- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
According to WHO statistics, in recent years in all countries there has been an increase in the number of patients who develop certain allergic reactions. This is due to the inexorable technological progress and its logical consequence - the emergence of industries using new chemicals and their compounds that are released into the atmosphere, get into the ground, into food, and are present in clothing fabrics. All this contributes to the fact that allergies are strengthening their positions, and the number of allergic people, both among people and among animals, is steadily growing.
One of the forms of this disease is atopic allergy. Its main feature is the hereditary predisposition of individuals to the fact that under certain circumstances they will have allergic reactions. Let's take a closer look at this disease.
Etiology
Some patients are puzzled by the term "atopic allergy". Let's explainwhat does it mean. The word "atopic" or "atopic" is derived from the Greek "atopy", which translates as "not like others, unusual." According to the scientist Kok, who introduced this term, some patients have an unusual functioning of their immune system, which, in response to certain stimuli (not toxins, but the most common substances that do not cause pathological reactions in the majority of people), begins to produce antibodies and some other specific substances that lead to unwanted reactions in the body.
The scientist observed groups of patients with allergies, in whom this disease was transmitted in the family, that is, it was hereditary. In the future, this interpretation of atopic allergy was fixed, and now means an allergic disease associated with a genetic predisposition to it.
Because genes are what we get from our parents, this disease is overwhelmingly inherited. However, there is a small percentage of patients (about 10%) in whom there were no cases of allergy in the family, and the development of the disease is associated with a violation of the flow of biochemical processes in the body.

Mechanism of development of allergic reactions
Perhaps, some readers will be interested to know how unpleasant reactions of the body to any stimuli arise. Immunologists can give a detailed answer to this question. Briefly, atopic allergy in humans occurs as follows: when moleculesFor some substances, the immune system responds by producing specific antibodies (reagins) that bind to foreign molecules in order to destroy them. This process involves special receptors found on almost all cells in our body.
Receptors turn out to be “guilty” in the fact that the combination of antibodies and “foreigners” occurs on the surface of cells, as a result of which the integrity of their membrane is violated, and cellular mediators, biologically quite active substances, enter the intercellular environment. Experts call this process pathochemical. The released mediators cause all those unpleasant manifestations of allergies, which are skin rashes, runny nose, sneezing, and so on.
Let's add that each of us has an individual immune system, so in some people it starts to produce reagins, for example, to pollen of flowers, and in others to the smell of gasoline. This suggests that each person has their own allergens.
Risk groups
As mentioned above, atopic allergy is a hereditary form of the disease. Perhaps some still remember from school biology that in organisms of higher forms (humans and mammals) there are so-called allelic genes inherited in pairs. Suppose one of the parents has the “H” gene (does not carry allergic manifestations to anything, the person is not allergic), and the other has “h” (carries allergic manifestations, the person is allergic to some specific substances). A child can get these pairs of these genes:
- "HH" (baby is not allergic to anything, despite the fact that his mother or father is allergic).
- "Hh" (Such children may or may not be allergic, with adverse reactions only beginning after they reach puberty).
- "hh" (this pair of genes means that another 100% allergic person has been born, and unwanted reactions can appear in him already in infancy).
Recall that, according to Mendel's law, the "h" gene can be inherited not only from dad or mom, but also from other direct relatives.
How to influence the formation of the desired allelic pairs, geneticists do not yet know.

Allergies and atopic dermatitis - is there a difference or not
To understand if there is a difference between these two ailments, let us recall what dermatitis is. This disease is an inflammation of the skin due to exposure to any irritant. In his role can be:
- chemicals (detergents, various solutions);
- parts of plants (leaves, flowers, juice);
- some food that a person touched with his hands when cooking;
- cosmetics (creams, lotions, etc.);
- clothing;
- dust (more precisely, dust mites);
- wool.
Dermatitis appears mainly locally. Symptoms include redness at the sites of contact with the reagent, rashes, itching, erosion, peeling. However, if it is the result of a food allergy, thenIt can also manifest itself in a generalized way (throughout the body). This disease belongs to the group of allergic dermatosis, that is, in fact, it is an allergic dermatitis. It becomes atopic when the patient has a hereditary predisposition to such reactions.
In other words, if someone in the family develops a rash on their body from a certain type of soap, and the child has the same reaction to this soap, he is diagnosed with atopic dermatitis. How is this condition different from an allergy? Only by the fact that dermatitis manifests itself on the skin, and allergies can affect other body systems. In our particular case, this may be a runny nose, appearing from the smell of "inappropriate" soap, sore throat, coughing. Note that any allergy (including atopic dermatitis) is not such a harmless disease as it might seem. In some cases, it can develop into anaphylactic shock, leading to death.

