- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
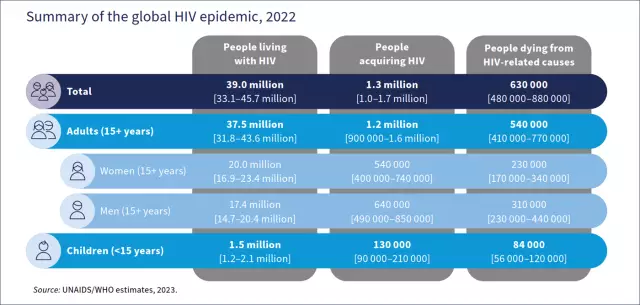
How many people live with HIV? The relevance of this question is simply undeniable, but it is difficult to give an unambiguous answer to it. Medicine is currently unable to cure people infected with the immunodeficiency virus, but scientists are making progress. At this time, doctors are able to control the amount of HIV in the body. A he althy lifestyle and medicines significantly prolong the life of patients.
How dangerous is HIV?
To understand how many years they live with HIV and what are the prospects for an infected person, you must first understand why the human immunodeficiency virus is so dangerous. This pathogen is quite young. It was opened only in the 80s of the last century. By itself, it is not fatal. HIV infects only one type of cell in the human body - T-leukocytes. However, they are a key element of the immune system. Because of this, the body cannot resist various infections. They are the ultimate cause of death. AIDS patients die from pneumonia, cancer, hepatitis, tuberculosis, candidiasis and other diseases.

Invisible infection
The virus appears in the body imperceptibly and does not manifest itself for a long time. Therefore, it is quite difficult to say exactly how many infected people in the world - how many live with HIV and are absolutely unaware of it. Once in the body, the pathogen begins to constantly and asymptomatically increase its population, while destroying he althy cells of the immune system. Whether a person is infected is determined by a special blood test. Important indicators are the level of viral load and the number of T-leukocytes in the blood. The lower threshold for the functioning of the immune system is 200 leukocyte cells per milliliter of blood. If there are fewer of them, the body's defense stops working altogether. Normally, this figure is 500-1500. At an indicator of 350 T-leukocytes, active antiretroviral treatment should be started, aimed at suppressing the pathogen and reducing its concentration in the blood. The answer to the question of how many people live with HIV directly depends on the degree of regularity and quality of therapy.
Evolution of infection
There are five stages of HIV. The period from two weeks to one year after infection is called the window period. It ends when antibodies to HIV appear in the blood. If a person has weakened immunity, this stage does not last longer than six months.
Followed by the prodromal period. It is also called the stage of primary infection. Clinical manifestations during this period are as follows:
- urticaria;
- subfebrile temperature;
- stomatitis;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes: they increase, become painful.
The final stage of this stage is characterized by the maximum concentration of antibodies and virus in the blood.
Further, the disease passes into a stage called the latent period. As a rule, it lasts 5-10 years. Usually the only manifestation of HIV at this stage is a periodic increase in lymph nodes. They become firm but not painful (lymphadenopathy).
The next step is called preAIDS. Its duration is 1-2 years. At this stage, a serious inhibition of cellular immunity begins. A person can be tormented by herpes (with frequent relapses). Ulcerations of the mucous membranes and genital organs do not heal for a very long time. There is stomatitis and leukoplakia of the tongue. There is candidiasis of the genital organs and oral mucosa.
Next comes the terminal stage - directly AIDS. It is accompanied by generalization of opportunistic tumors and infections. The prognosis at this stage is usually negative. At this stage, even ordinary flu can kill a person.

How HIV is transmitted
It is known that AIDS is one of the most terrible diseases of our time. Therefore, absolutely everyone needs to know how their pathogen is transmitted in order to avoid infection and so that the question of how many people live with HIV does not become urgent and burning. This information also does not interfere in order not to humiliate patients once again. The pathogen enters the body during unprotected intercourse, duringreusing a syringe, when transfusing blood, through mother's milk. Many mistakenly believe that AIDS is a disease of drug addicts and homosexuals. However, this is just a stereotype. Anyone can contract this disease. Nobody is immune from this. Many people become infected through contact with the blood of a patient or during donor sampling.

How long people with HIV live
As already mentioned, AIDS is a very dangerous disease. However, it is impossible to reliably predict how long people with HIV live. Even approximate data does not exist. After all, every body is different. Some die 3-5 years after infection, others live for decades.
Very roughly can tell about how long people live with HIV, heavily averaged statistics. On average, this is a period of 5 to 15 years.
The life expectancy of patients cannot be reliably measured for some reason. Firstly, it is no secret that many of the first infected are still alive. That is for over 30 years. However, this period is not a limit. Only time will tell how many people live with an HIV diagnosis as much as possible.
Secondly, medicine and science do not stand still. Since the discovery of the virus (in 1983), effective drugs have been developed that make it possible to stop the development of HIV. Proper drug therapy can prolong the life of the patient. Work on the creation of a cure for AIDS does not stop. New, more effective drugs are constantly emerging. Antiretroviral therapy allowsprevent the evolution of the stage of HIV infection into AIDS. Potent drugs block the substances necessary for the development of the virus, thereby preventing the disease from progressing.
Third, although being infected with the human immunodeficiency virus is not a death sentence, the disease is very serious. How long you can live with HIV depends largely on the rhythm and quality of life of the patient. And she's not easy. You need to constantly check the level of T-leukocytes with a doctor, maintain your he alth, lead a proper lifestyle - there should be no bad habits. With a decrease in the level of immunity, courses of appropriate therapy should be taken. Even not too serious illnesses should never be left to chance. They need to be treated on time. Children with HIV should also follow these instructions. How long they live also depends on the characteristics of a particular organism and the timeliness of therapy.

Precautions
People living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) need to be careful in their daily lives not to infect others and their loved ones. Avoid unprotected sex, do not breastfeed children, do not reuse needles and other piercing objects. It is also necessary to prevent the ingress of sperm, blood, vaginal secretions on the mucous membranes and wounds of he althy people.
How HIV is not transmitted
Many people mistakenly consider HIV-infected people to be extremely dangerous to others. However, the virus is not transmitted through:
- air;
- clothes and towels;
- handshakes (if there are no open wounds on the skin);
- bites of mosquitoes, mosquitoes and other insects;
- any kisses (in the absence of bleeding cracks and damage to the lips and oral cavity);
- dishes;
- swimming pool, toilet, bathroom, etc.
Therefore, it is almost impossible to get infected in everyday life.

HIV drug classes
There are three classes of HIV medications. The therapy is based on the simultaneous administration of three medications from two different classes. This combination is necessary so that the pathogen does not get used to drugs. If the chosen course of treatment is effective, it is prescribed for the rest of life.

What to do to survive with HIV
Infected people should do everything to strengthen immunity. You need to try to eliminate stress, as well as negative thoughts about how many people live with HIV. A lot depends on the inner mood. It is also necessary to adhere to a he althy lifestyle, eat well (a diet with a lot of proteins), take vitamin and mineral complexes. All this helps the body to better cope with the disease. You also need to keep the body in good shape or at least exercise regularly. You can not abuse alcohol - it reduces immunity and reduces the effectiveness of drugs. It is also recommended to stop smoking. When HIV-infected, in no case should you use drugs. First, against the background of thisnarcotic substances in themselves significantly shorten the life span. Second, the drugs are incompatible with most antiretroviral drugs.