- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Pneumococcal meningitis is an extremely serious infectious disease accompanied by inflammation of the membranes of the spinal cord and brain. In the presence of such a disease, it is very important to make a diagnosis in time and immediately begin treatment, since otherwise the development of complications up to death is not excluded.
Pneumococcal meningitis and its causes

As already mentioned, this is an infectious disease caused by the gram-positive bacterium pneumococcus. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the meninges through the nasopharyngeal mucosa, after which they cause local tissue inflammation. The source of infection is an infected person, the household route of transmission is much less common. In addition, the presence of a purulent focus contributes to the development of such a disease. For example, pneumococcal meningitis often develops against the background of pneumonia, otitis or sinusitis. It should be noted that if untreated, the infection spreads rapidly throughoutbody, affecting the joints, heart muscle and other organs.
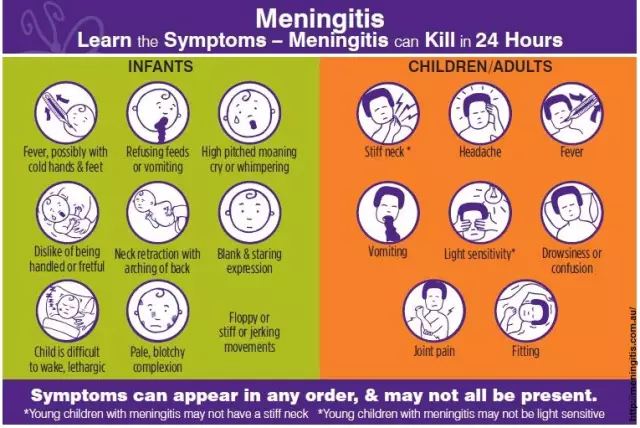
Pneumococcal meningitis: symptoms

In most cases, the disease begins acutely with weakness and a sharp rise in temperature to 38-40 degrees. In the future, very characteristic signs begin to appear:
- The very first and most striking symptom is extremely severe, persistent headaches.
- In addition, there is constant nausea and frequent vomiting, which, alas, does not bring any relief to the patient.
- After a few days, a stiff neck develops (the person cannot press their chin to their chest).
- Characteristic symptoms can also include convulsions, paresis and other disorders that are somehow associated with damage to the nerve roots.
- In some cases, there is also damage to the nerves that control the muscles of the eyeball. In addition, during an ophthalmological examination, you can notice the expansion of blood vessels in the fundus.
- Meningitis is often accompanied by sensitivity to light.
- The above symptoms are not all that an infection can lead to. Meningitis in the absence of timely medical care leads to the development of cerebral edema, pulmonary heart failure, or sepsis. Treatment in this case is simply necessary.
Pneumococcal meningitis: treatments

Of course, if a patient is suspected of having meningitishospitalized. Features of treatment depend on the form and severity of meningitis, as well as the presence of complications. To begin with, the patient must be prescribed a course of antibiotics - this is the only way to eliminate the infection. Along with this, the intake of vitamins and drugs that improve the functioning of the immune system is shown. Depending on the symptoms, doctors prescribe either sedatives or drugs that stimulate brain activity. In addition, drugs are used to normalize blood circulation in the central nervous system. With dehydration that has arisen against the background of constant vomiting and refusal of food and drink, the administration of solutions that can make up for the lack of water is prescribed. With cerebral edema, on the contrary, dehydration and removal of excess fluid from the body are carried out. In any case, the treatment of this form of meningitis can last several months.