Features of atopic form of allergy
Hereditary predisposition is not an indispensable condition for the appearance of atopic allergies in children and adults. This means that even in those who have inherited the allelic pair of “hh” genes, an allergy may never manifest itself even once in a lifetime if a person avoids contact with an irritating agent. That is, for an allergic reaction to occur, two conditions must be met simultaneously: a hereditary predisposition and an irritant.
Noted that children do not always have atopic allergies(dermatitis, gastrointestinal or respiratory forms of its manifestation) manifests itself in the same agents as in the parents who passed on the “h” gene to them. Why this happens, scientists have not yet established exactly, but for now they make the assumption that the individual characteristics of each organism are to blame.
Another feature of this disease is its cyclicity or dependence on the seasons. That is, in cold weather, relapses begin, and in warm weather, the disease fades. An important feature is the instant manifestation of allergic reactions upon contact with an irritant.
Scientists have long established that atopic allergies can have three interrelated forms of manifestation - atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma and hay fever (rhinoconjunctivitis). This combination of reactions is called the atopic triad and occurs in 34% of patients. In most patients, atopic dermatitis is the first of the triad.
Classification
There are several criteria according to which atopic allergies are classified. Treatment should be prescribed depending on what stage or type of disease is diagnosed.
1. Depending on the phase of the flow, the stages are differentiated:
- initial;
- clearly defined changes;
- sharp;
- subacute;
- chronic;
- complete remission;
- incomplete remission;
- recovery.
2. Age grade:
- infant allergy (0 to 2 years old);
- children's (under 13);
- teenage (under 18);
-adult.
3. Depending on the severity of the manifestation:
- easy;
- moderate;
- heavy.

Symptoms
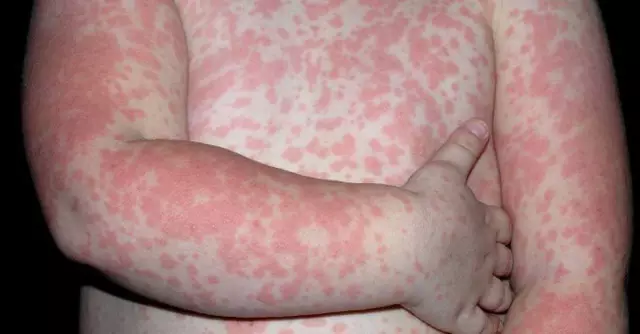
Manifestations of body reactions to an irritant are common (observed with all types of allergen) and specific. The most common allergic reactions to food (honey, chocolate, citrus fruits, red berries and others) are observed in children.
If food is found to be the irritant, a food allergy is diagnosed. Atopic dermatitis in this case can manifest itself on the face in the form of redness and on the body in the form of a rash. These skin reactions may not cause any particular inconvenience to the patient, or vice versa - cause significant inconvenience - unbearable itching, leading to scratching to blood, peeling of the skin with its thinning, soreness in places of redness. In rare cases, atopic dermatitis is accompanied by fever, lethargy, nausea, and vomiting. In medical practice, there are cases when food allergies caused anaphylactic shock in patients with subsequent cardiac arrest.
Adults can also have food allergies. Atopic dermatitis in this case manifests itself in the same way as in children. Among the adult population, food allergies often develop in response to the ingestion of low-quality alcohol. In these cases, there may be an immediate manifestation of allergy, which consists in the loss of consciousness of the patient, spasms of the organs of the pulmonary system, and pallor of the skin. In such cases, to save livespatient requires immediate resuscitation.
Atopic dermatitis in adults often develops after tactile contact with an irritant, which is most often cosmetics and detergents, chemical solutions that a person works with. As a rule, in such cases, the disease manifests itself locally (at the points of contact with the allergen). It can be redness, peeling, swelling, itching, soreness, cracks.
If the irritating agent is odors and any substances that enter the respiratory system (dust, fungal and mold spores, pollen), the main symptoms in such cases are cough, tearing, runny nose, shortness of breath, pulmonary spasms. Rashes on the skin with this form of allergy are rare.
Allergy in babies
In newborn babies, various allergic reactions are also possible, especially for those who have an innate predisposition to them. Atopic allergy in children under one year of age may have the following manifestations:
- rash all over the body or localized;
- redness and swelling of the skin;
- peeling skin;
- violation of the stool (color, smell, consistency of stool changes, the number of defecation acts increases);
- increased, often inexplicable anxiety of the child;
- refusal of food;
- tearfulness;
- capriciousness.
Allergen in young children can be any smell, animal hair, diapers, baby cosmetics, washing powder, low-quality material of undershirts and diapers. Treatment of infantsbased on the exclusion of his contact with the irritant, on the careful hygiene of the baby (frequent change of diapers, without waiting until they overflow), on the exclusion from the diet of the mother (nursing) of products that can cause allergies in her crumbs. In addition, the mother and all those who communicate with the child should remove from use cosmetics (creams, perfumes, etc.) that can cause allergies in the child.
Sometimes newborns have allergic reactions even to their mother's breast milk. They can manifest themselves as a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, dermatitis, hay fever. If the doctor has determined for sure that the irritant is breast milk, despite the fact that the woman has completely excluded all foods “dangerous” for the baby from her diet, you should stop breastfeeding and switch to artificial.
Good proven infant formula for atopic dermatitis "Nutrilon Pepti Allergy". Feedback from both pediatricians and parents about her is positive. The composition of the mixture contains all the substances necessary for the proper development of the baby, but does not include lactose. On this mixture, kids gain weight well, are active, develop without lagging behind age norms. The only drawback of this product, which is noted by parents, is its bitter taste. Therefore, it can be difficult at first to get the baby to eat this mixture with an appetite.

