- Author Curtis Blomfield blomfield@medicinehelpful.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 20:44.
- Last modified 2025-01-23 17:01.
Many people experience sudden jolts in the heart. This unpleasant sensation most often occurs after emotional experiences. It always causes panic in patients. There are disturbing thoughts about severe cardiac pathologies. With what such symptomatology can be connected? And how to get rid of tremors in the chest from the inside? We will answer these questions in the article.
What is this?
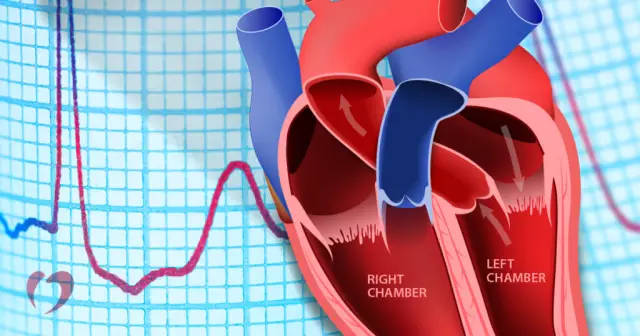
Normally, a person does not feel a heartbeat. But there are cases when there is an untimely contraction of the heart muscle. It is at this moment that the patient feels increased tremors of the heart. Doctors call this condition extrasystole.
This phenomenon is observed in quite he althy people. It can occur against the background of stress and emotional experiences. About 70% of young people have experienced extrasystole at least once. After the age of 50, the number of such patients increases to 90%.
Most often, extrasystole is not associated with cardiovascular disease. However, in some cases, tremors in the heart can be one of the signs of cardiacpathology. However, they are always accompanied by additional symptoms.
Types of extrasystoles
Extrasystoles can have different origins. In medicine, the following varieties of this condition are distinguished:
- functional;
- organic;
- toxic.
Sometimes tremors in the heart appear for no apparent reason. In this case, doctors talk about idiopathic extrasystoles.
Functional extrasystoles
As already mentioned, often in he althy people there are tremors in the heart. The reason for this may be the following conditions of the body:
- stress;
- overeating;
- intense sports training;
- smoking;
- drinking;
- abuse of strong tea and coffee;
- women's menstrual period.

Functional extrasystole can also develop with the following diseases:
- neuroses;
- depressive disorders;
- VSD;
- cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis.
Functional extrasystole is most common in young people. In most cases, it disappears after the normalization of lifestyle and the exclusion of neurogenic factors.
Organic extrasystole
Organic extrasystole develops against the background of cardiac pathologies:
- coronary heart disease;
- cardiomyopathy;
- cardiosclerosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- myocarditis;
- pericarditis;
- heart defects;
- cor pulmonale.
Threats in the heart of organic origin occur in people over 50 years old. This condition requires complex treatment.
Toxic premature beats
Toxic extrasystole occurs with severe fever or thyrotoxicosis. This condition may also be a side effect of the following medications:
- antidepressants;
- corticosteroids;
- cardiac glycosides;
- bronchodilators;
- psychostimulants;
- diuretics;
- sympatholytics.

Toxic extrasystole can develop at any age. It only goes away after the intoxication of the body is cured or the drugs are stopped.
Main symptoms
The main symptom of extrasystole is the feeling of a strong push of the heart into the chest from the inside. After this, there is a pause in the work of the heart muscle. It is necessary to normalize the rhythm. The patient feels this as a sinking heart.
Extrasystole is also accompanied by the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- strong anxiety and panic;
- feeling short of breath;
- hot flashes.

Tremors in the heart at rest are characteristic of functional extrasystole. If the symptoms appear during physical exertion, then this indicates the organic origin of the pathology. Symptoms of heart diseaseextrasystoles never appear at rest.
Additional symptoms
If extrasystole is organic, it leads to a decrease in the ejection of blood from the heart. This causes disorders of the cardiac, renal and cerebral circulation. An attack of extrasystole is accompanied not only by sharp shocks in the heart, but also by additional symptoms:
- pressive chest pain (angina);
- dizzy;
- speech disorders;
- weakness of limb muscles;
- fainting.
Neurological symptoms are more common in patients with atherosclerosis, and angina attacks occur in patients with cardiac ischemia.
Possible Complications
How dangerous is extrasystole? Even if this disorder is functional in nature, it cannot be ignored. Frequent seizures with a feeling of tremors and a sinking heart lead to disruption of the blood supply to the brain, heart and kidneys.
Early extrasystole associated with cardiac pathologies can lead to serious complications. It can cause severe heart failure:
- atrial flutter;
- atrial fibrillation;
- paroxysmal tachycardia.

Particularly dangerous are frequent attacks of extrasystole, accompanied by untimely contraction of the ventricles of the heart. This can lead to a serious condition - ventricular flutter, which often causes sudden death.exodus.
Diagnosis
Examination of a patient always begins with an anamnesis. It is necessary to find out under what circumstances shocks occur. If the attack develops at rest, then this suggests the functional nature of the disease. If jerks and freezes occur during or after physical activity, then most likely this is due to organic changes.
They also measure the pulse and auscultation. This allows you to determine the premature contraction of the heart, followed by a pause in its work.
The most accurate method for diagnosing extrasystole is an electrocardiogram. It is this examination that allows you to identify deviations in the contraction of the heart muscle. If heart disease is suspected, 24-hour ECG monitoring is carried out.

Sometimes the ECG does not show signs of extrasystole, but the patient complains of feeling dots in the chest from the inside. In such cases, an electrocardiogram with a stress test is performed. Concomitant cardiac pathologies are detected using ultrasound and MRI of the heart, as well as Echo-KG.
Treatment
The choice of method of therapy depends on the form of extrasystole. Tremors and tremors of the heart disappear only after the elimination of their cause.
If such symptoms appear occasionally, then this does not require special treatment. It is enough just to normalize your lifestyle. You should give up alcohol, smoking, drinking strong tea and coffee. It is also necessary to avoid unnecessary emotional and physicaloverload.
If extrasystole is provoked by neurosis, chronic stress or depression, then it is necessary to take herbal sedatives based on valerian, motherwort or lemon balm. With toxic extrasystole, it is necessary to cancel the medications taken or reduce their dosage.
If tremors are provoked by cardiac diseases, then antiarrhythmic drugs are prescribed:
- "Obzidan";
- "Verapamil";
- "Allapinin";
- "Metoprolol".

These drugs are symptomatic treatments. They do not last long and help only temporarily normalize the heart rhythm. It is possible to completely get rid of attacks of extrasystole only after the treatment of the underlying cardiovascular pathology.
Physiotherapeutic treatment is indicated for extrasystole on the background of osteochondrosis. Patients are prescribed sessions of therapeutic massage. This helps to improve the blood supply to the heart muscle.
All patients suffering from extrasystole are recommended to include dried fruits, sea kale, potatoes in the diet. These foods contain potassium, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the heart muscle.
Prevention
How to prevent heart tremors? If extrasystole is provoked by cardiac pathologies, then you need to carefully monitor your condition. You need to regularly see a cardiologist and undergo an electrocardiographic examination.
The following measures will help prevent the occurrence of functional heart rhythm disorders:
- giving up bad habits and drinking coffee;
- avoiding excessive exercise;
- Eating a diet rich in potassium and magnesium.
These tips will help reduce the likelihood of heart discomfort.