- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
According to the ICD, esophageal atresia is a congenital developmental defect characterized by partial or complete absence of the esophagus. This pathology is considered one of the most difficult in pediatric practice. If a newborn has been diagnosed with this terrible disease, it is urgent to perform a surgical operation. Otherwise, the baby is guaranteed to die.
Esophageal atresia in newborns is not so common. According to statistics, no more than 0.4% of children are born with such a pathology. At the same time, the disease affects both boys and girls equally.
Useful information
In some cases, atresia is diagnosed together with other defects. For example, a newborn may also be diagnosed with pyloric stenosis, abnormal development of the limbs, problems with the anus, congenital heart disease, and more. Also, according to statistics, in 40% of cases, babies suffer from developmental problems or are born prematurely. If a mother carries a baby with esophageal atresia under her heart, then in the third trimester of pregnancy there is a high risk of sudden termination of pregnancy. Therefore, it is important to understand howavoid this terrible disease, and is there any way to get rid of it.
Causes of occurrence
Even at the moment when the baby is only a small embryo, the first stages of the formation of the esophagus and other internal organs are already taking place. As a rule, this happens already at 4-5 weeks of gestation. By week 12, the esophagus is already completely differentiated. If certain failures occur during this period, then the growth of the necessary cells slows down and esophageal atresia is formed.
A variety of factors can lead to such an anomaly. If a woman drinks alcohol, drugs and smokes, then atresia may well develop due to the unhe althy lifestyle of the expectant mother. Also, the factors that cause such a pathology include a variety of events from a woman's life. For example:
- X-rays were taken in early pregnancy.
- The expectant mother is over 35 years old. The older the woman, the higher the risk of developing anomalies. However, younger mothers may also face a similar problem.
- Before 12 weeks of gestation, the woman took antibiotics with teratogenic or embryotoxic effects.
- Expectant mother lives in a bad environment. In this case, the presence of harmful components in the air, radiation exposure and much more can have a negative impact.
- After conception, the woman worked in a manufacturing plant, coming into contact with chemicals or strong poisons.
- One of the parents suffers from a chromosomal abnormality.

Very often, before the formation of esophageal atresia in newborns, mothers have a threat of miscarriage. As a rule, this happens in the first trimester of bearing a baby. Polyhydramnios can also be the cause. In this case, the baby swallows amniotic fluid.
Varieties
Esophageal atresia in newborn babies can be of different types depending on the damaging factors. For example, the lumen of the esophagus may be completely absent or it has developed in the form of two independent blind sacs.
In some situations, the upper part of the vital organ has a blind ending, while the lower zone is connected by a fistula along with the trachea. In this case, the connection point is at the place where the division into bronchi occurs.
There are cases when the upper part of the esophagus also ends blindly, and the lower part goes straight into the trachea. In other situations, the top of the organ is connected to the trachea, and the lower region ends blindly.
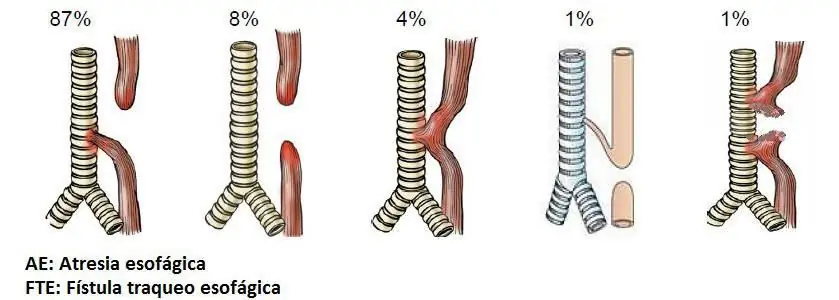
Also, both parts of the esophagus can communicate with the trachea.
How it manifests
Esophageal atresia in children is detected almost immediately after their birth. The most important symptom is that the baby has a strong foamy discharge from the nose and mouth. After the first breastfeeding, the baby immediately spits up milk. In this case, emergency parenteral nutrition is required. If the baby does not receive the necessary nutrients intravenously, then thiswill make him emaciated and dehydrated.
When connecting the esophagus to the trachea, the main symptom is a strong cough, to the point that the baby begins to choke. Against this background, respiratory failure can develop quite quickly. In this case, it is necessary to clean the respiratory channels as soon as possible. After this, an improvement in the condition will be noticeable, but it lasts only until the next feeding. If gastric juice gets into the lungs, it can lead to aspiration pneumonia. This is a very dangerous complication.
Also among the signs of esophageal atresia is a sharp weight loss, wheezing and blue skin of the newborn.
If a fistula has formed in the baby's body, this will lead to air entering directly into the improperly formed organ.