Diagnosis
As you can see from the above symptoms, atopic allergy is very similar in its manifestation to other diseases. So, signs of reaction to stimulirespiratory system can be mistaken for a cold, and signs of food allergies can be mistaken for disorders of the digestive tract. It is sometimes not difficult to determine that a person has an allergic reaction, and sometimes it is not difficult to get rid of it. It is only necessary to remove the source of the allergy so that the state of he alth returns to normal. But it also happens that the patient does not know about the allergic reaction, assuming completely different diseases. For example, atopic dermatitis is often mistaken for eczema, psoriasis, and lupus. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor must examine the patient and determine the so-called allergy criteria. They are divided into large and small.
Major or mandatory criteria include:
- the presence of an allergic person in the family;
- chronic course of the disease (with relapses and remissions);
- localization of skin rashes on characteristic areas of the skin (cheeks, neck, inguinal folds, armpits, on the bends of the knees and elbows);
- itching regardless of the extent of the rash.
Minor or additional criteria include:
- high level of IgE antibodies in the blood;
- wrinkling of soles and/or palms;
- whitish spots on the face and/or shoulders;
- peeling skin;
- dark circles around the eyes;
- itching when sweating;
- skin infections that happen too often;
- in children itching and redness of the skin after bathing.
If three main criteria and three additional criteria are met, atopic dermatitis is diagnosed.
Also, when making a diagnosis, it is possibleskin tests (suspected allergens are injected subcutaneously). This test is not 100% correct, since often the skin does not react to an irritant in any way, but a person has allergic reactions, for example, a runny nose. In addition, after skin tests, ulcers may remain for a long time.

Treatment
In atopic allergies, treatment begins with the identification and elimination of the allergen. Without this, no therapeutic measures will help. But getting rid of the irritant does not always lead to getting rid of allergic reactions, since the atopic form of allergy is self-sustaining. Therefore, the patient needs to conduct a long (2 months or more) course of complex therapy. Includes:
- antibiotics according to indications;
- for atopic dermatitis, external therapy (ointments to relieve itching, pain, peeling, healing cracks, such as "Betamethasone", "Clobetasol");
- vitamins and immunomodulating drugs;
- antihistamines (Theophylline, Cortisone, Adrenaline, Epinephrine);
- corticosteroids (as indicated);
- membrane stabilizing agents.
Often, patients are prescribed drugs that improve the functioning of the stomach and intestines, as well as regulate and stabilize the nervous system.
Atopic allergy in dogs, cats and other animals
Cats and dogs, our pets, and other mammals can also experience various allergic reactions. Their reasons may be:
- fleas(animal reacts to saliva and flea excrement);
- food;
- external irritants (dust, pollen, all kinds of odors);
- drugs;
- hygiene products.
The main symptom of an atopic allergy in an animal is almost incessant itching. The owner should definitely pay attention to such behavior of the pet and show it to the veterinarian. Other manifestations of the disease can be:
- hair loss;
- redness and sour eyes;
- dandruff;
- rash and redness behind the ears;
- bad smell.
For food allergies (most common with food changes), symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, food refusal, lethargy and weakness.
At the veterinary clinic where you should go if you have such symptoms, the doctor will examine the four-legged patient, take swabs from his ears, conduct a skin cytology, in some cases, may order a blood test.

Therapy Methods
Treatment of atopic allergies in dogs and cats, just like in humans, must begin by identifying the cause and eliminating the allergen. If these are fleas, you should sanitize the place where the animal is located, treat the pet from fleas.
If the allergy is food, avoid the food or ingredient in the food to which the pet has an allergic reaction.
If an animal is found to have a yeast or bacterial infection, prescribedrugs that help fight pathogenic yeasts and bacteria.
Also, the treatment of atopic allergies in cats and dogs includes the administration of antihistamines and vitamins to animals.
Prevention
For both humans and animals, preventive measures include:
- exclusion of contact with the allergen;
- quality food;
- strengthening immunity;
- a complete treatment for the primary manifestations of allergies.
Doctors believe that it is very important for allergic patients to lead a he althy full-fledged lifestyle, avoid stressful situations, and organize their daily routine.