulder blade or in the left hand);
- reduction of pain when the patient lies down horizontally.
Stagnation of feces causes inflammation of the intestinal walls, and their reflux into the small intestine, which happens often in Payr's syndrome, leads to reflux ileitis. In these cases, the symptoms of these associated diseases are added:
- mucus in feces, sometimes with blood;
- rising temperature.
Dolichosigma
One of the sections of the colon is the sigmoid colon, so named because of its shape, somewhat reminiscent of the letter "S". It is located directly in front of the rectum, the functions of which are to evacuate feces from the body. Dolichosigmoid is a pathology when a person's sigmoid colon has formed longer than anatomically necessary. At the same time, stagnation of feces unplanned by nature also occurs in it, and the symptoms resemble Payr's syndrome. Dolichosigma can be not only congenital, but also acquired. It is believed that the sigmoid colon can lengthen with prolonged (years) irrational nutrition, when eating too much meat and carbohydrates, during sedentary work. One of the main symptoms of this pathology is constipation. In addition, patients complain of pain in the navel and left hypochondrium, flatulence, general deterioration of he alth.
Diagnosis
Payr syndrome in adults and children is not easy to diagnose. The history of this disease is very similar to other problems with the digestive tract. It happens that patients with Payr's syndrome were even diagnosed with appendicitis and underwent surgery. At present, there is a very accurate methoddiagnosis of this pathology - irrigography. This is the most effective method that allows to determine with great accuracy the presence of an inflection of the colon in a patient. The procedure is carried out using a barium suspension. The process of its introduction to the patient is controlled by an X-ray screen. When the colon is full, the picture is taken in the patient's supine position, and when the intestine is emptied, it is taken while standing.
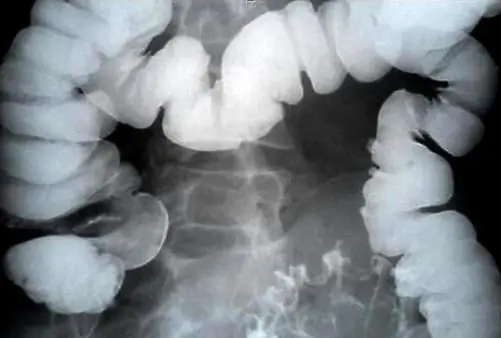
Children of the age category of 10-15 years old use a radioisotope method to study the colon. At the same time, a colloidal solution of radioactive gold.
When Payr's syndrome in the picture you can see that the colon, like a garland, sagged into the pelvic area.
Features of Payr's syndrome in children
Unfortunately, while Payr's syndrome in children has not been studied enough, therefore, there are no unequivocal recommendations on how to diagnose it more accurately, taking into account the age characteristics of young patients, and how to treat it more effectively. Studies conducted by medical scientists have shown that girls have this disease more often than boys.
The manifestation of Payr's syndrome begins already in the first 12 months after birth, most often during the period when the child begins to give complementary foods. The new food thickens the baby's stools, which helps them stay at the kink in the colon.
The first symptoms of the disease, indicating Payr's syndrome, are as follows: against the general background of complete he alth, the child develops constipation and abdominal pain. In the future, signs of intoxication (nausea, vomiting) are added due toaccumulation of feces and their long stay in the intestine. Without treatment in children by the age of 12-15, the same symptoms of Payr's syndrome are observed as in adults. When examining a child with suspicions of having Payr's syndrome, the doctor must definitely find out how the pregnancy proceeded, whether there are close relatives with gastrointestinal problems in the family, in order to exclude inflammatory processes in the intestine, prescribe a blood test. The final diagnosis should be based on the results of irrigography.
Payr's Syndrome: Diet Treatment
With this disease, patients should pay great attention to proper nutrition. Food should be high-calorie, but at the same time light, not containing a lot of toxins. The menu must contain cottage cheese, butter, sour cream, kissels. To increase the peristalsis of the intestines, patients should introduce whey, kefir, fermented baked milk, yogurt into their diet. You can not refuse sweets, which attract fluid into the intestines, which contributes to the liquefaction of feces and an easier defecation process. Patients should eat a lot of fruits, honey, fruit syrups.

In the presence of Payr's syndrome, as in constipation of another etiology, it is useful to drink vegetable decoctions and compotes, as well as freshly prepared juices from carrots and raw potatoes.
Compliance with the diet does not eliminate the disease, but greatly facilitates its course.
Conservative treatment
Doctors can often observe a situation that they are afraid of surgery and want to try firstdrug therapy for patients who have Payr's syndrome. Treatment with what pills can cope with this disease? Doctors may advise lactulose preparations. They can be given to children as early as infancy. Lactulose somewhat thins the stool, enhances intestinal motility and at the same time populates the intestines with beneficial microflora. Adults and everyone who, due to prolonged constipation, has begun to have inflammation of the intestinal walls, are prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs. To relieve pain syndromes, antispasmodics "Drotaverin" or "Platifillin" can be advised, courses of prebiotics, probiotics, vitamins are also useful.
Payr's syndrome is treated with medication only at the very initial stages of the disease, and the results are usually short-lived. In parallel with the pills, doctors prescribe physiotherapy (electrophoresis with a solution of novocaine, paraffin applications on the abdomen, diathermy, UHF, abdominal massage is mandatory, and exercises are prescribed to strengthen its walls.
Surgery
This is the most effective method of treatment, as a result of which all symptoms completely disappear, and forever, and not temporarily, as with other methods of therapy. Operations are performed according to different methods, depending on the anatomical indications. According to one of them, a median laparotomy is performed, a resection of the transverse section of the bypass intestine in the middle part, and a direct anastomosis is applied. Next, the transverse colon is moved under the base of the transverse gastric ligament and fixed using a special technology so that the bends in the arealiver and spleen were rounded.
According to the second method, the ligaments that fix the large intestine (colon-splenic and colon-diaphragmatic) are excised, the splenic flexure is lowered with a laparoscope in order to remove the kink of the intestine. The operation is performed using medical trocars and electrocautery.
Combined operations are performed on those who are diagnosed with "Payr's syndrome, dolichosigma". Feedback from patients after such treatment is very favorable. In people, pain completely disappears, constipation stops, and with them the symptoms of intoxication disappear. During combined operations, in addition to manipulations with the colon in the transverse part and the splenic flexure, patients undergo laparoscopic resection of the sigmoid colon.
Forecast
Conservative treatment gives results in the initial stages of the disease, but since it is caused by an anatomical pathology in the structure of the intestine, only surgical intervention helps to completely defeat Payr's disease. Treatment with folk remedies is used only as an auxiliary. Traditional medicine offers infusions and decoctions that thin feces (laxatives) and agents that enhance intestinal motility. There are also remedies that strengthen the immune system, improve the general condition. You can use decoctions of plantain, potato juice, prunes compotes, dried fruits. It is important to know that enemas are contraindicated in Payr's syndrome.
The prognosis in patients who received the correct treatment on time is completelyfavorable. If Payr's disease is neglected, life-threatening complications may appear in the form of tumors, ulceration of the walls, hemorrhoids, developing from constant trauma to the intestines with feces.