All these symptoms are very dangerous. Especially if the baby cannot fully eat and milk is rejected. In this case, fever and respiratory failure may develop against the background of dehydration. All this leads to death.
Diagnosis of esophageal atresia
If the doctor suspects the presence of this terrible disease, then in this case, emergency measures are taken to identify the pathology. To do this, it is necessary to carry out the procedure of intranasal sounding, when a flexible catheter is inserted into the esophagus. If the device rests against the blind end of an malformed organ and comes out, then this will be the clearest evidence that the baby really suffers from esophageal atresia. Ifspecialist still have doubts, then he additionally introduces air into the esophagus. If it starts to come out quickly with a loud sound, then the diagnosis is confirmed.
Thanks to hardware bronchoscopic methods, it is possible to obtain an image of the blind end of the esophagus. This allows you to quickly determine the type of pathology and prescribe a possible treatment for esophageal atresia.
However, in order to finally verify the diagnosis, some experts prefer to play it safe and introduce a contrast catheter into the baby's body. However, barium suspension is not always allowed to be used. This can lead to difficult breathing for the baby. Moreover, there is a huge probability that the newborn simply will not endure this difficult procedure for him. Among other things, the contrast composition that is used during this manipulation must be very quickly removed from the baby's body. Otherwise, it can enter the lungs and cause chemical pneumonitis.
Recommended a plain radiograph. Thanks to this procedure, you can get the clearest picture of the development of pathology. In addition, thanks to this method, it will be possible to timely establish other anomalies that could develop with atresia. For example, during the study, stenosis of the esophagus may be detected.
Additionally, prenatal ultrasound is performed. Thanks to this procedure, polyhydramnios can be detected, but it is not always a sign of the development of this pathology. In some situations, the appearance of these symptoms is associated with completely different ailments. Also, thanks to ultrasound, you can determine if the baby's stomach is missing by more than 50%.

After all these activities, if the diagnosis is confirmed, it is necessary to proceed with immediate measures.
Treatment
First of all, doctors should try to stabilize the baby's condition. To do this, they avoid mask ventilation. At this stage, every effort should be made to prepare the newborn for surgery. Thus, first of all, preoperative care is performed, after which surgical intervention is performed. If the procedure was successful, then post-operative measures are required.
Care before surgery for esophageal atresia
During the preoperative preparation, it is necessary to stop feeding the baby through the mouth. Only intravenous feeding is allowed. In addition, physicians must continuously suction the accumulated saliva from the upper part of the esophagus. This helps prevent aspiration. This procedure uses a special catheter equipped with a double lumen.
Suction can be done in two ways. In the first case, a special catheter is placed in a blind bag located in the upper part of the esophagus. After that, he is connected to the suction, which works without interruption.
The second method involves the use of suction drainage. This method is considered the best, since there is no risk of damage to the mucous membranes during these activities.
In this case, it is important to ensure that the baby's head is constantly raised by 30-40 degrees. It is best to lay it on its side. This will greatly simplify the emptying of the stomach and reduce the possible risk that aspiration of gastric secretions will occur. In addition, in this position, the baby will be much easier to breathe.

If the baby was stabilized and the doctors are ready to perform the operation, then in this case an extrapleural surgical correction is performed, during which the tracheoesophageal fistula is closed. In some particularly difficult situations, specialists insert an additional segment of the esophagus into the large intestine.
Post-operative measures
If specialists managed to improve the baby's condition and get rid of esophageal atresia, after surgery, it will be necessary to carefully monitor the vital signs of the newborn. To do this, the doctor must constantly be aware of the ventilator indicators.
In addition, a special wound drainage is installed. Also in the body of the baby there will be a gastric tube with the necessary marks. In no case should it be removed, as this device is necessary for the normal patency of the anastomosis.
After surgery for esophageal atresia, it is very important to monitor the position of the baby. It should be on the back, a small roller should be placed under the neck. The upper body should be on a slight elevation. In this case, gastroesophageal reflux should not be allowed. The baby's head must be fixed in the middle position and ensure that the newborn does not turn it. You also need to avoid stretching the neck. to the anastomotic areathere must be pressure.
If on the third day after surgery the baby is in a stable condition, then it can be started to lay on its side. However, you must first consult with the specialist who previously performed the operation.
In addition, it is important to constantly monitor a newborn who has undergone major surgery. The doctor should always be aware of the amount, color and consistency of the discharge passing through the drainage. If the fluid begins to turn greenish, then the anastomosis may fail.
Gastrostomy care
If the atresia is long or unstable, then the initial anastomosis may not be required. In such situations, a gastrostomy is applied. For this, a special balloon-type catheter is used, which is inserted into the baby's stomach through an opening in the abdominal wall.
At the next stage, the catheter is blocked and fixed with a swab roller. You will also need to connect a receiver.
Change the catheter after three weeks. As a rule, by this moment the walls of the peritoneum and stomach are already growing together. However, a special suction drain, which is connected to the suction equipment, must still be located in the upper zone of the operated esophagus. At the same time, marks must be made on the probe, which allow you to avoid the formation of bedsores.

If the baby feels well,then you can consult with the surgeon about the start of the introduction of enteral nutrition.
Possible Complications
Of course, such pathologies and operations at the age of a few days do not always go unnoticed. Among the most common consequences of esophageal atresia in newborns, acute complications can be distinguished, which manifest themselves in the form of leaks at the anastomosis sites. As a result, a stricture may form.
Since the distal segment of the esophagus cannot fully function after surgery, this leads to serious problems during the feeding of the baby. Similar consequences occur in 85% of cases. A defect of this kind is explained by gastroesophageal reflux. In this situation, additional correction may be required. However, in some cases it is ineffective. The doctor may then try a Nissen fundoplication.
At the same time, among the consequences of esophageal atresia, hoarseness of voice in a newborn is almost always noted. This state can last quite a long time, up to one year. This is due to the fact that during the operation the nerve of the larynx is damaged. It's almost impossible to avoid it.
In addition, after surgery, the baby may develop pneumonia, mediastinitis and anemia. In some cases, it is very difficult for small patients to swallow food. Against the background of complications, esophagoscopy may also develop.






